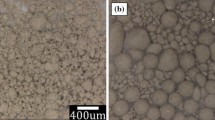
Uranium–molybdenum alloy dispersion fuel meats are being studied for utilization as a research reactor fuel. Thermophysical properties of U–Mo/Al dispersion fuel, where U–Mo was dispersed in aluminum in research reactor fuel for the study, were determined by computing the thermal conductivity through measurements of the specific heat capacity and thermal diffusivity. Uranium molybdenum powder was first fabricated and utilized as U–Mo/Al dispersion fuel; the molybdenum-to-uranium ratios were 6, 8, and 10 mass% to produce the initial powder, which was then combined with aluminum (Al 1060). The volume fractions of U–Mo powder to aluminum were 10, 30, 40, and 50 vol.% to fabricate the dispersion fuel. The thermal diffusivity and specific heat capacity were measured by the laser-flash and differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) methods, respectively. Although the thermal diffusivity showed a decreasing trend with the U–Mo volume fraction when the dispersion quantity was insignificant, the trend reversed with a higher dispersion level. The specific heat capacity increases monotonically with temperature; its value is larger for a smaller dispersion level. Additionally, the overall thermal conductivity increases with temperature. Finally, the thermal conductivity decreases with an increase in the amount of U–Mo powder in the dispersion fuel.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lee S.H., Kim J.C., Park J.M., Kim C.K. (2003). Int. J. Thermophys. 24:1355
C. K. Kim, H. J. Ryu, J. M. Park, K. H. Kim, H. R. Kim, and K. H. Lee, Proc. 2000 Int. Meeting on Reduced Enrichment for Research and Test Reactors, ANL/TD/TM01-12 (2000), p. 233.
S. L. Hayes, C. R. Clark, J. R. Stuart, and M. K. Meyer, Proc. 2000 Int. Meeting on Reduced Enrichment for Research and Test Reactors, ANL/TD/TM01-12 (2000), p. 225.
K. H. Kim, D. B. Lee, C. K. Kim, and I. H. Kuk, Proc. 19th Int. Meeting on Reduced Enrichment for Research and Test Reactors, Seoul, Korea (1996).
G. L. Hofman, M. K. Meyer, and A. E. Ray, Proc. 21st Int. Meeting on Reduced Enrichment for Research and Test Reactors, Sao Paulo, Brazil (1998).
J. M. Park, Y. S. Han, K. H. Kim, Y. S. Lee, and C. K. Kim, Proc. 22nd Int. Meeting on Reduced Enrichment for Research and Test Reactors, Budapest, Hungary (1999).
K. H. Kim, H. J. Kwon, J. S. Lee, H. J. Ryu, J. M. Park, and C. K. Kim, Proc. 2000 Int. Meeting on Reduced Enrichment for Research and Test Reactors, ANL/TD/TM01-12 (2000), p. 285.
S. H. Lee, J. C. Kim, J. M. Park, H. J. Ryu, and C. K. Kim, Proc. 2000 Int. Meeting on Reduced Enrichment for Research and Test Reactors, ANL/TD/TM01-12 (2000), p. 261.
Parker W.J., Jenkins R.J., Butler C.P., Abbott G.L. (1961). J. Appl. Phys. 32:1679
Azumi T., Takahashi Y. (1981). Rev. Sci. Instrum. 52:1411
Emsley J. (1990). The Elements, 2nd Ed. Oxford University Press, Oxford
R. E. Taylor, TPRL Report 2368 (2000), p. 4.
W.-S. Ryu, J.-M. Park, C.-K. Kim, and I.-H. Kuk, Proc. 1994 Int. RERTR Meeting, Williamsburg, Virginia (1994).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, S.H., Park, J.M. & Kim, C.K. Thermophysical Properties of U–Mo/Al Alloy Dispersion Fuel Meats. Int J Thermophys 28, 1578–1594 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10765-007-0212-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10765-007-0212-0