Abstract
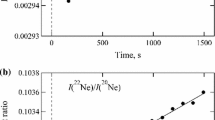
Since many years it is known that argon impurities in oxygen change the temperature of the oxygen triple point by \(+12 \hbox { K}{\cdot }\mathrm{mol}^{-1}\) (positive, while most impurities decrease the temperature) without any effect on the melting range of this transition, for the impurity concentrations usually encountered in nominally pure gases. It has been hypothesized that thermal measurements on the \(\alpha -\beta \) solid-to-solid transition at 23.8 K or the \(\beta -\gamma \) solid-to-solid transition at 43.8 K may give reliable evidence regarding the argon content. However, such measurements require very long times for full completion of each transition (with prohibitive costs if liquid helium is used) and for the \(\alpha -\beta \) solid-to-solid transition the heat pulse method cannot be applied reliably. The availability of closed-cycle refrigerators permits the first obstacle to be surmounted. The automatic system earlier developed at INRIM during the EU Multicells project and used extensively for the project on the isotopic effect in neon is perfectly suited for such measurements. Thus, the uncertainties of the temperature measurements are similar to those obtained previously (of the order of 0.1 mK or less). Three argon-in-oxygen mixtures were prepared gravimetrically and certified at KRISS, just as was previously done for the work on the neon isotopic compositions. Results of continuous-current measurements on the \(\alpha -\beta \) solid-to-solid transition, along with the triple-point data obtained with the heat pulse method, are presented for one cell with a known doped argon content, to be compared with similar data from a cell with oxygen of very high purity. In addition, some preliminary data for the \(\beta -\gamma \) solid-to-solid transition are given. The measurements on the mixture with the highest argon content, about \(1002\, \upmu \hbox {mol}{\cdot } \mathrm{mol}^{-1}\), imply a (linear) sensitivity of \((116 \pm 7) \hbox {K}{\cdot }\mathrm{mol}^{-1}\) for the \(\alpha -\beta \) transition. This sensitivity may be different at much lower argon contents, and follow-up measurements with the other (smaller) mixtures will shed light on the linearity of this dependence.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Eucken, Verh. Dtsch. Phys. Ges. 18, 4 (1916)
H.J. Hoge, J. Res. Natl. Bur. Stand. 44, 321 (1950)
M.P. Orlova, in Temperature, Its Measurement and Control in Science and Industry, vol. 3, ed. by C.M. Herzfeld (Reinhold, New York, 1962), pp. 179–184
R. Muijlwijk, M. Durieux, H. van Dijk, Physica 43, 475 (1969)
W.R.G. Kemp, C.P. Pickup, in Temperature, Its Measurement and Control in Science and Industry, vol. 4, ed. by H.H. Plumb (Instrument Society of America, Pittsburgh, 1972). pp. 217–224
J. Ancsin, in Temperature Measurement 1975, Institute of Physics Conf. Series No. 26 (1975), pp. 57–64
E.L. Pace, R.L. Bivens, J. Chem. Phys. 53, 748 (1970)
J. Cowan, R.C. Kemp, W.R.G. Kemp, Metrologia 12, 87 (1976)
K.H. Kang, K.H. Kim, B.J. Kim, M.J. Kim, C. Rhee, in Proceedings Tempmeko’96, ed. by P. Marcarino (Levrotto & Bella, Torino, 1997), pp. 101–104
K.H. Kang, C.H. Song, Y.G. Kim, K.S. Gam (KRISS), U.S. Patent US006324894B1—Device and method for measuring argon impurity by utilizing the triple point and the \(\gamma -\beta \) transition temperatures of oxygen (2001)
L. Lipinski, A. Szmyrka-Grzebyk, H. Manuszkiewicz, Cryogenics 36, 921 (1996)
L. Lipinski, A. Szmyrka-Grzebyk, H. Manuszkiewicz, P.P.M. Steur, F. Pavese, in Proceedings Tempmeko’96, ed. by P. Marcarino (Levrotto & Bella, Torino, 1997), pp. 105–109
A. Szmyrka-Grzebyk, L. Lipinski, H. Manuszkiewicz, J. Low Temp. Phys. 111, 399 (1998)
L. Lipinski, A. Kowal, A. Szmyrka-Grzebyk, H. Manuszkiewicz, P.P.M. Steur, I. Peroni, F. Sparasci, F. Pavese, 2nd International Seminar and Workshop on Low Temperature Thermometry, Wroclaw, Poland (2003), pp. 119–126
A. Szmyrka-Grzebyk, A. Kowal, L. Lipinski, H. Manuszkiewicz, P.P.M. Steur, F. Pavese, AIP Conf. Proc. 1552, 204–208 (2013). doi:10.1063/1.4819540
R. LeSar, R.D. Etters, Phys. Rev. B 37, 5364 (1988)
B. Kuchta, T. Luty, R.J. Meier, J. Phys. C Solid State Phys. 20, 585 (1987)
C.S. Barrett, L. Meyer, J. Wasserman, Phys. Rev. 163, 851 (1967)
F. Pavese, D. Ferri, Adv. Cryog. Engine 33, 1039 (1988)
Yu.A. Freiman, H.J. Jodl, Phys. Rep. 401, 1–228 (2004)
F. Pavese, Metrologia 46, 47 (2009)
P.P.M. Steur, J.S. Kim, D. Giraudi, F. Pavese, J. Chem. Thermodyn. 60, 87 (2013). doi:10.1016/j.jct.2013.01.011
I. Yang, J.B. Lee, D.M. Moon, J.S. Kim, Preparation of primary reference material of argon in oxygen by the gravimetric method for application to thermometry. Metrologia (submitted to)
F. Pavese, D. Ferri, I. Peroni, A. Pugliese, P.P.M. Steur, B. Fellmuth, D.I. Head, L. Lipinski, A. Peruzzi, A. Szmyrka-Grzebyk, L. Wolber, AIP Conf. Proc. 684, 173–178 (2003)
F. Pavese, P.P.M. Steur, N. Bancone, D. Ferri, D. Giraudi, Metrologia 47, 499 (2010)
B. Fellmuth, P. Seifert, H. Rudloff, in Proceedings Tempmeko’96, ed. by P. Marcarino (Levrotto & Bella, Torino, 1997), pp. 93–98
A.G. Steele, B. Fellmuth, D.I. Head, Y. Hermier, K.H. Kang, P.P.M. Steur, W.L. Tew, Metrologia 39, 551–571 (2002)
K.D. Hill, T. Nakano, P. Steur, Metrologia 52, 03003 (2015). Tech Suppl
B. Fellmuth, K.D. Hill, J.V. Pearce, A. Peruzzi, P.P.M. Steur, J. Zhang (2015), http://www.bipm.org/en/committees/cc/cct/publications-cc.html#thermometry-guides and http://www.bipm.org/utils/common/pdf/ITS-90/Guide-ITS-90-Impurities-2015.pdf
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
F. Pavese: Affiliated Scientist (2010–2015).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Steur, P.P.M., Yang, I. & Pavese, F. Evidence for Argon Content in Pure Oxygen from Thermal Data. Int J Thermophys 38, 20 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10765-016-2160-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10765-016-2160-z