Abstract
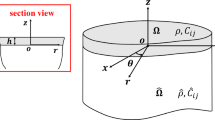
In this study, a theoretical method is applied to investigate the multiple scattering of thermal waves and temperature field resulting from a subsurface cylindrical inclusion in a semi-infinite functionally graded material (FGM). The adiabatic boundary condition at the semi-infinite surface is considered. The thermal waves are excited at the surface of semi-infinite functionally graded materials by modulated optical beams. The model includes the multiple scattering effects of the cylindrical thermal wave generated by the line heat source. According to the wave equation of heat conduction, a general solution of scattered thermal waves is presented. Numerical calculations illustrate the effect of subsurface inclusion on the temperature and phase change at the sample surface under different physical and geometrical parameters. It is found that the temperature above the conducting cylindrical inclusion decreases because of the existence of the inclusion. The effect of the inclusion on the temperature and phase change at the surface is also related to the non-homogeneous parameter of FGMs, the wave frequency of thermal waves, and the distance between the inclusion and the semi-infinite surface. Finally, the effect of the relaxation time of buried inclusion on the temperature and phase change at the surface is examined.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- λ :
-
Thermal conductivity of FGMs
- c p :
-
Specific heat capacity of FGMs
- ρ :
-
Mass density of FGMs
- D :
-
Thermal diffusivity of FGMs
- τ :
-
Relaxation time of FGMs
- λ 1 :
-
Thermal conductivity of the inclusion
- c p1 :
-
Specific heat capacity of the inclusion
- ρ 1 :
-
Mass density of the inclusion
- D 1 :
-
Thermal diffusivity of the inclusion
- τ 1 :
-
Relaxation time of the inclusion
- a :
-
Radius of fibers
- b :
-
Buried depth of the subsurface cylindrical inclusion
- f :
-
Frequency of ultrashort laser pulse
- σ :
-
Spatial variational exponent of physical parameters
- ∇:
-
Hamiltonian operator
- T :
-
Temperature in composite materials
- c :
-
Propagation speed of thermal waves in FGMs
- c 1 :
-
Propagation speed of thermal waves in the inclusion
- T 0 :
-
Average temperature
- ω :
-
Incident frequency of thermal waves
- \({\vartheta }\) :
-
Wave field of thermal waves
- κ :
-
Propagating wave number of complex variables
- k :
-
Wave number of thermal waves without diffusive effect
- α :
-
Wave number of thermal waves
- β :
-
Absorption coefficient of thermal waves
- \({\vartheta _0 }\) :
-
Temperature amplitude of incident thermal waves
- J n (·):
-
nth Bessel function of the first kind
- H n (·):
-
nth Hankel function of the first kind
- \({A_n^l,B_n^l,C_n^l,E_n^l }\) :
-
Mode coefficients
- 1:
-
Actual inclusion
- 2:
-
Image inclusion
- l:
-
Reflected time
- (in):
-
Incident thermal wave
- (s):
-
Scattered thermal wave
- (r):
-
Refracted thermal wave in the inclusion
- (t):
-
Total temperature field in FGMs
References
Ocariz A., Sanchez-Lavega A., Salazar A.: J. Appl. Phys. 81, 7552 (1997)
Ocariz A., Sanchez-Lavega A., Salazar A.: J. Appl. Phys. 81, 7561 (1997)
Salazar A., Sanchez-Lavega A., Celorrio R.: J. Appl. Phys. 93, 4536 (2003)
Terrón J.M., Sánchez-Lavega A., Salazar A: J. Appl. Phys. 89, 5659 (2001)
Terrón J.M., Sánchez-Lavega A., Salazar A.: J. Appl. Phys. 87, 2600 (2000)
Salazar A., Celorrio R.: J. Appl. Phys. 100, 113535 (2006)
Salazar A., Garrido F., Celorrio R.: J. Appl. Phys. 99, 066116 (2006)
Madariaga N., Salazar A.: J. Appl. Phys. 101, 103534 (2007)
Wang C., Mandelis A., Liu Y.: J. Appl. Phys. 96, 3756 (2004)
Wang C., Mandelis A., Liu Y.: J. Appl. Phys. 97, 014911 (2005)
Wang C., Liu Y., Mandelis A., Shen J.: J. Appl. Phys. 101, 083503 (2007)
Gray L.J., Kaplan T., Richardson J.D.: ASME J. Appl. Mech. 70, 543 (2003)
Salazar A., Sanchez-Lavega A.: J. Appl. Phys. 93, 4536 (2003)
Qiu T.Q., Tien C.L.: Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 35, 719 (1992)
Korner C., Bergmann H.W.: J. Appl. Phys. 67, 397 (1998)
Tzou D.Y.: ASME J. Heat Transf. 117, 8 (1995)
Cattaneo C.: Compte. Rend. 247, 431 (1958)
Ma X., Tan H.: J. Funct. Mater. 9, 1507 (2006) (in Chinese)
Abdel-Hamid B.: Appl. Math. Model. 23, 899 (1999)
Parameswaran V., Shukla A.: ASME J. Appl. Mech. 69, 240 (2002)
Ayhan A.O.: Int. J. Solids Struct. 44, 8579 (2007)
Erdogan F.: Compos. Eng. 7, 753 (1995)
Abramowitz M.A., Stegun I.A.: Handbook of Mathematical Functions. Natl. Bur. Stand., Washington, DC (1964)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fang, XQ., Duan, SM., Liu, SH. et al. Multiple Scattering of Thermal Waves from a Subsurface Cylindrical Inclusion in Semi-infinite Functionally Graded Materials Using Non-Fourier Model. Int J Thermophys 30, 1055–1073 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10765-009-0605-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10765-009-0605-3