Abstract
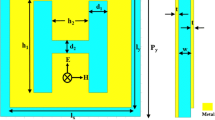
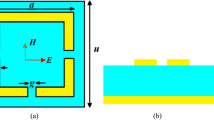
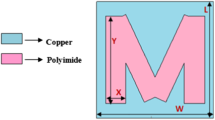
Multi-band terahertz filters with independence to polarization and insensitivity to incidence angles are designed, fabricated, and measured, respectively. The promoted multi-band terahertz filters consist of two and three concentric ring complementary structure. Compared with the dual-ring structure, the triple-ring structure not only increases numbers of the pass bands but also heightens the out-of-band rejection of the middle band. The physical mechanisms of the multi-band resonant responses are clarified using three different configurations and distribution of magnetic fields and current surfaces. At normal incidence, the triple-ring structure is independent to polarization due to the symmetry. At oblique incidences, transmission magnitudes as a function of the frequency are firstly demonstrated for the multi-band filter; it is found that this structure shows great insensitivity to incidence angles. The multi-band filter also has advantages in easy fabrication. The encouraging results afforded by the design of the filters could find applications in multi-band sensors, terahertz communication systems, and other emerging terahertz technologies.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
B. Ferguson and X.C. Zhang, Materials for terahertz science and technology. Nat. Mater. 1, 26 (2002).
G. P. Williams, Filling the THz gap-high power sources and applications. Reports on Progress in Physics 69, 301 (2006).
W. J. Padilla, M. T. Aronsson, C. Highstrete, M. Lee, A. J. Taylor, and R. D. Averitt, Electrically resonant terahertz metamaterials: Theoretical and experimental investigations. Phys. Rev. B 75, 041102 (R)(2007).
H. T. Chen, W. J. Padilla, J. M. O. Zide, A. C. Gossard, A. J. Taylor, and R. D. Averitt, Active metamaterial terahertz devices. Nature 444, 597 (2006).
V. Astley, K. S. Reichel, J. Jones), R. Mendis and D. M. Mittleman, Terahertz multichannel microfluidic sensor based on parallel-plate waveguide resonant cavities, Appl. Phys. Lett. 100, 231108 (2012).
L. Wang, Z. Geng, X. He, Y. Cao, Y. Yang, H. Chen, Realization of band-pass and low-pass filters on a single chip in terahertz regime, Optoelec. Lett. 11, 33 (2015)
X. Zhang, J. Gu, W. Cao, J. Han, A. Lakhtakia, and W. Zhang, Bilayer-fish-scale ultrabroad terahertz bandpass filter, Opt. Let. 37, 906 (2012).
R. Dickie, R. Cahill, V. F. Fusco, H. S. Gamble, and N. Mitchell, THz frequency selective surface filters for earth observation remote sensing instruments. IEEE Trans. Terahertz Sci. Technol. 2, 450 (2011).
A. K. Azad, Y. Zhao, W. Zhang, and M. He, Effect of dielectric properties of metals on terahertz transmission subwavelength hole arrays. Opt. Lett. 31, 2637 (2006).
X. Lu, J. Han, and W. Zhang, Resonant terahertz reflection of periodic arrays of subwavelength metallic rectangles. Appl. Phys. Lett. 92, 121103 (2008).
J. Li, Terahertz wave narrow bandpass filter based on photonic crystal, Optics Communications 283, 2647 (2010).
J. Han, J. Gu, X. Lu, M. He, Q. Xing, and W. Zhang, Broadband resonant terahertz transmission in a composite metal-dielectric structure. Opt. Express 17, 16527 (2009).
O. Paul, R. Beigang and M. Rahm, Highly selective terahertz bandpass filters based on trapped mode excitation. Opt. Express 17, 18590 (2009).
A. J. Beasley, R. Murowinski, and M. Tarenghi, The Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA). Proc. of SPIE 6267, 2 (2006).
M. Tarenghi, Astrophys. The Atacana large millimeter/submillimeter array: overview & status. Space Sci. 313, 1 (2008).
H. J. Song, and T. Nagatsuma, Present and future of terahertz communications, IEEE Trans. Terahertz Sci. Technol. 1, 256 (2011).
T. Kleine-Ostmann, and T. Nagatsuma, A Review on Terahertz Communications Research. J. Infrared Millim. Terahertz Waves 32, 143 (2011).
Q. Wen, H. Zhang, Y. Xie, Q. Yang, and Y. Liu, Dual band terahertz metamaterial absorber: Design, fabrication, and characterization. Appl. Phys. Lett. 95, 241111 (2009).
H. Tao C. Bingham, D. Pilon, K. Fan, A. Strikwerda, D. Shrekenhamer, W. Padilla, X. Zhang, and R. Averitt, A dual band terahertz metamaterial absorber. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 43, 225102 (2010).
Y. Ma, Q. Chen, J. Grant, S. Saha, A. Khalid, and R. Cumming, A terahertz polarization insensitive dual band metamaterial absorber, Opt. Let. 36, 945 (2011)
X. Shen, Y. Yang, Y. Zang, J. Gu, J. Han, W. Zhang, and T. Cui, Triple-band terahertz metamaterial absorber: Design, experiment, and physical interpretation. Appl. Phys. Lett. 101, 154102 (2012).
M. Lu, W. Li and E. R. Brown, Second-order bandpass THz filter achieved by multilayer complementary metamaterial structures. Opt. Let. 36, 1071 (2011).
F. Lan, Z. Yang, L. Qi, X. Gao and Z. Shi, Terahertz dual-resonance bandpass filter using bilayer reformative complementary metamaterial structures. Opt. Let. 39, 1709 (2014).
N. Papasimakis, Y. H. Fu, V. A. Fedotov, S. L. Prosvirnin, D. P. Tsai, and N. I. Zheludev, Metamaterial with polarization and direction insensitive resonant transmission response mimicking electromagnetically induced transparency. Appl. Phys. Lett. 94, 211902 (2009).
I. A. I. Al-Naib, C. Jansen, N. Born, and M. Koch, Polarization and angle independent terahertz metamaterials with high Q-factors, Appl. Phys. Lett. 98, 091107 (2011).
J. Shu, W. Gao, and Q. Xu, Fano resonance in concentric ring apertures. Opt. Express 21, 11101 (2013).
J. Shu, W. Gao, K. Reichel, D. Nickel, J. Dominguez, I. Brener, D. M. Mittleman, and Q. Xu, High-Q terahertz Fano resonance with extraordinary transmission in concentric ring apertures. Opt. Express 22, 3747 (2014).
B. A. Munk: Frequency Selective Surfaces: Theory and Design, 1st Edn., (John Wiley and Sons Inc., 2000) pp.5 and pp. 393
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (11174280 and 61107030), the Knowledge Innovation Program of Chinese Academy of Sciences (YYYJ-1123), and the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2012 M520377).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qi, L., Li, C. Multi-Band Terahertz Filter with Independence to Polarization and Insensitivity to Incidence Angles. J Infrared Milli Terahz Waves 36, 1137–1144 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10762-015-0202-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10762-015-0202-4