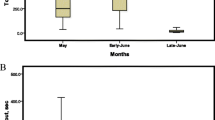
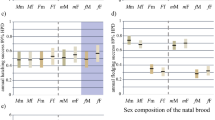
Abstract
Immature captive gibbons are often housed together to facilitate healthy social development. Zoo personnel have wondered if the familiarity acquired during peer-rearing results in sexual aversion at maturity. We discuss whether housing gibbons together before sexual maturity causes them to later reject each other as mates and therefore inhibits their reproductive potential. We conducted a survey of gibbons housed at zoos, conservation centers, and with private individuals. Our data suggest that early rearing experiences with potential mates do not prevent mating between gibbons housed together while immature. Using studbook data, we compared infant mortality in inbred and outbred captive gibbons. We found no significant difference in mortality rates for the 2 samples, though adverse effects of inbreeding may become apparent at later ages and in future generations. Our results indicate that early cohabitation is a feasible housing strategy for breeding programs and for rehabilitation/rescue projects in habitat countries where the main concern is the reproductive viability of gibbons.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bartlett, T. (1999). The gibbons. In Dolhinow, P., and Fuentes, A. (eds.), The Nonhuman Primates, Mayfield Publishing Company, Mountain View, CA, pp. 44–49.
Bartlett, T. Q. (2003). Intragroup and intergroup social interactions in white-handed gibbons. Int. J. Primatol. 24: 239–259.
Bengtsson, B. O. (1978). Avoiding inbreeding: At what cost? J. Theor. Biol. 73: 439–444.
Bercovitch, F. B. (1991). Mate selection, consortship formation, and reproductive tactics in adult female savanna baboons. Primates 32: 437–452.
Bleisch, W. J., and Chen, N. (1991). Ecology and behavior of wild black-crested gibbons in China with a reconsideration of evidence for polygyny. Primates 32: 539–545.
Brandon–Jones, D., Eudey, A. A., Geissmann, T., Groves, C. P., Melnick, D. J., Morales, J. C., Shekelle, M., and Stewart, C. B. (2004). Asian primate classification. Int. J. Primatol. 25: 97–164.
Brockelman, W. Y., Reichard, U., Treesucon, U., and Raemaekers, J. J. (1998). Dispersal, pair formation and social structure in gibbons (Hylobates lar). Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 42: 329–339.
Carpenter, C. R. (1940). A field study in Siam of the behavior and social relations of the gibbon (Hylobates lar). Comp. Psychol. Monogr. 16: 1–212.
Chivers, D. J., and Raemaekers, J. J. (1980). Long-term changes in behaviour. In Chivers, D. J. (ed.), Malayan Forest Primates. Ten Years' Study in Tropical Rain Forests, Plenum Press, New York, pp. 209–260.
Couturier, J., Dutrillaux, B., Turleau, C., and Grouchy, J. de. (1982). Comparaisons chromosomiques chez quatre especes ou sous–especes de gibbons. (Comparative karyotyping of four gibbon species or sub-species). Ann. Genet. 25: 5–10.
Crawford, M. H., and O'Rourke, D. H. (1978). Inbreeding, lymphoma, genetics and morphology of the Papio Hamadryas colony of Sakhumi. J. Med. Primatol. 7: 355–360.
Demarest, W. J. (1977). Incest avoidance among human and nonhuman primates. In Chevalier-Skolnikoff, S., and Poirier, F. E. (eds.), Primate Bio-Social Development: Biological, Social, and Ecological Determinants, Garland Publishing, New York, pp. 323–342.
Dutrillaux, B., Viegas-Pequignot, E., Dudos, C., and Masse, R. (1978). Complete or almost complete analogy of chromosome banding between baboon (Papio papio) and man. Hum. Genet. 43: 37–46.
Edwards, A. M. A. R., and Todd, J. D. (1991). Homosexual behaviour in wild white-handed gibbons (Hylobates lar). Primates. 32: 231–236.
Enomoto, T. (1975). The sexual behavior of wild Japanese monkeys: The sexual interaction pattern and the social preference. In Kondo, S., Kawai, M., and Ehara, A. (eds.), Contemporary Primatology, Proceedings of the Fifth International Congress of Primatology, S. Karger, Basel, pp. 275–279.
Erhart, E. M., Coehlo, Jr., A. M., and Bramblett, C. A. (1997). Kin recognition by paternal half–-sibling in captive (Papio cynocephalus). Am. J. Primatol. 43: 147–157
Fox, G. (1977). Social Dynamics in siamang. Unpublished Doctoral thesis. University of Wisconsin–Milwaukee, Milwaukee.
Fuentes, A. (2000). Hylobatid communities: Changing views on pair bonding and socialization in hominoids. Ybk. Phys. Anthropol. 43: 33–60.
Geissmann, T. (1991). Reassessment of age at sexual maturity in gibbons. Am. J. Primatol. 23: 11–22.
Goodall, J. (1986). The chimpanzees of Gombe: Patterns of behavior. Harvard University Press. Cambridge, MA, p. 673.
Gouzoules, S., and Gouzoules, H. (1987). Kinship. In Smuts, B. B., Cheney, D. L., Seyfarth, R. M., Wrangham, R. W., and Struhsaker, T. T. (eds.), Primate Societies, University of Chicago Press, Chicago, pp. 299–305.
Hirai, H., Mootnick, A. R., Takenaka, O., Suryobroto, B., Mouri, T., Kamanaka, Y., Katoh, A., Kimura, N., Katoh, A., and Maeda, N. (2003). Genetic mechanism and property of a whole-arm translocation (WAT) between chromosomes 8 and 9 of agile gibbons (Hylobates agilis). Chromosome Res. 11: 37–50.
Holmes, W. G., and Sherman, P. W. (1983). Kin recognition in animals. Am. Sci. 71: 46–55.
Leighton, D. R. (1987). Gibbons: Territoriality and monogamy. In Smuts, B. B., Cheney, D. L., Seyfarth, R. M., Wrangham, R. W., and Struhsaker, T. T. (eds.), Primate Societies, University of Chicago Press, Chicago, pp. 135–145.
Marks, J. (1983). Hominoid cytogenetics and evolution. Ybk. Phys. Anthropol. 25:131–159.
Melnick, D. J., Pearl, M. C., and Richard, A. F. (1984). Male migration and inbreeding avoidance in wild rhesus monkeys. Am. J. Primatol. 7: 229–243.
Merritt, D. A. Jr. (1980). Captive reproduction and husbandry of the douroucouli (Aotus trivirgatus) and the titi monkey (Callicebus) spp. Int. Zoo Ybk. 20: 52–59.
Moore, D. E. (1985). The natural breeding strategy of gibbons (Hylobates lar): Are we managing the captive population by design or by default? In Benirschke, K. (ed.), Primates: The Road to Self-Sustaining Populations, Springer Verlag, New York, pp. 161–169.
Mootnick, A. R., and Baker, E. (1994). Masturbation in captive Hylobates (gibbons). Zoo Biol. 13: 345–353.
Mootnick, A. R., and Groves, C. (2005). A new generic name for the hoolock gibbon (Hylobatidae). In. J. Primatol. 26(4): 971–976.
Mootnick, A. R., and Nadler, R. D. (1997). Sexual behavior of maternally separated gibbons (Hylobates spp.). Dev. Psycholbiol. 31: 149–161.
Murray, D., and Smith, E. (1983). The role of dominance and intrafamilial bonding in the avoidance of close inbreeding. J. Hum. Evol. 12: 481–486.
Palombit, R. A. (1992). Pair bonds and monogamy in wild siamang (Hylobates syndactylus) and white-handed gibbon (Hylobates lar) in northern Sumatra. Ph.D. thesis, University of California, Davis.
Palombit, R. A. (1994). Dynamic pair bonds in hylobatids: Implications regarding monogamous social systems. Behaviour, 128: 65–101.
Pusey, A. E. (1980). Inbreeding avoidance in chimpanzees. Anim. Behav. 28: 543–552.
Pusey, A. E., and Packer, C. (1987). Dispersal and Philopatry. In Smuts, B. B., Cheney, D. L., Seyfarth, R. M., Wrangham, R. W., and Struhsaker, T. T. (eds.), Primate Societies, University of Chicago Press, Chicago, pp. 250–266.
Ralls, K., and Ballou, J. (1982). Effects on inbreeding on infant mortality in captive primates. Int. J. Primatoll. 3: 491–505.
Reichard, U. (1995). Extrapair copulations in a monogamous gibbon (Hylobates lar). Ethology 100: 99–112.
Reichard, U. H. (2003). Social monogamy in gibbons: The male perspective. In Reichard, U. H., and Boesch, C. (eds.), Monogamy: Mating Strategies and Partnerships in Birds, Humans, and Other Mammals, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, MA. pp. 190–213.
Roos C., and Geissmann, T. (2001). Molecular phylogeny of the major hylobatid divisions. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 19: 486–494.
Sade, D. S. (1968). Inhibition of son-mother mating among free-ranging rhesus monkeys. Sci. Psychoanal. 12: 18–38.
Sheeran, L. K., Zhang, Y. Z., Poirier, F. E., and Yang, D. H. (1998). Preliminary report on black gibbon (Hylobates concolor) behavior. Trop. Biodiver. 5: 113–125.
Shields, W. M. (1982). Inbreeding and the paradox of sex: A resolution? Evol. Theory 5: 245–279.
Shields, W. M. (1987). Dispersal and mating systems: Investigating their causal connections. In Chepko-Sade, B. D., and Halpin, Z. T. (eds.), Mammalian Dispersal Patterns: The Effects of Social Structure on Population Genetics, University of Chicago Press, Chicago, pp. 3–24.
Smith, D. G. (1982). Inbreeding in three captive groups of rhesus monkeys. Am. J. Phys. Anthropol. 58: 447–451.
Sommer, V., and Rajpurohit, L. S. (1989). Male reproductive success in harem troops of Hanuman langurs (Presbytis entellus). Int. J. Primatol. 10: 293–317.
Sommer, V., and Reichard, U. (2000). Rethinking monogamy: The gibbon case. In Kappeler, P. M. (ed.), Primate Males: Causes and Consequences of Variation in Group Composition, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, MA, pp. 159–168.
Srikosamatara, S., and Brockelman, W. Y. (1987). Polygyny in a group of pileated gibbons via a familial route. Int. J. Primatol. 8: 389–393.
Taylor, L., and Sussman, R. W. (1985). A preliminary study of kinship and social organization in a semi-free-ranging group of Lemur catta. Int. J. Primatol. 6: 601–614.
Tenaza, R. R. (1975). Territory and monogamy among Kloss' gibbons (Hylobates klossii) in Siberut Island, Indonesia. Folia Primatol. 24: 60–80.
Tilson, R. L. (1981). Family formation strategies of Kloss' gibbons. Folia Primatol. 35: 259–287.
van Tuinen, P., and Ledbetter, D. H. (1983). Cytogenetic comparison and phylogeny of three species of Hylobatidae. Am. J. Phys. Anthropol. 6: 453–466.
Walters, J. R. (1987). Kin recognition in non-human primates. In Fletcher, D. J. C., and Michener, C. D. (eds.), Kin Recognition in Animals, John Wiley& Sons, New York, pp. 359–393.
Welker, C., Hohmann, H., and Schafer-Witt, C. (1990). Significance of kin relations and individual preferences in the social behaviour of Cebus apella. Folia Primatol. 54: 166–170.
Yunis, J. Y., and Prakash, O. (1982). The origin of man: A chromosomal pictorial legacy. Science 215: 1525–1530.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mootnick, A.R., Baker, E. & Sheeran, L.K. Familiarity During Immaturity: Implications for the Captive Propagation of Gibbons. Int J Primatol 26, 1417–1433 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10764-005-8860-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10764-005-8860-z