Abstract
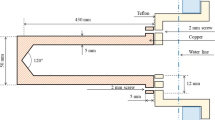
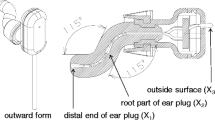
Body temperature is a basic vital sign of the human body, and the use of infrared ear thermometers for medical diagnosis and health management on human bodies has been widespread nowadays. To gain credibility and confidence in the usage of IR ear thermometers, a standard blackbody source (BBS) with a calibration traceable to ITS-90 is necessitated. Three types of cavity-shaped blackbodies (designated BBC-A, BBC-E, and BBC-J) vertically immersed in a temperature-controlled stirred water bath were developed at the Center for Measurement Standards (CMS) as standard BBSs to calibrate and verify 14 commercial IR ear thermometers produced by six manufacturers. The basic structure of each cavity was designed based on the informative examples recommended in ASTM E-1965, EN 12470-5, and JIS T 4207 standards. The temperature of the blackbody cavity shall be represented by the water temperature near the bottom of the cavity that is measured using an immersed platinum resistance thermometer (PRT) for which the calibration is traceable to our national standard and with an uncertainty no greater than 0.03 °C (k = 2). The water bath was evaluated using the PRT to be stable within ±3.5 mK over 1 h and uniform within ±1.1 mK. Three types of BBSs were compared and analyzed utilizing two IR ear thermometers of 0.01 °C resolution as well as the statistical technique of analysis of variance (ANOVA). On the contrary, IR ear thermometers were tested and verified against three BBSs at three blackbody temperatures of 35.5 °C, 37 °C, and 41 °C. The analysis results of ANOVA showed that there is no significant temperature difference among three different structured blackbodies, and the average measured radiance temperature of three BBSs at 35.5 °C, 37 °C, and 41 °C were within 0.026 °C, 0.024 °C, and 0.027 °C of each other. Three among fourteen IR ear thermometers tested were outside of the 0.2 °C MPE (maximum permissible error) recommended by ASTM E-1965, EN 12470-5, or JIS T 4207 standards while BBC-A and BBC-E were used; however, four were outside of MPE requirement when BBC-J was used.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Preston-Thomas H.: Metrologia 27, 3 (1990)
ASTM Designation E1965-98, ASTM Committee E20.20 (1998)
EN 12470-5, CEN TC205 (2003)
JIS T-4207, Japanese Standard Association (2005)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tsai, S.F. Comparison Measurements of Infrared Ear Thermometers Against Three Types of Blackbody Sources. Int J Thermophys 31, 1821–1831 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10765-010-0844-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10765-010-0844-3