Abstract
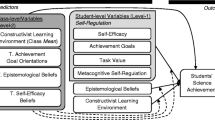
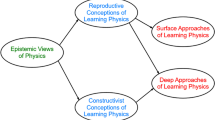
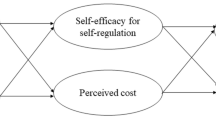
This article reports on an empirical exploration of the relations and strengths among Turkish grades 9–11 students’ (n = 209) personal epistemologies (justification of knowledge, certainty of knowledge, source of knowledge, development of knowledge), self-regulated learning (extrinsic motivation, intrinsic motivation, rehearsal, elaboration, organization, critical thinking, metacognitive self-regulation), and achievement in physics (course grades). Established instruments were used to collect data on these students’ beliefs about knowledge and components of self-regulated learning (SRL) such as goal orientations (extrinsic and intrinsic motivation) and learning strategies, critical thinking, and metacognitive regulation. Results from structural equation modeling revealed that students’ personal epistemologies directly influenced their motivation (extrinsic and intrinsic goal orientations), rehearsal and organization strategies, and metacognitive self-regulation to learn physics. Furthermore, students’ personal epistemologies indirectly (mediated through motivation beliefs) influenced rehearsal, elaboration and organization strategies, critical thinking, and metacognitive self-regulation to learn physics. Students’ ideas about knowledge and knowing about the source and development of knowledge significantly contributed to students’ self-regulatory skills and physics course grade. Implications and future directions are discussed.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bromme, R., Pieschl, S. & Stahl, E. (2010). Epistemological beliefs are standards for adaptive learning: A functional theory about epistemological beliefs and metacognition. Metacognition and Learning, 5(1), 7–26.
Cabrera-Nguyen, P. (2010). Author guidelines for reporting scale development and validation results in the Journal of Society for Social Work and Research. Journal of Society for Social Work and Research, 1, 99–103.
Chinn, C. A. & Malhotra, B. A. (2002). Epistemologically authentic inquiry in schools: A theoretical framework for evaluating inquiry tasks. Science Education, 86(2), 175–218.
Conley, A. M., Pintrich, P. R., Wekiri, I. & Harrison, D. (2004). Changes in epistemological beliefs in elementary science students. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 29, 186–204.
Cramer, D. (1998). Fundamental statistics for social research. London, England: Routledge.
Credé, M. & Phillips, L. A. (2011). A meta-analytic review of the motivated strategies for learning questionnaire. Learning and Individual Differences, 21(4), 337–346.
Creswell, J. W. (2007). Qualitative inquiry and research design: Choosing among five approaches. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Dole, J. A. & Sinatra, G. M. (1998). Reconceptualizing change in the cognitive construction of knowledge. Journal of Educational Psychology, 33, 109–128.
Duit, R., Neidderer, H. & Schecker, H. (2007). Teaching physics. In S. K. Abell & N. G. Lederman (Eds.), Handbook of research on science education (pp. 599–629). Hillsdale, MI: Erlbaum.
Ehrlich, R. (2002). How do we know if we are doing a good job in physics teaching? American Journal of Physics, 70, 24–29.
Eilam, B., Zeidner, M. & Aharon, I. (2009). Student conscientiousness, self-regulated learning, and science achievement: An explorative field study. Psychology in the Schools, 46(5), 420–433.
Elby, A. (1999). Another reason that physics students learn by rote. American Journal of Physics, 67(7), 52–57.
Elliot, A. & McGregor, H. A. (2001). A 2×2 achievement goal framework. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 80, 501–519.
Gungor, A. A., Eryilmaz, A. & Fakioglu, T. (2007). The relationship of freshmen’s physics achievement and their related affective characteristics. Journal of Research in Science Teaching, 44(8), 1036–1056.
Gürçay, D., & Balta, E. (2013). The effect of Turkish students’ motivational beliefs on their metacognition self-regulation in physics. Asia-Pacific Forum on Science Learning and Teaching, 14(2), Article 13. Retrieved from http://www.ied.edu.hk/apfslt/.
Hofer, B. K. (2000). Dimensionality and disciplinary differences in personal epistemology. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 25, 378–405.
Hofer, B. K. (2001). Personal epistemology research: Implications for learning and teaching. Educational Psychology Review, 13(4), 353–383.
Hofer, B. K. (2004). Epistemological understanding as a metacognitive process: Thinking aloud during online searching. Educational Psychologist, 39(1), 43–55.
Hofer, B. K. & Pintrich, P. R. (Eds.). (2002). Personal epistemology: The psychology of beliefs about knowledge and knowing. Mahwah, NJ: Erlbaum.
Hofer, B. K. & Sinatra, G. M. (2010). Epistemology, metacognition, and self-regulation: Musings on an emerging field. Metacognition and Learning, 5, 113–120.
Hsu, Y.-S., Yen, M.-H., Chang, W.-H., Wang, C.-Y. & Chen, S. (2014). Content analysis of 1998–2012 empirical studies in science reading using a self-regulated learning lens. International Journal of Science and Mathematics Education. Advance online publication. doi:10.1007/s10763-014-9574-5
Hu, L. & Bentler, P. M. (1999). Cutoff criteria for fit indexes in covariance structure analysis: Conventional criteria versus new alternatives. Structural Equation Modeling, 6(1), 1–55.
Ibrahim, B., Buffler, A. & Lubben, F. (2009). Profiles of freshman physics students’ views on the nature of science. Journal of Research in Science Teaching, 46, 248–264.
Kardash, C. & Scholes, R. J. (1996). Effects of pre-existing beliefs, epistemological beliefs, and need for cognition on interpretation of controversial issues. Journal of Educational Psychology, 88, 260–271.
Kenny, D. A. (2014). Measuring model fit. Retrieved from http://davidakenny.net/cm/fit.htm.
Kline, R. B. (2011). Principles and practice of structural equation modeling. New York, NY: Guilford.
Koksal, M. S. (2011). Epistemological predictors of self-efficacy on learning biology and test anxiety related to evaluation of learning on biology for pre-service elementary teachers. Journal of Science Teacher Education, 22(7), 661–677.
Koponen, I. & Mantyla, T. (2006). Generative role of experiments in physics and in teaching physics: A suggestion for epistemological reconstruction. Science & Education, 15(1), 31–54.
Kuhn, D. (2000). Metacognition development. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 9, 178–181.
Kurt, F. (2009). Investigating students’ epistemological beliefs through gender, grade level, and fields of the study (Unpublished master’s thesis), Middle East Technical University, Ankara, Turkey.
Lin, T.-C., Hsu, Y.-S., Lin, S.-S., Changlai, M.-L., Yang, K.-Y. & Lai, T.-L. (2012). A review of empirical evidence on scaffolding for science education. International Journal of Science and Mathematics Education, 10, 437–455.
Lin, Y.-C., Liang, J.-C. & Tsai, C.-C. (2012). The relationships between epistemic beliefs in biology and approaches to learning biology among biology-major university students in Taiwan. Journal of Science Education and Technology, 21, 796–807.
Meltzer, D. E. (2002). The relationship between mathematics preparation and conceptual learning gains in physics: A possible “hidden variable” in diagnostic pretest scores. American Journal of Physics, 70, 1259–1268.
Ministry of National Education (2011). Ortaogretim Fizik Dersi Ogretim Programi [Secondary school physics education program]. Ankara, Turkey: Milli Egitim Bakanligi.
Muis, K. R. (2007). The role of epistemic beliefs in self-regulated learning. Educational Psychologist, 42, 173–190.
Muis, K. R., Bendixen, L. D. & Haerle, F. (2006). Domain-generality and domain-specificity in personal epistemology research: Philosophical and empirical reflections in the development of a theoretical framework. Educational Psychology Review, 18, 3–54.
Muis, K. R. & Franco, G. M. (2009). Epistemic beliefs: Setting the standards for self-regulated learning. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 34(4), 306–318.
National Research Council (2007). Taking science to school: Learning and teaching science in grades K–8. In R. A. Duschl, H. A. Schweingruber, & A. W. Shouse (Eds.). Washington, DC: National Academies Press.
Ozkan, S. (2008). Modeling elementary students’ science achievement: The interrelationships among epistemological beliefs, learning approaches, and self-regulated learning strategies. Unpublished doctoral dissertation, Middle East Technical University, Ankara, Turkey.
Paulsen, M. B. & Feldman, K. A. (2007). The conditional and interaction effects of epistemological beliefs on the self-regulated learning of college students: Cognitive and behavioral strategies. Research in Higher Education, 48(3), 353–401.
Pintrich, P. R. (2000). The role of goal orientation in self-regulated learning. In M. Boekaerts, P. R. Pintrich & M. Zeidner (Eds.), Handbook of self-regulation (pp. 451–502). San Diego, CA: Academic.
Pintrich, P. R., Smith, D. A. F., Garcia, T. & McKeachie, W. J. (1991). A manual for the use of the Motivated Strategies for Learning Questionnaire (MSLQ). Ann Arbor, MI: National Center for Research to Improve Postsecondary Teaching and Learning.
Popham, J. W. (2012). Assessment bias: How to banish it? (2nd ed.). Boston, MA: Pearson Education.
Redish, E. F. & Steinberg, R. N. (1999). Teaching physics: Figuring out what works. Physics Today, 52(1), 24–30.
Ryu, S. & Sandoval, W. A. (2012). Improvements to elementary children’s epistemic understanding from sustained argumentation. Science Education, 96(3), 488–526.
Samarapungavan, A., Westby, E. L. & Bodner, G. M. (2006). Contextual epistemic development in science: A comparison of chemistry students and research chemists. Science Education, 90, 468–495.
Schommer-Aikins, M., Duell, O. K. & Hutter, R. (2005). Epistemological beliefs, mathematical problem-solving beliefs, and academic performance of middle school students. The Elementary School Journal, 105(3), 289–304.
Sin, C. (2014). Epistemology, sociology, and learning and teaching in physics. Science Education, 98, 342–365.
Sinatra, G. M. (2005). The warming trend in conceptual change research: The legacy of Paul R. Pintrich. Educational Psychologist, 40, 107–115.
Stathopoulou, C. & Vosniadou, S. (2007). Exploring the relationship between physics-related epistemological beliefs and physics understanding. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 32, 255–281.
Sungur, S. (2004). The implementation of problem-based learning in high school biology courses (Unpublished doctoral dissertation). Middle East Technical University, Ankara, Turkey.
Taasoobshirazi, G. & Sinatra, G. M. (2011). A structural equation model of conceptual change in physics. Journal of Research in Science Teaching, 48, 901–918.
Thomas, G. P. (2013). Changing the metacognitive orientation of a classroom environment to stimulate metacognitive reflection regarding the nature of physics learning. International Journal of Science Education, 35(7), 1183–1207.
Topçu, M. S. (2013). Preservice teachers’ epistemological beliefs in physics, chemistry, and biology: A mixed study. International Journal of Science and Mathematics Education, 11, 433–458.
Winne, P. H. & Hadwin, A. F. (1998). Studying as self-regulated learning. In D. J. Hacker, J. Dunlosky & A. C. Graesser (Eds.), Metacognition in educational theory and practice (pp. 277–304). Mahwah, NJ: Erlbaum.
Yang, F.-Y. & Tsai, C.-C. (2012). Personal epistemology and science learning: A review on empirical studies. In B. J. Fraser, K. Tobin & C. J. McRobbie (Eds.), Second international handbook of science education (pp. 259–280). New York, NY: Springer. doi:10.1007/978-1-4020-9041-7_19.
Yore, L. D. & Treagust, D. F. (2006). Current realities and future possibilities: Language and science literacy—empowering research and informing instruction. International Journal of Science Education, 28(2–3), 291–314.
Yumusak, N., Sungur, S. & Cakiroglu, J. (2007). Turkish high school students’ biology achievement in relation to academic self-regulation. Educational Research and Evaluation, 13(1), 53–69.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alpaslan, M.M., Yalvac, B., Loving, C.C. et al. Exploring the Relationship Between High School Students’ Physics-Related Personal Epistemologies and Self-regulated Learning in Turkey. Int J of Sci and Math Educ 14, 297–317 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10763-015-9685-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10763-015-9685-7