Abstract
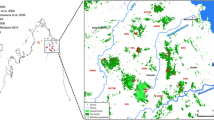
The evolution of the high level of microendemism in Madagascar’s biota remains poorly understood. Allopatric speciation or adaptations to local conditions along continuous gradients are two mechanisms that could have contributed to the extraordinary radiation of lemurs. Here we tested whether mouse lemurs (Microcebus griseorufus) occurring across three adjacent but distinct vegetation formations (ranging from dry forest to spiny bush) in southwestern Madagascar showed signs of genetic differentiation that could be interpreted as incipient speciation and adaptation to different environmental conditions using analysis of molecular variance and distance-based redundancy analysis. In the context of a mark-recapture study, mouse lemurs were captured with Sherman live traps set eight times for four nights per trapping session in standardized trapping grids in the three vegetation formations between October 2007 and February 2009. For genetic analyses, we used tissue samples from 41 female and 35 male M. griseorufus. Genetic differentiation between demes as estimated by amplified fragment length polymorphism (AFLP) data (as parental markers) and mitochondrial D-loop sequences (as maternally inherited markers) was more pronounced in philopatric females than in males, which are the dispersing sex in this species. In single-factor analyses, isolation-by-ecology had about the same statistical effect as isolation by distance, but isolation-by-ecology was no longer significant once isolation by distance was taken into account. Despite some differentiation between local demes, STRUCTURAMA, a Bayesian approach for inferring population structure from genetic data, assigned all individuals to a single population. Thus, we did not find evidence for incipient ecological speciation as a result of adaptation to the three investigated habitat types on a small geographic scale based on the available samples.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, M. J. (2004). DISTML v.5: A FORTRAN computer program to calculate a distance-based multivariate analysis for a linear model. Department of Statistics, University of Auckland.
Andriatsimietry, R., Goodman, S. M., Razafimahatratra, E., Jeglinski, J. W. E., Marquard, M., & Ganzhorn, J. U. (2009). Seasonal variation in the diet of Galidictis grandidieri Wozencraft, 1986 (Carnivora: Eupleridae) in a sub-arid zone of extreme southwestern Madagascar. Journal of Zoology, 279, 410–415.
Arrigo, N., Tuszynski, J. W., Ehrich, D., Gerdes, T., & Alvarez, N. (2009). Evaluating the impact of scoring parameters on the structure of intra-specific genetic variation using RawGeno, an R package for automating AFLP scoring. BMC Bioinformatics, 10, 33.
Bandelt, H.-J., Forster, P., & Röhl, A. (1999). Median-joining networks for inferring intraspecific phylogenies. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 16, 37–48.
Bohr, Y. E. M. B., Giertz, P., Ratovonamana, Y. R., & Ganzhorn, J. U. (2011). Gray-brown mouse lemurs (Microcebus griseorufus) as an example of distributional constraints through increasing desertification. International Journal of Primatology, 32, 901–913.
Brown, J. L., Cameron, A., Yoder, A. D., & Vences, M. (2014). A necessarily complex model to explain the biogeography of the amphibians and reptiles of Madagascar. Nature Communications, 5, Article 5046.
Buntjer, J. B. (2001). PhylTools version 1.32. Laboratory of plant breeding. Wageningen: Wageningen University and Research Centre.
Chaveerach, A., Tanee, T., Sattayasai, N., Tanomtong, A., Suareze, S. A., & Nuchadomrong, S. (2007). Genetic relationships of langur species using AFLP markers. Pakistan Journal of Biological Sciences, 10, 1445–1451.
Dammhahn, M., & Kappeler, P. M. (2005). Social system of Microcebus berthae, the world's smallest primate. International Journal of Primatology, 26, 407–435.
Dewar, R. E., & Richard, A. F. (2007). Evolution in the hypervariable environment of Madagascar. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 104, 13723–13727.
Eberle, M., & Kappeler, P. M. (2002). Mouse lemurs in space and time: a test of the socioecological model. Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology, 51, 131–139.
Eberle, M., & Kappeler, P. M. (2004). Selected polyandry: female choice and inter-sexual conflict in a small nocturnal solitary species (Microcebus murinus). Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology, 57, 91–100.
Edgar, R. C. (2004). MUSCLE: a multiple sequence alignment method with reduced time and space complexity. BMC Bioinformatics, 5, 113.
Excoffier, L., Smouse, P. E., & Quattro, J. M. (1992). Analysis of molecular variance inferred from metric distances among DNA haplotypes: application to human mitochondrial DNA restriction data. Genetics, 131, 479–491.
Falush, D., Stephens, M., & Pritchard, J. K. (2007). Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data: dominant markers and null alleles. Molecular Ecology Notes, 7, 574–578.
Fischer, M. C., Foll, M., Excoffier, L., & Heckel, G. (2011). Enhanced AFLP genome scans detect local adaptation in high-altitude populations of a small rodent (Microtus arvalis). Molecular Ecology, 20, 1450–1462.
Fredsted, T., Pertoldi, C., Olesen, J. M., Eberle, M., & Kappeler, P. M. (2004). Microgeographic heterogeneity in spatial distribution and mtDNA variability of gray mouse lemurs (Microcebus murinus, Primates: Cheirogaleidae). Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology, 56, 393–403.
Génin, F. (2008). Life in unpredictable environments: first investigation of the natural history of Microcebus griseorufus. International Journal of Primatology, 29, 303–321.
Gligor, M., Ganzhorn, J. U., Rakotondravony, D., Ramilijaona, O. R., Razafimahatratra, E., Zischler, H., & Hapke, A. (2009). Hybridization between mouse lemurs in an ecological transition zone in southern Madagascar. Molecular Ecology, 18, 520–533.
Goodman, S. M., & Ganzhorn, J. U. (2004). Biogeography of lemurs in the humid forests of Madagascar: the role of elevational distribution and rivers. Journal of Biogeography, 31, 47–55.
Guillot, G., & Rousset, F. (2013). Dismantling the Mantel tests. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 4, 336–344.
Hapke, A., Gligor, M., Rakotondranary, S. J., Rosenkranz, D., & Zupke, O. (2011). Hybridization of mouse lemurs: different patterns under different ecological conditions. BMC Evolutionary Ecology, 11, 297.
Hasegawa, M., Kishino, H., & Yano, T. (1985). Dating the human-ape splitting by a molecular clock of mitochondrial DNA. Journal of Molecular Evolution, 22, 160–174.
Huelsenbeck, J. P., & Andolfatto, P. (2007). Inference of population structure under a Dirichlet process model. Genetics, 175, 1787–1802.
Huelsenbeck, J. P., Andolfatto, P., & Huelsenbeck, E. T. (2011). Structurama: Bayesian inference of population structure. Evolutionary Bioinformatics, 7, 55–59.
Legendre, P., & Anderson, M. J. (1999). Distance-based redundancy analysis: testing multispecies responses in multifactorial ecological experiments. Ecological Monographs, 69, 1–24.
Leigh, J. W., & Bryant, D. (2014). PopART: Full-feature software for population genetics. http://popart.otago.ac.nz.
McArdle, B. H., & Anderson, M. J. (2001). Fitting multivariate models to community data: a comment on distance-based redundancy analysis. Ecology, 82, 290–297.
Olivieri, G. L., Zimmermann, E., Randrianambinina, B., Rasoloharijaona, S., Rakotondravony, D., Guschanski, K., & Radespiel, U. (2007). The ever-increasing diversity in mouse lemurs: three new species in north and northwestern Madagascar. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 43, 309–327.
Peakall, R., & Smouse, P. E. (2006). genalex 6: genetic analysis in Excel. Population genetic software for teaching and research. Molecular Ecology Notes, 6, 288–295.
Pearson, R. G., & Raxworthy, C. J. (2009). The evolution of local endemism in Madagascar: watershed versus climatic gradient hypotheses evaluated by null biogeographic models. Evolution, 63, 959–967.
R Core Team. (2013). R: A language and environment for statistical computing, version 2.15.2. Vienna: R Foundation for Statistical Computing. Available at www.R-project.org.
Radespiel, U., Lutermann, H., Schmelting, B., Bruford, M. W., & Zimmermann, E. (2003). Patterns and dynamics of sex-biased dispersal in a nocturnal primate, the grey mouse lemur, Microcebus murinus. Animal Behaviour, 65, 709–719.
Radespiel, U., Rakotondravony, R., & Chikhi L. (2008). Natural and anthropogenic determinants of genetic structure in the largest remaining population of the endangered golden-brown mouse lemur, Microcebus ravelobensis. American Journal of Primatology 70, 860–870.
Radespiel, U., Sarikaya, Z., Zimmermann, E., & Bruford, M. W. (2001). Sociogenetic structure in a free-living nocturnal primate population: sex-specific differences in the grey mouse lemur (Microcebus murinus). Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology, 50, 493–502.
Rakotondranary, J. S., Ratovonamana, Y. R., & Ganzhorn, J. U. (2010). Distributions et caractéristiques des microhabitats de Microcebus griseorufus (Cheirogaleidae) dans le Parc National de Tsimanampetsotsa (Sud-ouest de Madagascar). Malagasy Nature, 4, 55–64.
Rakotondranary, S. J., & Ganzhorn, J. U. (2011). Habitat separation of sympatric Microcebus spp. in the dry spiny forest of south-eastern Madagascar. Folia Primatologica, 82, 212–223.
Rakotondranary, S. J., Struck, U., Knoblauch, C., & Ganzhorn, J. U. (2011). Regional, seasonal and interspecific variation in 15N and 13C in sympatric mouse lemurs. Naturwissenschaften, 98, 909–917.
Ratovonamana, Y. R., Rajeriarison, C., Edmond, R., & Ganzhorn, J. U. (2011). Phenology of different vegetation types in Tsimanampetsotsa National Park, south-western Madagascar. Malagasy Nature, 5, 14–38.
Raufaste, N., & Rousset, F. (2001). Are partial mantel tests adequate? Evolution, 55, 1703–1705.
Rundle, H. D., & Nosil, P. (2005). Ecological speciation. Ecology Letters, 8, 336–352.
Schluter, D. (2001). Ecology and the origin of species. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 7, 372–380.
Schluter, D. (2009). Evidence for ecological speciation and its alternative. Science, 323, 737–741.
Schwab, D., & Ganzhorn, J. U. (2004). The distribution and population structure of Microcebus berthae, the smallest known primate and its habitat use in relation to other sympatric cheirogaleids. International Journal of Primatology, 25, 307–330.
Shafer, A. B. A., & Wolf, J. B. W. (2013). Widespread evidence for incipient ecological speciation: a meta-analysis of isolation-by-ecology. Ecology Letters, 16, 940–950.
Sommer, S., Rakotondranary, S. J., & Ganzhorn, J. U. (2014). Maintaining microendemic primate species identity along an environmental gradient – parasites as drivers for species differentiation. Ecology and Evolution, 4, doi: 10.1002/ece3.1311.
Swofford, D. L. (2002). PAUP*: Phylogenetic analysis using parsimony and other methods, version 4.0b10. Sunderland: Sinauer Associates.
Tamura, K., Stecher, G., Peterson, D., Filipski, A., & Kumar, S. (2013). MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 30, 2725–2729.
Thibert-Plante, X., & Hendry, A. P. (2010). When can ecological speciation be detected with neutral loci? Molecular Ecology, 19, 2301–2314.
Vences, M., Wollenberg, K. C., Vieites, D. R., & Lees, D. C. (2009). Madagascar as a model region of species diversification. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 24, 456–465.
Wilmé, L., Goodman, S. M., & Ganzhorn, J. U. (2006). Biogeographic evolution of Madagascar’s microendemic biota. Science, 312, 1063–1065.
Wimmer, B., Tautz, D., & Kappeler, P. M. (2002). The genetic population structure of the gray mouse lemur (Microcebus murinus), a basal primate from Madagascar. Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology, 52, 166–175.
Wollenberg, K. C., Vieites, D. R., van der Meijden, A., Glaw, F., Cannatella, D. C., & Vences, M. (2008). Patterns of endemism and species richness in Malagasy cophyline frogs support a key role of mountainous areas for speciation. Evolution, 62, 1890–1907.
Wright, P. C. (1999). Lemur traits and Madagascar ecology: coping with an island environment. Yearbook of Physical Anthropology, 42, 31–72.
Wright, S. (1943). Isolation by distance. Genetics, 28, 114–138.
Yoder, A. D., Burns, M. M., & Génin, F. (2002). Molecular evidence of reproductive isolation in sympatric sibling species of mouse lemurs. International Journal of Primatology, 23, 1335–1343.
Acknowledgments
The study was conducted under the “Accord de Collaboration” between Madagascar National Parks (MNP, formerly ANGAP), the University of Antananarivo, and the University of Hamburg. We thank MNP, Chantal Andrianarivo, Jocelyn Rakotomalala, Domoina Rakotomalala, the late Olga Ramilijaona, Daniel Rakotondravony, Charlotte Rajeriarison, and Roger Edmond for their collaboration and support. We acknowledge the authorization and support of this study by the Ministère de l’Environement, des Eaux et Forêts et du Tourisme, MNP, and the University of Antananarivo. Tolona Andrianasolo kindly managed administrative affairs. Kasola Charles (Edson), Fisy Luis, and Kateffona Florent (Antsara) provided important help in the field. For their excellent support we acknowledge Sabine Baumann, Yvonne Bohr, Jutta Hammer, Matthias Marquart, Jana Jeglinski, Iris Kiefer, Susanne Kobbe, and the staff of the camp Andranovao. Andreas Hapke provided very helpful suggestions on the genetic analyses. We thank Joanna Setchell and the reviewers for their work and very helpful comments. The study was financed by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (Ga 342/15), the Volkswagen Foundation, and WWF Germany.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Bettina M. Scheel and Johanna Henke-von der Malsburg contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Table S1
(XLSX 226 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Scheel, B.M., Henke-von der Malsburg, J., Giertz, P. et al. Testing the Influence of Habitat Structure and Geographic Distance on the Genetic Differentiation of Mouse Lemurs (Microcebus) in Madagascar. Int J Primatol 36, 823–838 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10764-015-9855-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10764-015-9855-z