Abstract
In this study, to facilitate the integration of environmental education in science curricula and achieve a more sustainable future, the relationships among scientific epistemic views, decision-making style, and recycling intention based on the theory of planned behavior were investigated. Three instruments (i.e. SEVs, DMS, and RI) were implemented on a sample of 515 Taiwanese high school students and revealed sufficient validity and reliability by employing exploratory and confirmatory factor analyses. Structural equation modeling analysis showed that students’ scientific epistemic views do not directly link to recycling intention, whereas SEVs predict decision-making styles and decision-making styles predict recycling intention. The research findings suggest that teachers might consider encouraging students to develop the ability to think deeply and holistically by adopting the scientific approach in environmental education. This research also provided important information for educators to deliver environmental education effectively under the environment of Confucian culture. Limitations of the study and future research recommendations are discussed.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abd-El-Khalick, F., & Lederman, N. G. (2000). Improving science teachers’ conceptions of nature of science: A critical review of the literature. International Journal of Science Education, 22(7), 665–701.
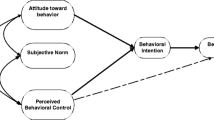
Ajzen, I. (1991). The theory of planned behavior. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 50(2), 179–211.
Armitage, C. J., & Conner, M. (2001). Efficacy of the theory of planned behaviour: A meta-analytic review. British Journal of Social Psychology, 40(4), 471–499.
Bakewell, C., & Mitchell, V. W. (2003). Generation Y female consumer decision-making styles. International Journal of Retail & Distribution Management, 31(2), 95–106.
Bamberg, S., & Möser, G. (2007). Twenty years after Hines, Hungerford, and Tomera: A new meta-analysis of psycho-social determinants of pro-environmental behaviour. Journal of Environmental Psychology, 27(1), 14–25.
Bell, P., & Linn, M. C. (2002). Beliefs about science: How does science instruction contribute? In B. Hofer & P. R. Pintrich (Eds.), Personal epistemology: The psychology of beliefs about knowledge and knowing (pp. 321–346). Mahwah, NJ: Erlbaum.
Bell, R. L., & Lederman, N. G. (2003). Understandings of the nature of science and decision making on science and technology based issues. Science Education, 87(3), 352–377.
Berisha, G., Pula, J. S., & Krasniqi, B. (2018). Convergent validity of two decision making style measures. Journal of Dynamic Decision Making, 4(1), 1–8.
Carmi, N., Arnon, S., & Orion, N. (2015). Seeing the forest as well as the trees: General vs. specific predictors of environmental behavior. Environmental Education Research, 21(7), 1011–1028.
Chan, L., & Bishop, B. (2013). A moral basis for recycling: Extending the theory of planned behaviour. Journal of Environmental Psychology, 36, 96–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvp.2013.07.010.
Chang, H. Y., Hsu, Y. S., Wu, H. K., & Tsai, C. C. (2018). Students’ development of socio-scientific reasoning in a mobile augmented reality learning environment. International Journal of Science Education, 40(12), 1410–1431.
Chang, H. Y., Liang, J. C., & Tsai, C. C. (2020). Students’ context-specific epistemic justifications, prior knowledge, engagement, and socioscientific reasoning in a mobile augmented reality learning environment. Journal of Science Education and Technology, 29(3), 399–408.
Cheng, T. M., & Wu, H. C. (2015). How do environmental knowledge, environmental sensitivity, and place attachment affect environmentally responsible behavior? An integrated approach for sustainable island tourism. Journal of Sustainable Tourism, 23(4), 557–576.
Chiou, G. L., Lee, M. H., & Tsai, C. C. (2013). High school students’ approaches to learning physics with relationship to epistemic views on physics and conceptions of learning physics. Research in Science & Technological Education, 31(1), 1-15.
Conley, A. M., Pintrich, P. R., Vekiri, I., & Harrison, D. (2004). Changes in epistemological beliefs in elementary science students. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 29(2), 186–204.
De Leeuw, A., Valois, P., Ajzen, I., & Schmidt, P. (2015). Using the theory of planned behavior to identify key beliefs underlying pro-environmental behavior in high-school students: Implications for educational interventions. Journal of Environmental Psychology, 42, 128–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvp.2015.03.005.
Deng, F., Chen, D. T., Tsai, C. C., & Chai, C. S. (2011). Students’ views of the nature of science: A critical review of research. Science Education, 95(6), 961–999.
Dewberry, C., Juanchich, M., & Narendran, S. (2013). The latent structure of decision styles. Personality and Individual Differences, 54(5), 566–571.
Diekmann, A., & Preisendörfer, P. (2003). Green and greenback: The behavioral effects of environmental attitudes in low-cost and high-cost situations. Rationality and Society, 15(4), 441–472.
Dillon, J., & Scott, W. (2002). Perspectives on environmental education-related research in science education. International Journal of Science Education, 24(11), 1111–1117.
Driver, M. J., Brousseau, K. R., & Hunsaker, P. L. (1990). The dynamic decision maker. New York, NY: Harper and Row.
Environmental Protection Administration. (2019). Recycling Fund 20th Anniversary Exhibition Reflects New Values. Retrieved from https://www.epa.gov.tw/eng/F7AB26007B8FE8DF/d85399bc-5976-4dbc-938f-3436cb843974. Accessed 17 Nov 2020
Gifford, R. (2014). Environmental psychology matters. Annual Review of Psychology, 65, 541–579.
Goldman, D., Yavetz, B., & Pe'er, S. (2006). Environmental literacy in teacher training in Israel: Environmental behavior of new students. The Journal of Environmental Education, 38(1), 3–22.
Greaves, M., Zibarras, L. D., & Stride, C. (2013). Using the theory of planned behavior to explore environmental behavioral intentions in the workplace. Journal of Environmental Psychology, 34, 109–120.
Greene, J. A., Sandoval, W. A., & Bråten, I. (2016). An introduction to epistemic cognition. In J. A. Greene, W. A. Sandoval, & I. Bråten (Eds.), Handbook of epistemic cognition (pp.1–15). New York, NY: Routledge.
Hamilton, K., Shih, S. I., & Mohammed, S. (2016). The development and validation of the rational and intuitive decision styles scale. Journal of Personality Assessment, 98(5), 523–535.
Harren, V. A. (1979). A model of career decision making for college students. Journal of Vocational Behavior, 14(2), 119–133.
Heimlich, J. E., & Ardoin, N. M. (2008). Understanding behavior to understand behavior change: A literature review. Environmental Education Research, 14(3), 215–237.
Hines, J. M., Hungerford, H. R., & Tomera, A. N. (1987). Analysis and synthesis of research on responsible environmental behavior: A meta-analysis. The Journal of Environmental Education, 18(2), 1–8.
Hofer, B. K., & Pintrich, P. R. (1997). The development of epistemological theories: Beliefs about knowledge and knowing and their relation to learning. Review of Educational Research, 67(1), 88–140.
Hsu, S. J. (2004). The effects of an environmental education program on responsible environmental behavior and associated environmental literacy variables in Taiwanese college students. The Journal of Environmental Education, 35(2), 37–48.
Huang, H. P., & Yore, L. D. (2005). A comparative study of Canadian and Taiwanese grade 5 children’s environmental behaviors, attitudes, concerns, emotional dispositions, and knowledge. International Journal of Science and Mathematics Education, 1(4), 419–448.
Khishfe, R. (2012). Nature of science and decision-making. International Journal of Science Education, 34(1), 67–100.
Khishfe, R., & Abd-El-Khalick, F. (2002). Influence of explicit and reflective versus implicit inquiry-oriented instruction on sixth graders’ views of nature of science. Journal of Research in Science Teaching: The Official Journal of the National Association for Research in Science Teaching, 39(7), 551–578.
King, P. M., & Kitchener, K. S. (2004). Reflective judgment: Theory and research on the development of epistemic assumptions through adulthood. Educational Psychologist, 39(1), 5–18.
Klöckner, C. A. (2013). A comprehensive model of the psychology of environmental behaviour—A meta-analysis. Global Environmental Change, 23(5), 1028–1038.
Knussen, C., Yule, F., MacKenzie, J., & Wells, M. (2004). An analysis of intentions to recycle household waste: The roles of past behaviour, perceived habit, and perceived lack of facilities. Journal of Environmental Psychology, 24(2), 237–246.
Kollmuss, A., & Agyeman, J. (2002). Mind the gap: Why do people act environmentally and what are the barriers to pro-environmental behavior? Environmental Education Research, 8(3), 239–260.
Kolstø, S. D. (2001). Scientific literacy for citizenship: Tools for dealing with the science dimension of controversial socioscientific issues. Science Education, 85(3), 291–310.
Kortland, K. (1996). An STS case study about students’ decision making on the waste issue. Science Education, 80(6), 673–689.
Larson, L. R., Stedman, R. C., Cooper, C. B., & Decker, D. J. (2015). Understanding the multi-dimensional structure of pro-environmental behavior. Journal of Environmental Psychology, 43, 112–124.
Liang, J. C., Lee, M. H., & Tsai, C. C. (2010). The relations between scientific epistemological beliefs and approaches to learning science among science-major undergraduates in Taiwan. Asia-Pacific Education Researcher, 19(1), 43-59.
Lee, M.-H., Chai, C. S., & Hong, H.-Y. (2019). STEM education in asia pacific: Challenges and development. The Asian-Pacific Education Researcher, 28, 1-4.
Li, P. J., Hong, H. Y., Chai, C. S., Tsai, C. C., & Lin, P. Y. (2020). Fostering students’ scientific inquiry through computer-supported collaborative knowledge building. Research in Science Education, 50, 2035–2053.
Liem, G. A. D., & Bernardo, A. B. (2010). Epistemological beliefs and theory of planned behavior: Examining beliefs about knowledge and knowing as distal predictors of Indonesian tertiary students’ intention to study. The Asia-Pacific Education Researcher, 19(1), 127–142.
Lin, T.-J., Deng, F., Chai, C. S., & Tsai, C.-C. (2013). High school students’ scientific epistemological beliefs, motivation in learning science, and their relationships: A comparative study within the Chinese culture. International Journal of Educational Development, 33(1), 37–47.
Lin, T. J., Lin, T. C., Potvin, P., & Tsai, C. C. (2019). Research trends in science education from 2013 to 2017: A systematic content analysis of publications in selected journals. International Journal of Science Education, 41(3), 367–387.
Li, T.-L., & Lee, M.-H. (2016). Exploring the relationships between Taiwanese high school students’ scientific epistemic views and decision-making style under the context of environmental education. Paper presented at the International Conference of The East-Asian Association for Science Education (EASE 2016), Tokyo.
Littledyke, M. (2004). Primary children’s views on science and environmental issues: Examples of environmental cognitive and moral development. Environmental Education Research, 10(2), 217–235.
Liu, S. Y., Lin, C. S., & Tsai, C. C. (2011). College students’ scientific epistemological views and thinking patterns in socioscientific decision making. Science Education, 95(3), 497–517. https://doi.org/10.1002/sce.20422.
Miafodzyeva, S., & Brandt, N. (2013). Recycling behaviour among householders: Synthesizing determinants via a meta-analysis. Waste and Biomass Valorization, 4(2), 221–235.
National Environmental Education and Training Foundation (NEETF). (2005). Environmental literacy in America: What ten years of NEETF/roper research studies say about environmental literacy in the US. Washington, DC: Author. Retrieved from http://www.neefusa.org/resources/publications.htm.
North American Association of Environmental Education. (2004). Excellence in environmental education: Guidelines for learning. Washington, DC: Author.
Park, J., & Ha, S. (2014). Understanding consumer recycling behavior: Combining the theory of planned behavior and the norm activation model. Family and Consumer Sciences Research Journal, 42(3), 278e291.
Passafaro, P., & Livi, S. (2017). Comparing determinants of perceived and actual recycling skills: The role of motivational, behavioral and dispositional factors. Journal of Environmental Education, 48(5), 347–356.
Perry, W. G. (1970). Forms of intellectual and ethical development in the college years: A scheme. New York, NY: Holt, Rinehart and Winston.
Rhodes, R. E., Beauchamp, M. R., Conner, M., de Bruijn, G. J., Kaushal, N., & Latimer-Cheung, A. (2015). Prediction of depot-based specialty recycling behavior using an extended theory of planned behavior. Environment and Behavior, 47(9), 1001–1023.
Robelia, B., & Murphy, T. (2012). What do people know about key environmental issues? A review of environmental knowledge surveys. Environmental Education Research, 18(3), 299–321.
Sadler, T. D. (2004). Informal reasoning regarding socioscientific issues: A critical review of research. Journal of Research in Science Teaching: The Official Journal of the National Association for Research in Science Teaching, 41(5), 513–536.
Sadler, T. D., & Zeidler, D. L. (2005). Patterns of informal reasoning in the context of socioscientific decision making. Journal of Research in Science Teaching: The Official Journal of the National Association for Research in Science Teaching, 42(1), 112–138.
Schommer-Aikins, M., & Hutter, R. (2002). Epistemological beliefs and thinking about everyday controversial issues. The Journal of Psychology, 136(1), 5–20.
Scott, S. G., & Bruce, R. A. (1995). Decision-making style: The development and assessment of a new measure. Educational and Psychological Measurement, 55(5), 818–831.
Shen, K. M., Li, T. L., & Lee, M. H. (2018). Learning biology as ‘Increase ones’ knowledge and understanding’: studying Taiwanese high school students’ learning strategies in relation to their epistemic views and conceptions of learning in biology. International Journal of Science Education, 40(17), 2137-2157.
Smith, E. R., & DeCoster, J. (2000). Dual-process models in social and cognitive psychology: Conceptual integration and links to underlying memory systems. Personality and Social Psychology Review, 4(2), 108–131.
Syu, Y.-L., & Lee, M.-H. (2016). Exploring undergraduates’ conceptions of environmental education in Taiwan: A phenomenographic analysis. Paper presented at the International Conference of the East-Asian Association for Science Education (EASE 2016), Tokyo.
Taylor, S., & Todd, P. (1995). An integrated model of waste management behavior: A test of household recycling and composting intentions. Environment and Behavior, 27(5), 603–630.
Tonglet, M., Phillips, P. S., & Read, A. D. (2004). Using the theory of planned behaviour to investigate the determinants of recycling behaviour: A case study from Brixworth, UK. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 41(3), 191–214.
Tsai, C. C. (1998). Science learning and constructivism. Curriculum and Teaching, 13(1), 31–52.
Tsai, C. C., & Liu, S. Y. (2005). Developing a multi-dimensional instrument for assessing students’ epistemological views toward science. International Journal of Science Education, 27(13), 1621–1638.
Tsai, W. T. (2012). An investigation of Taiwan’s education regulations and policies for pursuing environmental sustainability. International Journal of Educational Development, 32(2), 359–365.
Tweed, R., & Lehman, D. R. (2002). Learning considered within a cultural context: Confucian and Socratic approaches. American Psychologist, 57, 89–99.
UNESCO. (1978). The Tbilisi Declaration. Connect, III(1), 3. [Online]. Available from: http://unesdoc.unesco.org/images/0015/001563/156393eb.pdf. Assessed September 11, 2018.
Walsh, G., Mitchell, V. W., & Hennig-Thurau, T. (2001). German consumer decision-making styles. The Journal of Consumer Affairs, 35(1), 73–95.
Webb, T. L., & Sheeran, P. (2006). Does changing behavioral intentions engender behavior change? A meta-analysis of the experimental evidence. Psychological Bulletin, 132(2), 249–268.
Whitmarsh, L., & O'Neill, S. (2010). Green identity, green living? The role of pro-environmental self-identity in determining consistency across diverse pro-environmental behaviours. Journal of Environmental Psychology, 30(3), 305–314.
Wu, P. H., & Wu, H.-K. (2020). Constructing a model of engagement in scientific inquiry: Investigating relationships between inquiry-related curiosity, dimensions of engagement, and inquiry abilities. Instructional Science, 48, 79–113. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11251-020-09503-8.
Wu, Y. T., & Tsai, C. C. (2011). High school students’ informal reasoning regarding a socio-scientific issue, with relation to scientific epistemological beliefs and cognitive structures. International Journal of Science Education, 33(3), 371–400.
Yang, F. Y., Bhagat, K. K., & Cheng, C. H. (2019). Associations of epistemic beliefs in science and scientific reasoning in university students from Taiwan and India. International Journal of Science Education, 41(10), 1347–1365.
Yang, F.-Y., Liu, S.-Y., Hsu, C.-Y., Chiou, G.-L., Wu, H.-K., Wu, Y.-T., . . . Tsai, C.-C. (2018). High-school students' epistemic knowledge of science and its relation to learner factors in science learning. Research in Science Education, 48, 325-344.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the “Institute for Research Excellence in Learning Sciences” of the National Taiwan Normal University (NTNU) from the Featured Areas Research Center Program within the framework of the Higher Education Sprout Project by the Ministry of Education (MOE) in Taiwan and by the Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan, under the following grant numbers: 106-2628-S-003-002-MY3 and 109-2628-H-003-001-MY3.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luan, H., Li, TL. & Lee, MH. High School Students’ Environmental Education in Taiwan: Scientific Epistemic Views, Decision-Making Style, and Recycling Intention. Int J of Sci and Math Educ 20, 25–44 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10763-020-10136-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10763-020-10136-z