Abstract
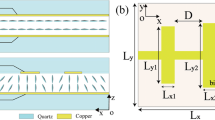
We present a reflective spatial phase shifter which operates at terahertz regime above 325 GHz. The controllable permittivity of the nematic liquid crystals was utilized to realize a tunable terahertz (THz) reflective phase shifter. The reflective characteristics of the terahertz electromagnetic waves and the liquid crystal parameters were calculated and analyzed. We provide the simulation results for the effect of the incident angle of the plane wave on the reflection. The experiment was carried out considering an array consisting of 30 × 30 patch elements, printed on a 20 × 20 mm quartz substrate with 1-mm thickness. The phase shifter provides a tunable phase range of 300° over the frequency range of 325 to 337.6 GHz. The maximum phase shift of 331° is achieved at 330 GHz. The proposed phase shifter is a potential candidate for THz applications, particularly for reconfigurable reflectarrays.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
N. Vieweg, M. K. Shakfa, B. Scherger, M. Mikulics, and M. Koch, "THz Properties of Nematic Liquid Crystals," Journal Of Infrared Millimeter And Terahertz Waves 31, 1312–1320 (2010).
N. Vieweg, M. A. Celik, S. Zakel, V. Gupta, G. Frenking, and M. Koch, "Terahertz Absorption of Nematic Liquid Crystals," Journal Of Infrared Millimeter And Terahertz Waves 35, 478–485 (2014).
X. F. Li, N. Tan, M. Pivnenko, J. Sibik, J. A. Zeitler, and D. P. Chu, "High-birefringence nematic liquid crystal for broadband THz applications," Liquid Crystals 43, 955–962 (2016).
M. Jost, A. Gaebler, C. Weickhmann, S. Strunck, W. Hu, O. H. Karabey, et al., "Evolution of Microwave Nematic Liquid Crystal Mixtures and Development of Continuously Tuneable Micro- and Millimetre Wave Components," Molecular Crystals And Liquid Crystals 610, 173–186 (2015).
X. W. Lin, J. B. Wu, W. Hu, Z. G. Zheng, Z. J. Wu, G. Zhu, et al., "Self-polarizing terahertz liquid crystal phase shifter," Aip Advances 1 (2011).
S. Bildik, S. Dieter, C. Fritzsch, W. Menzel, and R. Jakoby, "Reconfigurable Folded Reflectarray Antenna Based Upon Liquid Crystal Technology," Ieee Transactions on Antennas And Propagation 63, 122–132 (2015).
S. J. Ge, J. C. Liu, P. Chen, W. Hu, and Y. Q. Lu, "Tunable terahertz filter based on alternative liquid crystal layers and metallic slats," Chinese Optics Letters 13, (2015).
N. Vieweg, N. Born, I. Al-Naib, and M. Koch, "Electrically Tunable Terahertz Notch Filters," Journal Of Infrared Millimeter And Terahertz Waves 33, 327–332 (2012).
B. Vasic, D. C. Zografopoulos, G. Isic, R. Beccherelli, and R. Gajic, "Electrically tunable terahertz polarization converter based on overcoupled metal-isolator-metal metamaterials infiltrated with liquid crystals," Nanotechnology 28 (2017).
D. C. Zografopoulos and R. Beccherelli, "Tunable terahertz fishnet metamaterials based on thin nematic liquid crystal layers for fast switching," Scientific Reports 5 (2015).
L. Yang, F. Fan, M. Chen, X. Z. Zhang, and S. J. Chang, "Active terahertz metamaterials based on liquid-crystal induced transparency and absorption," Optics Communications 382, 42–48 (2017).
G. Perez-Palomino, J. A. Encinar, M. Barba, and E. Carrasco, "Design and evaluation of multi-resonant unit cells based on liquid crystals for reconfigurable reflectarrays," IEC Microwaves Antennas & Propagation, 6, 348–354 (2012).
R. Florencio, J. Encinar, R. R. Boix, and G. Perez-Palomino, "Dual-polarisation reflectarray made of cells with two orthogonal sets of parallel dipoles for bandwidth and cross-polarisation improvement," Microwaves, Antennas & Propagation, IET 8, 1389–1397 (2014).
S. Bildik, C. Fritzsch, A. Moessinger, and R. Jakoby, "Tunable liquid crystal reflectarray with rectangular elements," in Microwave Conference, 2010 German, 1–4 (2010).
R. Marin, A. Moessinger, F. Goelden, S. Mueller, and R. Jakoby, "77 GHz Reconfigurable Reflectarray with Nematic Liquid Crystal," in The Second European Conference on Antennas and Propagation, EuCAP 2007, 1–5(2007).
G. Perez-Palomino, M. Barba, J. A. Encinar, R. Cahill, R. Dickie, P. Baine, et al., "Design and Demonstration of an Electronically Scanned Reflectarray Antenna at 100GHz Using Multiresonant Cells Based on Liquid Crystals," IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation 63, 3722–3727 (2015).
G. Perez-Palomino, J. A. Encinar, R. Dickie, and R. Cahill, "Preliminary design of a liquid crystal-based reflectarray antenna for beam-scanning in THz," in Antennas and Propagation Society International Symposium (APSURSI), 2013 IEEE, 2277–2278 (2013).
C. A. Balanis, ‘Antenna theory’, Wiley, 2005, 3rd edn, pp. 816–820.
H. B. Lu, S. C. Jing, T. Y. Xia, J. Yang, Z. P. Yin, and G. S. Deng, "Measurement of LC dielectric constant at lower terahertz region based on metamaterial absorber," IEICE Electronics Express, 14, 20170469 (2017).
G. Perez-Palomino, R. Florencio, J. A. Encinar, M. Barba, R. Dickie, R. Cahill, et al., "Accurate and Efficient Modeling to Calculate the Voltage Dependence of Liquid Crystal-Based Reflectarray Cells," IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 62, 2659–2668, (2014).
Funding
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51607050), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant No. JD2017JGPY0006), and the Sichuan Science and Technology Support Project (No. 2016GZ0250).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, J., Xia, T., Jing, S. et al. Electrically Tunable Reflective Terahertz Phase Shifter Based on Liquid Crystal. J Infrared Milli Terahz Waves 39, 439–446 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10762-018-0469-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10762-018-0469-3