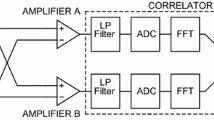
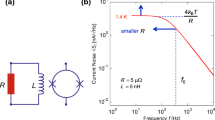
Johnson noise thermometry (JNT) is a primary method of measuring temperature which can be applied over wide ranges. The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is currently using JNT to determine the deviations of the International Temperature Scale of 1990 (ITS-90) from the thermodynamic temperature in the range of 505–933 K, overlapping the ranges of both acoustic gas-based and radiation-based thermometry. Advances in digital electronics have now made viable the computationally intensive and data-volume-intensive processing required for JNT using noise-voltage correlation in the frequency domain. The spectral noise power, and consequently the thermodynamic temperature T, of a high-temperature JNT probe is determined relative to a known reference spectrum using a switched-input digital noise-voltage correlator and simple resistance-scaling relationships. Comparison of the JNT results with standard platinum resistance thermometers calibrated on the ITS-90 gives the deviation of the thermodynamic temperature from the temperature on the ITS-90, T − T 90. Statistical uncertainties under 50 μK·K−1 are achievable in less than 1 day of integration by fitting the effects of transmission-line time constants over bandwidths of 450 kHz. The methods and results in a 3 K interval near the zinc freezing point (T 90-ZnFP ≡ 692.677 K) are described. Preliminary results show agreement between the JNT-derived temperatures and the ITS-90.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Preston-Thomas, Metrologia 27:3 (1990); Metrologia 27:107 (erratum).
G. F. Strouse, D. R. Defibaugh, M. R. Moldover, and D. C. Ripple, in Temperature: Its Measurement and Control in Science and Industry, Vol. VII, D. C. Ripple, ed. (American Institute of Physics, New York, 2003), pp. 31–36.
D. R. Taubert, J. Hartmann, J. Hollandt, and J. Fischer, in Temperature: Its Measurement and Control in Science and Industry, Vol. VII, D. C. Ripple, ed. (American Institute of Physics, New York, 2003), pp. 7–12.
White D.R., Galleano R., Actis A., Brixy H., de Groot M., Dubbeldam J., Reesink A., Edler F., Sakurai H., Shepard R.L., Gallop J.C. (1996) . Metrologia 33:325
Labenski J.R., Tew W.L., Nam S.W., Benz S.P., Dresselhaus P.D., Burroughs C.J. (2007) . IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 56:481
White D.R. (1989) . IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. IM-38:1036
Rusby R.L., Hudson R.P., Durieux M., Schooley J.F., Steur P.P.M., Swenson C.A. (1991) . Metrologia 28:9
Nam S., Benz S., Dresselhaus P., Tew W.L., White D.R., Martinis J.M. (2003) . IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 52:550
Nam S.W., Benz S.P., Dresselhaus P., Burroughs C.J., Tew W.L., White D.R., Martinis J.M. (2005) . IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 54:653
B. W. Mangum and G. T. Furukawa, NIST Tech. Note 1265 (1990).
G. F. Strouse, in Temperature: Its Measurement and Control in Science and Industry, Vol. VI, J. F. Schooley, ed. (American Institute of Physics, New York, 1993), pp. 169–174.
R. Rusby, M. R. Moldover, J. Fischer, D. R. White, P. P. M. Steur, R. P. Hudson, M. Durieux, and K. D. Hill, Consultative Committee on Thermometry, CCT/05–19, BIPM, Sevres, France (2005).
White D.R., Zimmermann E. (2000) . Metrologia 37:11
D. R. White, R. S. Mason, and P. Saunders, Proc. Tempmeko 2001, B. Fellmuth, J. Seidel, and G. Scholz, eds. (VDE Verlag, Berlin, 2002), pp. 129–134.
D. R. White, Proc. Tempmeko 2004, D. Zvizdic, ed. (LPM and FSB, University of Zagreb, Croatia, 2005), pp. 485–490.
W. Setiawan, Systematische Untersuchung von Fehlerquellen bei der Prazisionsrauschthermometrie, Ph. D. Dissertation (Forschungszentrum Jülich, Germany, 1992).
M. de Groot, J. F. Dubbeldam, H. Brixy, F. Edler, and E. Tegeler, Consultative Committee on Thermometry Report, CCT/96–30, BIPM, Sevres, France (1996).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tew, W.L., Labenski, J.R., Nam, S.W. et al. Johnson Noise Thermometry near the Zinc Freezing Point Using Resistance-Based Scaling. Int J Thermophys 28, 629–645 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10765-007-0196-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10765-007-0196-9