Abstract
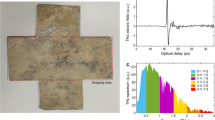
Nondestructive analysis of historical objects is of significance for cultural heritage conservation. In this paper, terahertz time-domain spectroscopy (THz-TDS) was used to distinguish seven red mineral pigments used in ancient Chinese artworks. Two absorption features of natural minerals HgS and four highly resolved spectral features of mineral pigment Pb3O4 were observed and identified as their fingerprints in the range 0.2 to 3.0 THz, based on which the spatial distribution of individual chemical substances including cinnabar, vermilion, and red lead were clearly revealed at various frequencies using terahertz spectroscopy imaging. Moreover, a noncontact evaluation of thickness changing and dehydration of a wet painting was monitored by inferring time delay as well as signal amplitude of THz pulses transmitted through the painting. In order to demonstrate the feasibility of THz-TDS and THz imaging for authentic artworks detection, a complete set of THz analysis of two nineteenth century wall paintings discovered in the Fuchen Temple of the Forbidden City, Beijing, was performed and the results indicate that THz measurement techniques provide a noninvasive and nondestructive solution for the care, preservation, and restoration of cultural relics.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. Burgio, R. J. H. Clark, “Library of FT-Raman spectra of pigments, minerals, pigment media and varnishes, and supplement to existing library of Raman spectra of pigments with visible excitation”, Spectrochim. Acta. A., 57, 1491–1521(2001).
K. Castro, S. Pessanha, N. Proietti, and E. Princi, “Noninvasive and nondestructive NMR, Raman and XRF analysis of a Blaeu coloured map from the seventeenth century”, Anal. Bioanal. Chem., 391, 433–441 (2008).
K. Castro, M. Pérez-Alonso, M. D. Rodríguez-Laso, N. Etxebarria, J. M. Madariaga, “Non-invasive and non-destructive micro-XRF and micro-Raman analysis of a decorative wallpaper from the beginning of the 19th century”, Anal. Bioanal. Chem., 387,847–860 (2007)
J. B. Jackson, J. Bowen, G. Walker, L Labaune, G. Mourou, M. Menu, K. Fukunaga, “A Survey of Terahertz Applications in Cultural Heritage Conservation Science”, IEEE Trans. Terahertz Sci. Technol., 1(1), 220–231 (2011).
T. Hong, K. Choi, T. Ha, B. C. Park, K. I. Sim, J. H. Kim, J. E. Know, S. Lee, D. I. Kang, H. H. Lee, “Terahertz time-domain and Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy of Traditional Korean pigments”, J. Korean Phys. Soc., 64(5), 727–732 (2014).
K. Fukunaga, M. Picollo, “Terahertz spectroscopy applied to the analysis of artists’ materials”,Appl. Phys. A., 100, 591–597(2010).
K. Fukunaga, I. Hosako, “Innovative non-invasive analysis techniques for cultural heritage using terahertz technology”, C. R. Physique, 1, 519–526(2010)
S. Zhang, G. Zhao, and X. Zhao, “Terahertz spectra of edible pigments”, Chin. Opt. Lett., 9(suppl), S10502 (2011).
G. Filippidis, M. Massaouti, A. Selimis, E. J. Gualda, J. M. Manceau, S. Tzortzakis, “Nonlinear imaging and diagnostic tools in the service of cultural heritage”, Appl. Phys. A., 106, 257–263(2012).
K. Fukunaga, “Terahertz analysis of an East Asian historical mural painting”, J. Eur. Opt. Soc-Rapid., 5, 100024 (2010).
J. B. Jackson, M. Mourou, J. F. Whitaker, I.N. Duling III, S. L. Williamson, M. Menu, G. A. Mourou, “Terahertz imaging for non-destructive evaluation of mural paintings”, Opt. Commun., 281, 527–532(2008).
A. J. L Adam, P. C. M. Planken, S. Meloni, J. Dik, “Terahertz imaging of hidden paint layers on canvas”, Opt. Express, 17(5), 3407–3416 (2009).
T. Yasuda, T. Iwata, T. Araki, and T. Yasui, “Improvement of minimum paint film thickness for THz paint meter by multiple-regression analysis”, Appl. Opt., 46(30),7518–7526 (2007).
Y. Yang, X. Lei, A. Yue, Z. Zhang, “Temperature-dependent THz vibrational spectra of clenbuterol hydrochloride”, Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron., 56(4), 713–717 (2013)
N. Qi, Z. Zhang, Y. Xiang, Y. Yang, X. Liang, P. B. Harrington, “Terahertz time-domain spectroscopy combined with support vector machines and partial least squares-discriminant analysis applied for the diagnosis of cervical carcinoma”, Anal. Methods, 7, 2333–2338 (2015).
S. V Gotoshia and L. V Gotoshia, “Laser Raman and resonance Raman spectroscopies of natural semiconductor mineral cinnabar, α-HgS, from various mines”, J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys., 41, 115406 (2008)
Y. P. Yang, S. Sree Harsha, Alisha J. Shutler, D. Grischkowsky, “Identification of Genistein and Biochanin A by THz (far-infrared) vibrational spectra”, J. Pharmaceut. Biomed., 6, 2177–181 (2012).
B. B Hu, and M. C. Nuss, “Imaging with terahertz waves”, Opt. Lett., 20(16), 1995–1997 (1995).
Z. Zhang, Y. Zhang, G. Zhao, C. Zhang, “Terahertz time-domain spectroscopy for explosives imaging”, Optik, 118, 325–329 (2007).
Z. Zhang, W. Cui, G. Zhao, Y. Zhang and C. Zhang, “Data processing methods for terahertz transmitted spectral imaging”, Proc. SPIE, 6027, 60270K (2006)
M. Herrmann, M. Tani, K. Sakai, “Display modes in time-resolved terahertz imaging,” Jpn. J. Appl. Phys., 39, 6254–6258 (2000)
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge Dr. XXX Sedao of the University of Lyon, France, for his fruitful discussions. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 11574408, 11374378, 61627814 and 61675238), the National Instrumentation Program (Grant No. 2012YQ14000508), The National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant No. 2017YFB0405402), Technology Foundation for Selected Overseas Chinese Scholar, Beijing Science and Technology Project (Grant No. D151100006015002), and the Young-talent Plan of State Affairs Commission (Grant No. 2016-3-02).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Y., Zhai, D., Zhang, Z. et al. THz Spectroscopic Identification of Red Mineral Pigments in Ancient Chinese Artworks. J Infrared Milli Terahz Waves 38, 1232–1240 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10762-017-0408-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10762-017-0408-8