Abstract
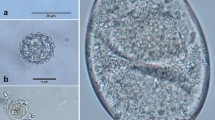
Translocation programs releasing animals into the wild need to assess the potential risks associated with the exchange of parasites and other pathogens between native and translocated species. We assessed the composition of the parasite communities in sympatric native and introduced primates. Over a 3-yr period we monitored the gastrointestinal parasites of 3 primate species living in the isolated ecosystem of Rubondo Island National Park, Tanzania: translocated chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes) and guerezas (Colobus guereza) and the indigenous vervets (Chlorocebus aethiops pygerythrus). We detected Troglodytella abrassarti and Enterobius cf. anthropopitheci only in chimpanzees and Chilomastix mesnili in chimpanzees and guerezas. In vervets, we recorded Anatrichosoma sp. and Subulura sp., previously reported in Rubondo chimpanzees. We found Blastocystis sp., Giardia sp., Iodamoeba buetschlii, Entamoeba coli, Entamoeba spp., Trichuris sp., Strongyloides spp., spirurids (cf. Protospirura muricola), and undetermined strongylids in all 3 primate species. Considering the absence of Protospirura muricola in other wild populations of chimpanzees and guerezas, it has probably been acquired from the native vervets, as have Anatrichosoma sp. and Subulura sp. Lower parasite load in Rubondo chimpanzees, in comparison with wild populations at other study sites of this species, might be due to their stay in captivity in Europe before being released on the island. Despite a lack of any apparent health problems from infections in introduced Rubondo primates, parasite monitoring during reintroduction/introduction projects is necessary to decrease potential risks resulting from the exchange of parasites between translocated and native species.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, R. C. (2000). Nematode parasites of vertebrates: Their development and transmission. Wallingford: CABI.
Appleton, C. C., Krecek, R. C., Verster, A., Bruorton, M. R., & Lawes, M. J. (1994). Gastro-intestinal parasites of Samango monkey, Cercopithecus mitis, in Natal, South Africa. Journal of Medical Primatology, 23, 52–55.
Ash, L. R., & Orihel, T. C. (2007). Atlas of human parasitology. Singapore: American Society for Clinical Pathology Press.
Ashford, R. W., Reid, G. D. F., & Wrangham, R. W. (2000). Intestinal parasites of the chimpanzee Pan troglodytes in Kibale Forest, Uganda. Annals of Tropical Medicine and Parasitology, 94, 173–179.
Baldwin, P. J., McGrew, W. C., & Tutin, C. E. G. (1982). Wide-ranging chimpanzees at Mt. Assirik, Senegal. International Journal of Primatology, 3, 367–385.
Beck, B., Walkup, K., Rodrigues, M., Uwin, S., Travis, D., & Stoinski, T. (2007). Best practice guidelines for the re-introduction of Great Apes. Gland: IUCN/SSC Primate Specialist Group of the World Conservation Union.
Beer, R. J. S. (1976). The relationship between Trichuris trichiura (Linnaeus, 1758) of man and Trichuris suis (Schrank, 1788) of the pig. Research in Veterinary Science, 20, 47–54.
Blagg, W., Schloegel, E. L., Mansour, N. S., & Khalal, G. I. (1955). A new concentration technic for the demonstration of protozoa and helminth eggs in feces. The American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene, 4, 23–28.
Borner, M. (1985). The rehabilitated chimpanzees of Rubondo Island. Oryx, 19, 151–154.
Cameron, T. W. M. (1930). The species of Subulura Molin in primates. Journal of Helminthology, 8, 49–58.
Chapman, C. A., Saj, T. L., & Snaith, T. V. (2007). Temporal dynamics of nutrition, parasitism, and stress in colobus monkeys: implications for population regulation and conservation. American Journal of Physical Anthropology, 134, 240–250.
Collet, J., Galdikas, B. M. F., Sugarjito, J., & Jojosudharmo, S. (1986). A coprological study of parasitism in orangutans (Pongo pygmaeus) in Indonesia. Journal of Medical Primatolology, 15, 121–129.
Conrad, H. D., & Wong, M. M. (1973). Studies of Anatrichosoma (Nematoda: Trichinellida) with descriptions of Anatrichosoma rhina sp. n. and Anatrichosoma nacepobi sp. n. from nasal mucosa of Macaca mulatta. Journal of Helminthology, 47, 289–302.
Cowan, P. E., & Rhodes, D. S. (1992). Restricting the movements of brushtail possum (Trichosurus vulpecula) on farmland with electric fencing. Wildlife Research, 19, 47–58.
Cunningham, A. A. (1996). Disease risks of wildlife translocations. Conservation Biology, 10, 349–353.
Cutillas, C., Callejon, R., de Rojas, M., Tewes, B., Ubeda, J. M., Ariza, C., et al. (2009). Trichuris suis and Trichuris trichiura are different nematode species. Acta Tropica, 111, 299–307.
Daszak, P., & Ball, S. J. (1998). Description of the oocysts of three new species of Eimeria (Apicomplexa: Eimeriidae) from Iguanid lizards (Sauria: Iguanidae) of Central and South America. Memórias do Instituto Oswaldo Cruz, 93, 471–475.
Davidson, W. R., & Nettles, V. F. (1992). Relocation of wildlife: identifying and evaluating disease risks. Transactions of the North American Wildlife & Natural Resources Conference, 57, 466–473.
Deem, S. L., Karesh, W. B., & Weisman, W. (2001). Putting theory into practice: wildlife health in conservation. Conservation Biology, 15, 1224–1233.
Dupain, J., van Elsacker, L., Nell, C., Garcia, P., Ponce, F., & Huffman, M. A. (2002). New evidence for leaf swallowing and Oesophagostomum infection in bonobos (Pan paniscus). International Journal of Primatology, 23, 1053–1062.
Dupain, J., Nell, C., Petrželková, K. J., Garcia, P., Modrý, D., & Gordo, F. P. (2009). Gastrointestinal parasites of bonobos in the Lomako Forest, Democratic Republic of Congo. In M. A. Huffman & C. Chapman (Eds.), Primate parasite ecology: The dynamics of host-parasite relationships (pp. 297–310). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Duszynski, D. W., Wilson, W. D., Upton, S. J., & Levine, N. D. (1999). Coccidia (Apicomplexa: Eimeriidae) in the primates and the scandentia. International Journal of Primatology, 20, 761–797.
Foster, A. O., & Johnson, C. M. (1939). A preliminary note on identity, life cycle, and pathogenicity of an important parasite of captive monkeys. The American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene, 19, 265–277.
Gasser, R. B., de Gruijter, J. M., & Polderman, A. M. (2009). The utility of molecular methods for elucidating primate-pathogen relationships—the Oesophagostomum bifurcum example. In M. A. Huffman & C. Chapman (Eds.), Primate parasite ecology: The dynamics of host-parasite relationships (pp. 47–62). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Gillespie, T. R. (2006). Noninvasive assessment of gastrointestinal parasite infections in free-ranging primates. International Journal of Primatology, 27, 1129–1143.
Gillespie, T. R., Greiner, E. C., & Chapman, C. A. (2004). Gastrointestinal parasites of the guenons of western Uganda. The Journal of Parasitology, 90, 1356–1360.
Gillespie, T. R., Greiner, E. C., & Chapman, C. A. (2005a). Gastrointestinal parasites of the colobus monkeys of Uganda. The Journal of Parasitology, 91, 569–573.
Gillespie, T. R., Chapman, C. A., & Greiner, E. C. (2005b). Effects of logging on gastrointestinal parasite infections and infection risk in African primates. Journal of Applied Ecology, 42, 699–707.
Graczyk, T. K., Bosco-Nizeyi, J., Ssebide, B., Thompson, R. C. A., Read, C., & Cranfield, M. R. (2002). Anthropozoonotic Giardia duodenalis genotype (Assemblage) A infections in habitats of free-ranging human-habituated gorillas, Uganda. The Journal of Parasitology, 88, 905–909.
Grzimek, B. (1970). Among animals of Africa. New York: Stein & Day.
Hasegawa, H., & Udono, T. (2007). Chimpanzee pinworm, Enterobius anthropopitheci (Nematoda: Oxyuridae), maintained for more than twenty years in captive chimpanzees in Japan. The Journal of Parasitology, 93, 850–853.
Hasegawa, H., Kano, T., & Mulavwa, M. (1983). A parasitological survey on the feces of pygmy chimpanzees, Pan paniscus, at Wamba, Zaire. Primates, 24, 419–423.
Hasegawa, H., Ikeda, Y., Fujisaki, A., Moscovice, L. R., Petrželková, K. J., Kaur, T., et al. (2005). Morphology of chimpanzee pinworms, Enterobius (Enterobius) anthropopitheci (Geldoelst, 1916) (Nematoda: Oxyuridae), collected from chimpanzees, Pan troglodytes, on Rubondo Island, Tanzania. The Journal of Parasitology, 91, 1314–1317.
Hasegawa, H., Hayashida, S., Ikeda, Y., & Sato, H. (2009). Hyper-variable regions in 18S rDNA of Strongyloides spp. as markers for species-specific diagnosis. Parasitology Research, 104, 869–874.
Hegner, R. W. (1924). Giardia and Chilomastix from monkeys, Giardia from the wild cat and Blantidium from sheep. The Journal of Parasitology, 11, 75–78.
Huffman, M. A., Gotoh, S., Turner, L. A., Hamai, M., & Yoshida, K. (1997). Seasonal trends in intestinal nematode infection and medicinal plant use among chimpanzees in the Mahale Mountains, Tanzania. Primates, 38, 111–125.
Huffman, M. A., Petrželková, K. J., Moscovice, L. R., Mapua, M. I., Bobáková, L., Mazoch, V., et al. (2008). Introduction of chimpanzees onto Rubondo Island National Park, Tanzania. In P. S. Soorae (Ed.), Global re-introduction perspectives: re-introduction case-studies from around the globe (pp. 213–215). Abu Dhabi: IUCN/SSC Re-introduction Specialist Group.
Huffman, M. A., Pebsworth, P., Bakuneeta, C., Gotoh, S. G., & Bardi, M. (2009). Chimpanzee-parasite ecology at Budongo Forest (Uganda) and the Mahale Mountains (Tanzania): Influence of climatic differences on self-medicative behavior. In M. A. Huffman & C. Chapman (Eds.), Primate parasite ecology: The dynamics of host-parasite relationships (pp. 331–350). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Hugot, J. P. (1993). Redescription of Enterobius anthropopitheci (Gedoelst, 1916) (Nematoda, Oxyurida), a parasite of chimpanzees. Systematic Parasitology, 26, 201–207.
IUCN (International Union for Conservation of Nature). (1987). The IUCN position statement on translocation of living organisms. Gland: IUCN/SSC Re-introduction Specialist Group.
IUCN. (1998). Guidelines for re-introductions. Gland: IUCN/SSC Re-introduction Specialist Group.
IUCN. (2002). Guidelines for nonhuman primate re-introductions. Gland: IUCN/SSC Re-introduction Specialist Group.
Jessee, M. T., Schilling, P. W., & Stunkard, J. A. (1970). Identification of intestinal helminth eggs in old world primates. Laboratory Animal Care, 20, 83–87.
Kawazoe, U., & Gouvea, H. (1999). Description of Pythonella scleruri n. sp. (Apicomplexa: Eimeriidae) from a Brazilian bird rufous-breasted-leaftosser Scerurus scansor, 1835 (Passeriformes: Furnariidae). Memórias do Instituto Oswaldo Cruz, 94, 157–159.
Kilbourn, A. M., Karesh, W. B., Wolfe, N. D., Bosi, E. J., Cook, R. A., & Andau, M. (2003). Health evaluation of free-ranging and semi-captive orangutans (Pongo pygmaeus pygmaeus) in Sabah, Malaysia. Journal of Wildlife Diseases, 39, 73–83.
Kiwango, J. (2002). Ecological survey RINP. Unpublished report of Tanzanian National Parks.
Krief, S., Huffman, M. A., Sevenet, T., Guillot, J., Bories, B., Hladik, C. M., et al. (2005). Non-invasive monitoring of the health of Pan troglodytes schweinfurthii in the Kibale National Park, Uganda. International Journal of Primatology, 26, 467–490.
Kulda, J., & Nohynkova, E. (1978). Flagellates of the human intestine and of the intestines of other species. In J. P. Kreiner (Ed.), Parasitic protozoa (pp. 1–138). New York: Academic.
Kuntz, R. E., & Myers, B. J. (1969). Parasitic protozoa, commensals and helminths of chimpanzees imported from the Republic of the Congo. Proceedings of the 2nd International Congress of Primatology, 3, 184–190.
Landsoud-Soukate, J., Tutin, C. E., & Fernandez, M. (1995). Intestinal parasites of sympatric gorillas and chimpanzees in the Lope Reserve, Gabon. Annals of Tropical Medicine and Parasitology, 89, 73–79.
Legesse, M., & Erko, B. (2004). Zoonotic intestinal parasites in Papio anubis (baboon) and Cercopithecus aethiops (vervet) from four localities in Ethiopia. Acta Tropica, 90, 231–236.
Levecke, B., Dorny, P., Geurden, T., Vercammen, F., & Vercruysse, J. (2007). Gastrointestinal protozoa in non-human primates of four zoological gardens in Belgium. Veterinary Parasitology, 148, 236–246.
Levine, N. D. (1985). Veterinary protozoology. Iowa: Iowa State University Press.
Lilly, A. A., Mehlman, P. T., & Doran, D. (2002). Intestinal parasites in gorillas, chimpanzees, and humans at Mondika Research Site, Dzanga-Ndoki National Park, Central African Republic. International Journal of Primatology, 23, 555–573.
Long, G. G., Lichtenfels, J. R., & Stookey, J. L. (1976). Anatrichosoma cynamolgi (Nematoda: Trichinellida) in rhesus monkeys, Macaca mulatta. The Journal of Parasitology, 62, 111–115.
Mbora, D. N. M., & Munene, E. (2006). Gastrointestinal parasites of critically endangered primates endemic to Tana River, Kenya: Tana River red colobus (Procolobus rufomitratus) and crested mangabey (Cercocebus galeritus). The Journal of Parasitology, 92, 928–932.
McCallum, H., & Dobson, A. (1995). Detecting disease and parasite threats to endangered species and ecosystem. Tree, 10, 190–194.
McGrew, W. C., Tutin, C. E. G., Collins, D. A., & File, S. K. (1989a). Intestinal parasites of sympatric Pan troglodytes and Papio spp., at two sites—Gombe (Tanzania) and Mt. Assirik (Senegal). American Journal of Primatology, 17, 147–155.
McGrew, W. C., Tutin, C. E. G., & File, S. K. (1989b). Intestinal parasites of two species of free-living monkeys in far western Africa, Cercopithecus (aethiops) sabaeus and Erythrocebus patas patas. African Journal of Ecology, 27, 261–262.
Moscovice, L. R. (2006). Behavioral ecology of chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes) on Rubondo Island, Tanzania: habitat, diet, grouping and ranging at a release site. Dissertation Abstracts International, B 67(6), AADAA.
Moscovice, L. R., Issa, M. H., Petrželková, K. J., Keuler, N. S., Snowdon, C. T., & Huffman, M. A. (2007). Fruit availability, chimpanzee diet, and grouping patterns on Rubondo Island, Tanzania. American Journal of Primatology, 69, 487–502.
Mudakikwa, A. B., Sleeman, J. M., Foster, J. W., Madder, L. L., & Patton, S. (1998). An indicator of human impact: gastrointestinal parasites of mountain gorillas (Gorilla gorilla beringei) from the Virunga Volcanoes Region, Central Africa. In C. K. Baer (Ed.), Proceedings of the American Association of Zoo Veterinarians/American Association of Wild Veterinarians Joint Conference (pp. 436–437). Philadelphia: American Association of Zoo Veterinarians.
Muehlenbein, M. P. (2005). Parasitological analyses of the male chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes schweinfurthii) at Ngogo, Kibale National Park, Uganda. American Journal of Primatology, 65, 167–179.
Mul, I. F., Paembonan, W., Singleton, I., Wich, S. A., & van Bolhuis, H. G. (2007). Intestinal parasites of free-ranging, semicaptive and captive Pongo abelii in Sumatra, Indonesia. International Journal of Primatology, 28, 407–420.
Munene, E., Otsyula, M., Mbaabu, D. A. N., Mutahi, W. T., Muriuki, S. M. K., & Muchemi, G. M. (1998). Helminth and protozoan gastrointestinal tract parasites in captive and wild-trapped African non-human primates. Veterinary Parasitology, 78, 195–201.
Murata, K., Hasegawa, H., Nakano, T., Noda, A., & Yanai, T. (2002). Fatal infection with human pinworm, Enterobius vermicularis, in a captive chimpanzee. Journal of Medical Primatology, 31, 104–108.
Murray, S., Stem, C., Boudreau, B., & Goodall, J. (2000). Intestinal parasites of baboons (Papio cynocephalus anubis) and chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes) in Gombe National Park. Journal of Zoo and Wildlife Medicine, 31, 176–178.
Nakano, T., Okamoto, M., Ikeda, Y., & Hasegawa, H. (2006). Mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit 1 gene and nuclear rDNA regions of Enterobius vermicularis parasitic in captive chimpanzees with special reference to its relationship with pinworms in humans. Parasitology Research, 100, 51–57.
Nizeyi, J. B., Mwebe, R., Nanteza, A., Cranfield, M. R., Kalema, G. R. N. N., & Graczyk, T. K. (1999). Cryptosporidium sp. and Giardia sp. infections in mountain gorillas (Gorilla gorilla beringei) of the Bwindi Impenetrable National Park, Uganda. The Journal of Parasitology, 85, 1084–1088.
Nkurunungi, J. B. (1999). A survey of the gastro-intestinal helminths of the wild mountain gorilla (Gorilla gorilla beringei Matschie) and man in Bwindi Impenetrable National Park of southwestern Uganda. Proceedings of the Ecological Monitoring Programme Workshop: Research as an important tool of ecological monitoring in Bwindi Impenetrable National Park, Uganda, 9–11.
Nunn, C. L., Altizer, S., Jones, K. E., & Sechrest, W. (2003). Comparative tests of parasite species richness in primates. The American Naturalist, 162, 597–614.
Okanga, S., Muchemi, G., Maingi, N., Mogoa, E., & Munene, E. (2006). Gastrointestinal parasites of free-ranging colobus monkeys (Colobus angolensis palliatus) in Kwale District, Kenya coast. African Journal of Ecology, 44, 410–412.
Orihel, T. C. (1970). Anatrichosomiasis in African monkeys. The Journal of Parasitology, 56, 982–985.
Parkar, U., Traub, R. J., Vitali, S., Elliot, A., Levecke, B., Robertson, I., et al. (2010). Molecular characterization of Blastocystis isolates from zoo animals and their animal-keepres. Veterinary Parasitology, 169, 8–17.
Pedersen, A. B., Altizer, S., Poss, M., Cunningham, A. A., & Nunn, C. L. (2005). Patterns of host specificity and transmission among parasites of wild primates. International Journal for Parasitology, 35, 647–657.
Petrželková, K. J., Hasegawa, H., Moscovice, L. R., Kaur, T., Mapua, M. I., & Huffman, M. A. (2006). Parasitic nematodes in the chimpanzee population on Rubondo Island, Tanzania. International Journal of Primatology, 27, 767–777.
Petrželková, K. J., Hasegawa, H., Appleton, C. C., Huffman, M. A., Archer, C. E., Moscovice, L. R., et al. (2010). Gastrointestinal parasites of the chimpanzee population introduced onto Rubondo Island National Park, Tanzania. American Journal of Primatology, 72, 307–316.
Pomajbiková, K., Petrželková, K. J., Profousová, I., Petrášová, J., Kisidayová, S., Varadyová, Z., et al. (2010). A survey of entodiniomorphid ciliates in chimpanzees and bonobos. American Journal of Physical Anthropology, 142, 42–48.
Reptová, Z. (2008). Morfologicka variabilita vajicok hlistic rodu Trichuris u primatov. [Morphologic variability of eggs of genus Trichuris in primates]. VMD thesis, The University of Veterinary and Pharmaceutical Sciences, Brno, Czech Republic.
Reynolds, V. (2005). The chimpanzees of the Budongo forest. Ecology, behaviour, and conservation. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Rice, W. R. (1989). Analyzing tables of statistical tests. Evolution, 43, 223–225.
Ruch, T. C. (1959). Diseases of laboratory primates. Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders.
Salzer, J. S., Rwego, I. B., Goldberg, T. L., Kuhlenschmidt, M. S., & Gillespie, T. R. (2007). Giardia sp. and Cryptosporidium sp. infections in primates in fragmented and undisturbed forest in Western Uganda. The Journal of Parasitology, 93, 439–440.
Sheather, A. L. (1923). The detection of intestinal protozoa and mange parasites by a flotation technique. Journal of Comparative Pathology, 36, 266–275.
Sleeman, J. M., Meader, L. L., Mudakikwa, A. B., Foster, J. W., & Patton, S. (2000). Gastrointestinal parasites of mountain gorillas (Gorilla gorilla beringei) in the Parc National des Volcans, Rwanda. Journal of Zoo and Wildlife Medicine, 31, 322–328.
Solaymani-Mohammadi, S., Rezaian, M., Hooshyar, H., Mowlavi, G. R., Babaei, Z., & Anwar, M. A. (2004). Intestinal protozoa in wild boars (Sus scrofa) in Western Iran. Journal of Wildlife Diseases, 40, 801–803.
Spakulova, M. (1994). Discriminant analysis as a method for the numerical evaluation of taxonomic characters in male trichurid nematodes. Systematic Parasitology, 29, 113–119.
Stensvold, C. R., Arendrup, M. C., Jespersgaard, C., Molbak, K., & Nielsen, H. V. (2007). Detecting Blastocystis using parasitologic and DNA-based methods: a comparative study. Diagnostic Microbiology and Infectious Disease, 59, 303–307.
Stensvold, C. R., Alfellani, M. A., Norskov-Lauritsen, S., Prip, K., Victory, E. L., Maddox, C., et al. (2009). Subtype distribution of Blastocystis isolates from synanthropic and zoo animals and identification of a new subtype. International Journal for Parasitology, 39, 473–479.
Teichroeb, J. A., Kutz, S. J., Parkar, U., Thompson, R. C. A., & Sicotte, P. (2009). Ecology of the gastrointestinal parasites of Colobus vellerosus at Boabeng-Fiema, Ghana: possible anthropozoonotic transmission. American Journal of Physical Anthropology, 140, 498–507.
Torchin, M. E., Lafferty, K. D., Dobson, A. P., McKenzie, V. J., & Kuris, A. M. (2003). Introduced species and their missing parasites. Nature, 421, 628–630.
Verweij, J. J., Vermeer, J., Brienen, E. A. T., Blotkamp, C., Laeijendecker, D., van Lieshout, L., et al. (2003). Entamoeba histolytica infections in captive primates. Parasitology Research, 90, 100–103.
Viggers, K. L., Lindenmayer, D. B., & Spratt, D. M. (1993). The importance of disease in reintroduction programmes. Wildlife Research, 20, 678–698.
Vitazkova, S. K., & Wade, S. E. (2006). Parasites of free-ranging black howler monkeys (Alouatta pigra) from Belize and Mexico. American Journal of Primatology, 68, 1089–1097.
Volotao, A. C. C., Souza Junior, J. C., Grassini, C., Peralta, J. M., & Fernandes, O. (2008). Genotyping of Giardia duodenalis from southern brown howler monkeys (Alouatta clamitans) from Brazil. Veterinary Parasitology, 158, 133–137.
Wolfe, N. D., Escalante, A. A., Karesh, W. B., Kilbourn, A., Spielman, A., & Lal, A. A. (1998). Wild primate populations in emerging infectious disease research: the missing link? Emerging Infectious Diseases, 4, 149–158.
Woodford, M. H., & Rossiter, P. B. (1993). Disease risks associated with wildlife translocations projects. Revue Scientifique et Technique—Office International des Epizooties, 12, 115–135.
Yamashita, J. (1963). Ecological relationships between parasites and primates. I. Helminth parasites and primates. Primates, 4, 1–96.
Yoshikawa, H., Yamada, M., Matsumoto, Y., & Yoshida, Y. (1989). Variations in egg size of Trichuris trichiura. Parasitology Research, 75, 649–654.
Yoshikawa, H., Morimoto, K., Wu, Z., Yap, E. H., Singh, M., & Hashimoto, T. (2004). Problems in speciation in the genus Blastocystis. Trends in Parasitology, 20, 251–255.
Yoshikawa, H., Wu, Z., Pandey, K., Pandey, B. D., Sherchand, J. B., Yanagi, T., et al. (2009). Molecular characterization of Blastocystis isolates from children and rhesus monkey in Kathmandu, Nepal. Veterinary Parasitology, 160, 295–300.
Zajac, A., & Conboy, G. A. (2006). Veterinary clinical parasitology. Ames: Blackwell.
Acknowledgments
The present research was supported by the Grant Agency of the Academy of Sciences of the Czech Republic (KJB600930615) and Grant Agency of the Czech Republic (524/06/0264, 206/09/0927). J. Petrášová was partially supported by the Internal Grant Agency of the University of Veterinary and Pharmaceutical Sciences (IGA 77/2007/FVL). We express our sincere appreciation to the Government of Tanzania, the Tanzania Commission for Science and Technology, Tanzania National Parks, and the Tanzania Wildlife Research Institute for their support and for granting permission to conduct this research in Tanzania. We thank our Tanzanian trackers for their participation in the collection of fecal samples and their help and wonderful companionship in the field. Our best wishes go to Rubondo Island National Park Wardens and staff for their kind hospitality and important logistical support. We thank our 2 anonymous reviewers and the editor for their helpful comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Petrášová, J., Modrý, D., Huffman, M.A. et al. Gastrointestinal Parasites of Indigenous and Introduced Primate Species of Rubondo Island National Park, Tanzania. Int J Primatol 31, 920–936 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10764-010-9439-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10764-010-9439-x