Abstract
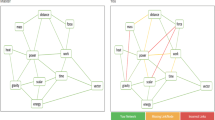
Since the initial recognition that human knowledge is structured in a relational manner, technologies have been developed for assessing and analyzing the structure of knowledge for a variety of purposes. A computer-based text analytic offline software system, ALA-Reader, that was developed to assess this knowledge structure (KS) reflected in a text has been modified and improved since its initial announcement (Clariana 2004) through a number of investigations in various kinds of learning environments across several languages. Based on the empirical evidence from the ALA-Reader, we have recently developed the online version of the ALA-Reader, called Graphical Interface of Knowledge Structure (GIKS), that can immediately convert students’ writings into visually represented KS network graphs to indicate specific areas of their knowledge strengths and weaknesses compared to the referent KS (e.g., a teacher), regardless of which language is used. This paper presents an overview of the ALA-Reader system and applications, as well as the implication of the GIKS system in online contexts.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Clariana, R. B. (2004). ALA-Reader (beta version). Retrieved from http://www.personal.psu.edu/rbc4.
Clariana, R. B. (2010). Multi-decision approaches for eliciting knowledge structure. In Computer-based diagnostics and systematic analysis of knowledge (pp. 41–59). Boston, MA: Springer US. doi:10.1007/978-1-4419-5662-0_4.
Clariana, R. B., Engelmann, T., & Yu, W. (2013). Using centrality of concept maps as a measure of problem space states in computer-supported collaborative problem solving. Educational Technology Research and Development, 61(3), 423–442. doi:10.1007/s11423-013-9293-6.
Clariana, R., & Wallace, P. (2007). A computer-based approach for deriving and measuring individual and team knowledge structure from essay questions. Journal of Educational Computing Research, 37(3), 211–227. doi:10.2190/EC.37.3.a.
Clariana, R. B., Wallace, P. E., & Godshalk, V. M. (2009). Deriving and measuring group knowledge structure from essays: The effects of anaphoric reference. Educational Technology Research and Development, 57(6), 725–737. doi:10.1007/s11423-009-9115-z.
Clariana, R. B., Wolfe, M. B., & Kim, K. (2014). The influence of narrative and expository lesson text structures on knowledge structures: Alternate measures of knowledge structure. Educational Technology Research and Development, 62(5), 601–616. doi:10.1007/s11423-014-9348-3.
Council, N. R. (2000). How people learn. Washington, DC: National Academies Press. doi:10.17226/9853.
Emig, J. (1977). Writing as a mode of learning. College Composition and Communication, 28(2), 122. doi:10.2307/356095.
Fesel, S. S., Segers, E., Clariana, R. B., & Verhoeven, L. (2015). Quality of children’s knowledge representations in digital text comprehension: Evidence from pathfinder networks. Computers in Human Behavior, 48, 135–146. doi:10.1016/j.chb.2015.01.014.
Herr, N. (2009). The sourcebook for teaching science, grades 6–12: Strategies, activities, and instructional resources. Education Review//Reseñas Educativas. Retrieved from http://edrev.asu.edu/index.php/ER/article/view/1111.
Ifenthaler, D. (2014). AKOVIA: Automated knowledge visualization and assessment. Technology, Knowledge and Learning, 19(1–2), 241–248.
Ifenthaler, D., & Pirnay-Dummer, P. (2014). Model-based tools for knowledge assessment. In J. M. Spector, M. D. Merrill, J. Elen, & M. J. Bishop (Eds.), Handbook of research on educational communications and technology (4th ed., pp. 289–301). New York: Springer.
Kim, M. K. (2012). Cross-validation study of methods and technologies to assess mental models in a complex problem solving situation. Computers in Human Behavior, 28(2), 703–717. doi:10.1016/j.chb.2011.11.018.
Kim, K., & Clariana, R. B. (2015). Knowledge structure measures of reader’s situation models across languages: Translation engenders richer structure. Technology, Knowledge and Learning, 20(2), 249–268.
Kim, K., & Clariana, R. B. (2016). Text signals influence second language expository text comprehension: Knowledge structure analysis. Educational Technology Research and Development, 1-22. doi:10.1007/s11423-016-9494-x.
Meyer, B. J. F., Ray, M. N., & Middlemiss, W. (2012). Children’s use of comparative text signals: The relationship between age and comprehension ability. Discours. doi:10.4000/discours.8637.
Mun, Y. (2015). The effect of sorting and writing tasks on knowledge structure measure in bilinguals’ reading comprehension. Retrieved from https://scholarsphere.psu.edu/files/x059c7329.
Sarwar, G. (2011). Structural assessment of knowledge for misconceptions: Effectiveness of structural feedback provided by pathfinder networks in the domain of physics. Kolln: LAP Lambert Academic Publishing.
Sarwar, G. S., & Trumpower, D. L. (2015). Effects of conceptual, procedural, and declarative reflection on students’ structural knowledge in physics. Educational Technology Research and Development, 63(2), 185–201.
Schlomske, N., & Pirnay-Dummer, P. (2009). Model based assessment of learning dependent change within a two semester class. Educational Technology Research and Development, 57(6), 753–765. doi:10.1007/s11423-009-9125-x.
Schvaneveldt, R. W. (2004). Finding meaning in psychology. In A. F. Healy (Ed.), Experimental cognitive psychology and its applications: Festschrift in honor of Lyle Bourne, Walter Kintsch, and Thomas Landauer. Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
Spector, J., & Koszalka, T. (2004). The DEEP methodology for assessing learning in complex domains. Final report to the National Science Foundation Evaluative Research and Evaluation. Syracuse, NY: Syracuse University.
Su, I-H., & Hung, Pi-H. (2010). Validity study on automatic scoring methods for the summarization of scientific articles. A paper presented at the 7th Conference of the International Test Commission 19–21 July, 2010, Hong Kong. https://bib.irb.hr/datoteka/575883.itc_programme_book_-final_2.pdf.
Tang, H., & Clariana, R. (2016). Leveraging a sorting task as a measure of knowledge structure in bilingual settings. Technology, Knowledge and Learning. doi:10.1007/s10758-016-9290-z.
Acknowledgements
This material is based upon work supported by the Penn State University's Center for Online Innovation in Learning (COIL). I would like to express my heartfelt appreciation to Dr. Roy B. Clariana for his guidance and encouragement throughout my academic study. I am fortunate to have you as my academic advisor.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, K. Graphical Interface of Knowledge Structure: A Web-Based Research Tool for Representing Knowledge Structure in Text. Tech Know Learn 24, 89–95 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10758-017-9321-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10758-017-9321-4