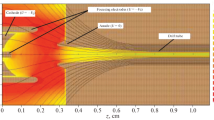
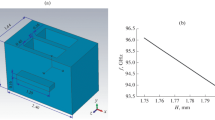
Abstract
To improve the output performance of G-band extended interaction klystron (EIK), several practicable methods have been discussed. Firstly, the synchronization characteristics of the electron beam with the operating mode are analyzed in order to obtain large output power for optimized period. The influence of input gap voltage on the beam-wave interaction is studied, and the well-matched condition is established by optimizing the structure of input cavity. The gap length of output cavity is optimized to improve the electric field distribution. By adopting the optimized gap length and non-uniform gap lengths, the output power significantly increases from 360 to 570 W and 660 W, respectively; the corresponding bandwidth reaches to 650 MHz and 470 MHz. Moreover, AJDISK calculation is adopted to compare the results with CST simulation, and the similar gains and tendencies validate the relative reliability of our designed beam-wave interaction circuit. Therefore, our proposed methods for improving the output performance of G-band EIK are feasible and utilizable.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. H. Siegel, IEEE Trans. Micro. Theory Tech. 3, 910 (2002).
J. H. Booske, Phys. Plasmas 15, 055502 (2008).
R. A. Lewis, J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 47, 374001 (2014).
B. Steer, A. Roitman, P. Horoyski, M. Hyttinen, R. Dobbs, and D. Berry, in Proceedings of the IEEE International Pulsed Power Conference, Albuquerque, USA, 17–22 June 2007, pp. 1049–1053.
J. H. Booske, R. J. Dobbs, C. D. Joye, C. L. Kory, G. R. Neil, G. Park, J. Park, and R. J. Temkin, IEEE Trans. Terahertz Sci. Technol. 1, 54 (2011).
M. Chodorow and T. Wessel-Berg, IRE Trans. Electron Devices 8, 44 (1961).
A. Roitman, D. Berry, and B. Steer, IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 52, 895(2005).
G. Liu, W. He, A. W. Cross, H. Yin, and D. Bowes, J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 46, 345102 (2013).
Y. Yin, W. He, L. Zhang, H. Yin, and A. W. Cross, Phys. Plasmas 22, 073102 (2015).
A. Srivastava, Eur. J. Adv. Eng. Technol. 2, 54 (2015).
K. T. Nguyen, J. Pasour, E. L. Wright, D. E. Pershing, and B, Levush, in Proceedings of the IEEE International Vacuum Electronics Conference, Rome, Italy, 28–30 April 2009, pp. 298–299.
D. Berry, H. Deng, R. Dobbs, P. Horoyski, M. Hyttinen, A. Kingsmill, R. MacHattie, A. Roitman, E. Sokol, and B. Steer, IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 61, 1830 (2014).
R. Li, C. Ruan, and H. Zhang, Phys. Plasmas 25, 033107 (2018).
S. Chen, C. Ruan, W. Yong, C. Zhang, D. Zhao, X. Yang, and S. Wang, IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 42, 91 (2014).
Y. Huang, M.S. thesis (University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu, China, 2014).
A. S. Gilmour, Klystrons, Traveling Wave Tubes, Magnetrons, Crossed-Field Amplifiers, and Gyrotrons (Artech HouseBooks, Norwood, US, 2011), Chap. 11.
C. B. Wilsen, J. W. Luginsland, Y. L. Yue, T. M. Antonsen, D. P. Chernin, P. M. Tchou, M. W. Keyser, R. M. Gilgenbach, and L. D. Ludeking, IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 30, 1160 (2002).
J. M. Vaughan, IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 11, 2510 (1985).
G. Caryotakis, Stanford Linear Accelerator Center, paper No. SLAC-PUB-10620, 2004.
Y. Ding, Design, Manufacture and Application of High Power Klystron (National Defense Industry Press, Beijing, 2010), p. 53.
Y. M. Shin, L. R. Barnett, and N. C. Luhmann, IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 56, 3196 (2009).
A. Baig, D. Gamzina, T. Kimura, J. Atkinson, C. Domier, B. Popovic, L. Himes, R. Barchfeld, M. Field, and N. C. Luhmann, IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 64, 2390 (2017).
CST Corp, “CST PS Tutorial,” Darmstadt, Germany, see http://www.cst-china.cn
“User Manual CST Particle Studio SUITE” (CST Corp., Darmstadt, Germany, 2012).
A. Jensen, M. Fazio, J. Neilson, and G. Scheitrum, IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 61, 1666 (2014).
Acknowledgments
The authors give thanks to Prof. Jinjun Feng in the Vacuum Electronics National Laboratory, Beijing Vacuum Electronics Research Institute, China, for his sincere supports for the CST software supporting and research works in the paper.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 61831001, the High-Level Talent Introduction Project of Beihang University (Grant No. 29816248), and the Youth-Top-Talent Support Project of Beihang University (Grant No. KG12000801).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, R., Ruan, C., Zhang, H. et al. Optimization and Improvement of Output Performance in G-Band Extended Interaction Klystron. J Infrared Milli Terahz Waves 40, 5–16 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10762-018-0546-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10762-018-0546-7