Abstract
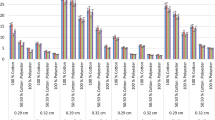
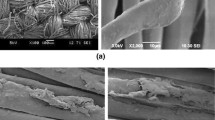
In this paper, the effects of oxygen and atmospheric plasma on air and water-vapor permeability properties of single jersey bamboo fabric have been investigated. The changes in these properties are believed to be related closely to the inter-fiber and inter-yarn friction force induced by the plasma treatments. The outcomes showed that the water-vapor permeability increased, although the air permeability decreased along with the plasma treatments. The SEM images clearly showed that the plasma modified the fiber surface outwardly. The results showed that the atmospheric plasma has an etching effect and increases the functionality of a bamboo surface, which is evident from SEM and FTIR–ATR analysis. These results reveal that atmospheric pressure plasma treatment is an effective method to improve the performance of bamboo fabric. Statistical analysis also indicates that the results are significant for air permeability and water-vapor permeability of the plasma-treated bamboo fabric.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.R. Sanchisa, V. Blanesa, M. Blanesa, D. Garciab, R. Balartb, Eur. Polym. J. 42, 1558 (2006)
H. Hesse, H. Thomas, H. Höcker, Text. Res. J. 65, 335 (1995)
F. Johan, G. Paul, H.P. Schreiber, J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 51, 285 (1994)
W. Rakowski, M. Okoniewski, K. Bartos, J. Zawadzki, Melliand Textilber. Int. Text. Rep. 11, 301 (1982)
V.V. Rybkin, A.L. Maximov, B.L. Gorberg, V.A. Titov, Asian Text. J. 6, 3 (1997)
M.S. Subbulakshmi, K.N. Hansraj, Indian J. Text. 109, 12 (1998)
K. Wong, X. Tao, C. Yuen, K. Yeung, Text. Res. J. 69, 846 (1999)
N. Abidi, E. Hequet, J. Appl. Sci. 93, 145 (2004)
A. Rashidi, H. Moussavipourgharbi, M. Mirjalili, M. Ghoranneviss, Indian J. Fibre Text. Res. 29, 74 (2004)
R.M.A. Malek, I. Holme, Iran. Polym. J. 12, 271 (2003)
T. Yasuda, T. Okuno, K. Yoshida, Sen’i Gakkaishi 42, T11 (1986)
K. Kale, S. Palaskar, P.J. Hauser, A. El-Shafei, Indian J. Fibre Text. Res. 36, 137 (2011)
H.Y. Yu, L.Q. Liu, Z.Q. Tang, M.G. Yan, J.S. Gu, X.W. Wei, J. Membr. Sci. 311, 216 (2008)
O.J. Kwon, S. Tang, S.W. Myung, N. Lu, H.S. Choi, Surf. Coat. Technol. 192, 1 (2005)
W.M. Raslan, E.M. El-Khatib, A.A. El-Halwagy, S. Ghalab, J. Ind. Text. 40, 246 (2011)
N. Yaman, E. Ozdogan, N. Seventekin, Tekstil ve Konfeksiyon 2, 102 (2012)
N.V. Bhat, R.N. Bharati, A.V. Gore, A.J. Patil, Indian J. Fibre Text. Res. 36, 42 (2011)
H.A. Karahan, E. Özdogan, A. Demir, H. Ayhan, N. Seventekin, Fibres Text. East. Eur. 17, 19 (2009)
D. Sun, G.K. Stylios, Text. Res. J. 75, 639 (2005)
X. Xu, Y. Wang, X.Z. Hang, G. Jing, D. Yu, S. Wang, Surf. Interface Anal. 38, 1211 (2006)
M. Ergun, SPSS for Windows (Ocak, Ankara, 1995)
C. Prakash, G. Ramakrishnan, J. Text. Inst. doi:10.1080/00405000.2013.765090 (2013)
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to express their sincere thanks to R. Govindaraj, C. Karthikeyan, V. Karthikumar, S. Vignesh, M. Selvakumar, and V. Vimalraj for their assistance in the experimental part, to the management of Sona College of Technology and Pavendar Bharathidasan College of Engineering and Technology for permission to use the laboratory facilities, and lastly to the Textile Research Centre, TIFAC-CORE in Textile Technology and Machinery of Kumaraguru College of Technology, Coimbatore, India for testing all the samples in their advanced manufacturing laboratory.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Prakash, C., Ramakrishnan, G., Chinnadurai, S. et al. Effect of Plasma Treatment on Air and Water-Vapor Permeability of Bamboo Knitted Fabric. Int J Thermophys 34, 2173–2182 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10765-013-1509-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10765-013-1509-9