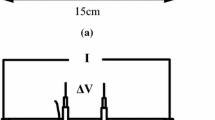
Measurements of the thermal conductivity of a cement-based composite material are performed as a function of moisture content from a dry state to a fully water-saturated state using an impulse technique. Then, the obtained data are analyzed using Brugemann and Wiener homogenization formulas. The validity of applied homogenization techniques is assessed comparing the measured and calculated results. On the basis of the experimental data and the homogenization analyses, the effects of total pore volume, pore distribution, and moisture content on the thermal conductivity are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lide D.R., ed., In CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 79th Ed. (CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, 1998).
Černý R., Rovnaníková P., (2002). Transport Processes in Concrete. Spon Press, London
Neville A.M., (1973). Properties of Concrete. Pitman, London
Bažant Z.P., Kaplan M.F., (1996). Concrete at High Temperatures: Material Properties and Mathematical Models. Longman, Harlow
IEA-Annex XIV, Condensation and Energy, Vol. 3, Material Properties (International Energy Agency, Leuven, 1991).
Černý R., Maděra J., Poděbradská J., Toman J., Drchalová J., KleČka T., Jurek K., Rovnaníková P., (2000). Cem. Concr. Res. 30:1267
Toman J., Černý R., (2001). Acta Polytechnica 41:8
Grunewald J., (2000). DELPHIN 4.1 – Documentation, Theoretical Fundamentals. TU Dresden, Dresden
Christensen R.M., (1979). Mechanics of Composite Materials. Wiley, New York
Sihvola A., (1999). Electromagnetic Mixing Formulas and Applications. The Institution of Electrical Engineers, London
Ogacho A.A., Aduda B.O., Nyongesa F.W., (2003). J. Mater. Sci. 38:2293
Smith D.S., Fayette S., Grandjean S., Martin C., (2003). J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 86:105
Felske J.D., (2004). Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 47:3453
Macedo F., Ferreira J.A., (2003). Rev. Sci. Instrum. 74:828
Polder D., Van Santen J.H., (1946). Physica 12:257
Lord Rayleigh, (1892). Phil. Mag. 34:481
Wiener O., (1912). Abh. D. Leipz. Akad. 32:509
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Paper presented at the Seventeenth European Conference on Thermophysical Properties, September 5–8, 2005, Bratislava, Slovak Republic.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mňahončáková, E., Jiřičková, M., Pavlík, Z. et al. Effect of Moisture on the Thermal Conductivity of a Cementitious Composite. Int J Thermophys 27, 1228–1240 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10765-006-0073-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10765-006-0073-y