Abstract
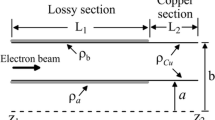
In this paper, the effect of distributed wall losses on the starting length and starting frequency of a TE21 mode gyro-BWO is investigated for different operating magnetic fields by using a linear theory. Numerical results show that, for the efficient suppression of a gyro-BWO in a distributed wall losses gyro-TWA consisting of a lossy section followed by a copper section, the wall losses applied in the lossy section should be able to provide a cold attenuation approximately equal to the linear growth rate of the gyro-BWO in the case of wall losses neglected and the copper section length should be shorter than the starting length of the corresponding gyro-BWO without wall losses loaded.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. R. Chu, “The electron cyclotron maser,” Reviews of Modern Physics 76 (2), 489–540 (2004).
K. R. Chu, “Overview of research on the gyrotron traveling-wave amplifier,” IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science 30 (3), 903–908 (2002).
W. C. Tsai, T. H. Chang, N. C. Chen, and K. R. Chu, “Absolute instabilities in a high-order-mode gyrotron traveling-wave amplifier,” Physical Review E 70 (5), 056402 (2004).
D. B. McDermott et al., “Design of a W-band TE01 mode gyrotron traveling wave amplifier with high power and broad-band capabilities,” IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science 30 (3), 894–900 (2002).
M. Garven, J. P. Calame, B. G. Danly et al., “A gyrotron-traveling-wave tube amplifier experiment with a ceramic loaded interaction region,” IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science 30 (3), 886–893 (2002).
K. R. Chu, H. Y. Chen, C. L. Hung et al., “Theory and experiment of ultrahigh gain gyrotron traveling-wave amplifier,” IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science 27 (2), 391–404 (1999).
C. Q. Jiao and J. R. Luo, “Preliminary design of a harmonic-doubling gyrotron traveling wave amplifier,” International Journal of Infrared and Millimeter Waves 28 (12), 1095–1101 (2007).
J. Rodgers, H. Guo, V. L. Granaatstein et al., “High efficiency, phase-locked operation of the harmonic-multiplying inverted gyrotwystron oscillator,” IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science 27 (2), 412–421 (1999).
V. L. Bratman, A. W. Cross, G. G. Denisov et al., “High-gain wide-band gyrotron traveling-wave amplifier with a helically corrugated waveguide,” Physical Review Letters 84 (12), 2746–2749 (2000).
Q. S. Wang, D. B. McDermott, and N. C. Luhmann Jr., “Operation of a stable 200 kW second-harmonic gyro-TWA amplifier,” IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science 24 (3), 700–706 (1996).
Q. S. Wang, C. S. Kou, D. B. McDermott et al., “High-power harmonic gyro-TWAT’s—part II: nonlinear theory and design,” IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science 20 (3), 163–169 (1992).
Y. S. Yeh et al., “W band second harmonic gyrotron traveling wave amplifier with distributed-loss and severed structures,” International Journal of Infrared and Millimeter Waves 25 (1), 29–42 (2004).
C. S. Kou, Q. S. Wang, D. B. McDermott et al., “High-power harmonic gyro-TWAT’s —part I: linear theory and oscillation study,” IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science 20 (3), 155–162 (1992).
C. Q. Jiao and J. R. Luo, “Linear and nonlinear analysis of a gyrotron traveling wave amplifier with misaligned electron beam,” Physics of Plasmas 13 (11), 113101 (2006).
J. R. Luo and C. Q. Jiao, “Effect of the lossy layer thickness of metal cylindrical waveguide wall on the propagation constant of electromagnetic modes,” Applied Physics Letters 88 (6), 061115 (2006).
C. Q. Jiao and J. R. Luo, “Linear theory of the electron cyclotron maser based on the TM circular waveguide mode,” Physics of Plasmas 13 (7), 073104 (2006).
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by the Funds for Doctor Degree Teacher of North China Electric Power University (Grant No. 200822008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiao, CQ., Luo, JR. Study on the Suppression of Gyro-BWO by Distributed Wall Losses. J Infrared Milli Terahz Waves 30, 924–930 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10762-009-9522-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10762-009-9522-6