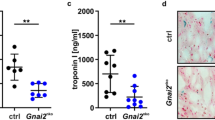
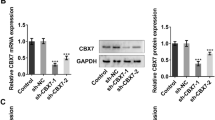
Abstract
Cardiac insufficiency is a common complication of sepsis with high mortality. Inflammatory programmed cell death (pyroptosis) executed by NLRP3/gasdermin D (GSDMD) is intrinsically correlated with septic myocardial injury. However, it remains unclear whether PIK3CG, a classical target of septic myocardial injury, can affect pyroptosis by regulating NLRP3/GSDMD signaling. In this study, a series of experimental methods were used to observe the effect of PIK3CG on NLRP3/GSDMD-mediated pyroptosis in Cecal ligation and puncture (CLP)-injured BALB/c mice and lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-injured HL-1 cardiomyocytes. Transcriptome analysis of CLP-injured myocardium revealed a regulatory relationship between PIK3CG and NLRP3/GSDMD signaling, which was further verified in clinical myocardium samples from GEO database. Both in vitro and in vivo experiments showed that the protein and mRNA levels of PIK3CG, GSDMD, NLRP3, IL-1β, Caspase-1, and IL-18 were significantly increased. Importantly, PIK3CG siRNA was found to improve these changes, while PIK3CG overexpression worsened them. Notably, pyroptosis induced by CLP in the myocardium was reversed by the PIK3CG inhibitor (AS-604850). In conclusion, PIK3CG activates NLRP3 inflammasomes, thus promoting pyroptosis in septic myocardial injury.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data generated and/or analyzed during the current study are included in this published article and its supplementary information files, or available from the corresponding authors on reasonable request..
Abbreviations
- GSDMD:
-
Gasdermin D
- CLP:
-
Cecal ligation and puncture
- LPS:
-
Lipopolysaccharide
- PI3Ks:
-
Phosphoinositide 3-kinases
- NLRP3:
-
NOD-like receptor family pyrin domain containing 3
- GSEA:
-
Gene set enrichment analysis
- DEGs:
-
Differentially expressed genes
- CCC:
-
Chronic Chagasic cardiomyopathy
- qRT-PCR:
-
Quantitative Real-Time PCR
- OE:
-
Overexpression
- SD:
-
Standard deviation
References
Larche, J., S. Lancel, S.M. Hassoun, R. Favory, B. Decoster, P. Marchetti, C. Chopin, and R. Neviere. 2006. Inhibition of mitochondrial permeability transition prevents sepsis-induced myocardial dysfunction and mortality. Journal of the American College of Cardiology 48 (2): 377–385.
Kakihana Y., T. Ito, M. Nakahara, K. Yamaguchi and T. Yasuda. 2016. Sepsis-induced myocardial dysfunction: pathophysiology and management. Journal Intensive Care 4(22).
Bi C. F., J. Liu and L. S. Yang. 2022. Research Progress on the Mechanism of Sepsis Induced Myocardial Injury. 15(4275–4290).
Venable, J.D., M.K. Ameriks, J.M. Blevitt, R.L. Thurmond, and W.P. Fung-Leung. 2010. Phosphoinositide 3-kinase gamma (PI3Kgamma) inhibitors for the treatment of inflammation and autoimmune disease. Recent Patents on Inflammation & Allergy Drug Discovery 4 (1): 1–15.
Fan T. T., X. Y. Feng, Y. Z. Yang, F. Gao and Q. Liu. 2017. Downregulation of PI3K-γ in a mouse model of sepsis-induced myocardial dysfunction. Cytokine 96(208–216).
Liu Q., Y. Dong, G. Escames, X. Wu, J. Ren, W. Yang, S. Zhang, Y. Zhu, Y. Tian, D. Castroviejo. 2022. Identification of PIK3CG as a hub in septic myocardial injury using network pharmacology and weighted gene co-expression network analysis. Bioengineering & Translational Medicine n/a (n/a): e10384.
Liu Y., X. Xu, W. Lei, Y. Hou, Y. Zhang, R. Tang, Z. Yang, Y. Tian, Y. Zhu, C. Wang. 2022. The NLRP3 inflammasome in fibrosis and aging: The known unknowns. Ageing Research Reviews 79 (101638).
Coll, R.C., K. Schroder, and P. Pelegrín. 2022. NLRP3 and pyroptosis blockers for treating inflammatory diseases. Trends in Pharmacological Sciences 43 (8): 653–668.
Jia Y., R. Cui, C. Wang, Y. Feng, Z. Li, Y. Tong, K. Qu, C. Liu and J. Zhang. 2020. Metformin protects against intestinal ischemia-reperfusion injury and cell pyroptosis via TXNIP-NLRP3-GSDMD pathway. Redox Biol 32(101534).
Lieberman, J., H. Wu, and Kagan Jc. 2019. Gasdermin D activity in inflammation and host defense. Science Immunology 4 (39): 1447.
Orning, P., and E. Lien. 2019. Gasdermins and their role in immunity and inflammation. 216 (11): 2453–2465.
Xu S., J. Wang, J. Zhong, M. Shao, J. Jiang, J. Song, W. Zhu, F. Zhang, H. Xu, G. Xu. 2021. CD73 alleviates GSDMD-mediated microglia pyroptosis in spinal cord injury through PI3K/AKT/Foxo1 signaling. 11(1):e269.
He, W.T., H. Wan, L. Hu, P. Chen, X. Wang, Z. Huang, Z.H. Yang, C.Q. Zhong, and J. Han. 2015. Gasdermin D is an executor of pyroptosis and required for interleukin-1β secretion. Cell Research 25 (12): 1285–1298.
Zhao Y. Y., D. M. Wu, M. He, F. Zhang, T. Zhang, T. Liu, J. Li, L. Li and Y. Xu. 2021. Samotolisib Attenuates Acute Liver Injury Through Inhibiting Caspase-11-Mediated Pyroptosis Via Regulating E3 Ubiquitin Ligase Nedd4. Front Pharmacol 12(726198).
Sun M., H. Zhao, Z. Jin, W. Lei, C. Deng, W. Yang, C. Lu, Y. Hou, Y. Zhang, R. Tang. 2022. Silibinin protects against sepsis and septic myocardial injury in an NR1H3-dependent pathway. Free Radical Biology Medicine 187(141–157).
Di, W., Z. Jin, W. Lei, Q. Liu, W. Yang, S. Zhang, C. Lu, X. Xu, and Y. Yang. 2023. Protection of melatonin treatment and combination with traditional antibiotics against septic myocardial injury 28 (1): 35.
Yang Y., W. Lei, L. Qian, S. Zhang, W. Yang, C. Lu, Y. Song, Z. Liang, C. Deng, Y. Chen. 2023. Activation of NR1H3 signaling pathways by psoralidin attenuates septic myocardial injury. Free Radic Biol Med 204(8–19).
Lu C., W. Lei, M. Sun, X. Wu, Q. Liu, J. Liu, Y. Yang, W. Yang, Z. Zhang, X. Li. 2023. Identification of CCR2 as a hub in septic myocardial injury and cardioprotection of silibinin. Free Radical Biology Medicine 197(46–57).
Liang Z., Y. Chen, Z. Wang, X. Wu, C. Deng, C. Wang, W. Yang, Y. Tian, S. Zhang, C. Lu. 2022. Protective effects and mechanisms of psoralidin against adriamycin-induced cardiotoxicity. Journal of Advanced Research 40(249–261).
Delano, M.J., and P.A. Ward. 2016. The immune system’s role in sepsis progression, resolution, and long-term outcome. Immunological Reviews 274 (1): 330–353.
Pizzuto M., P. Pelegrin and J. M. Ruysschaert. 2022. Lipid-protein interactions regulating the canonical and the non-canonical NLRP3 inflammasome. Progress in Lipid Research 87(101182).
Li N., H. Zhou, H. Wu, Q. Wu, M. Duan, W. Deng and Q. Tang. 2019. STING-IRF3 contributes to lipopolysaccharide-induced cardiac dysfunction, inflammation, apoptosis and pyroptosis by activating NLRP3. Redox Biol 24(101215).
Zhou, R., X. Yang, X. Li, Y. Qu, Q. Huang, X. Sun, and D. Mu. 2019. Recombinant CC16 inhibits NLRP3/caspase-1-induced pyroptosis through p38 MAPK and ERK signaling pathways in the brain of a neonatal rat model with sepsis. Journal of Neuroinflammation 16 (1): 239.
Wang, K., Q. Sun, X. Zhong, M. Zeng, H. Zeng, X. Shi, Z. Li, Y. Wang, Q. Zhao, and F. Shao. 2020. Structural Mechanism for GSDMD Targeting by Autoprocessed Caspases in Pyroptosis. Cell 180 (5): 941-955.e20.
Burdette, B.E., A.N. Esparza, H. Zhu, and S. Wang. 2021. Gasdermin D in pyroptosis. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B 11 (9): 2768–2782.
Kayagaki, N., I.B. Stowe, B.L. Lee, K. O’rourke, K. Anderson, S. Warming, T. Cuellar, B. Haley, M. Roose-Girma, and Q.T. Phung. 2015. Caspase-11 cleaves gasdermin D for non-canonical inflammasome signalling. Nature 526 (7575): 666–671.
Rathkey J. K., J. Zhao, Z. Liu and Y. Chen. 2018. Chemical disruption of the pyroptotic pore-forming protein gasdermin D inhibits inflammatory cell death and sepsis. 3(26).
Yan X., Y. L. Zhang, X. Han, P. B. Li, S. B. Guo and H. H. Li. 2022. Time Series Transcriptomic Analysis by RNA Sequencing Reveals a Key Role of PI3K in Sepsis-Induced Myocardial Injury in Mice. Front Physiol 13(903164).
Suárez-Fueyo, A., J.M. Rojas, A.E. Cariaga, E. García, B.H. Steiner, D.F. Barber, K.D. Puri, and A.C. Carrera. 2014. Inhibition of PI3Kδ reduces kidney infiltration by macrophages and ameliorates systemic lupus in the mouse. The Journal of Immunology 193 (2): 544–554.
Rommel, C., M. Camps, and H. Ji. 2007. PI3K delta and PI3K gamma: Partners in crime in inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis and beyond? Nature Reviews Immunology 7 (3): 191–201.
Martin, E.L., D.G. Souza, C.T. Fagundes, F.A. Amaral, B. Assenzio, V. Puntorieri, L. Del Sorbo, V. Fanelli, M. Bosco, and L. Delsedime. 2010. Phosphoinositide-3 kinase gamma activity contributes to sepsis and organ damage by altering neutrophil recruitment. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 182 (6): 762–773.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82300319, 82070422, 81960080, and 82200330), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2023T160526 and 2022M722571), Youth Science and Technology Rising Star Project of Shaanxi Province (2020KJXX-036), High-end Foreign Expert Introduction Program of National Science and Technology (G2022040014L), and Innovation Capability Strong Foundation Plan of Xi'an City (Medical Research Project, 21YXYJ0037).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors have significantly contributed to this work and meet criteria for authorship by the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors recommendations. Conception and design: XW and DAC. Acquisition of data: CXL, JL, GE, and XW. Analysis and interpretation of data: CXL, JL, QL, YY, XW, ZW, XW, and CD. Drafting the manuscript for important intellectual content: QL, WX, CXL, YBS, and ZW. Revising the manuscript for important intellectual content: All authors.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All experimental procedures complied with the National Institutes of Health Guidelines for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals and were approved by the Animal Care Ethics Committee of Northwestern University (Approval number: 2020024).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, C., Liu, J., Escames, G. et al. PIK3CG Regulates NLRP3/GSDMD-Mediated Pyroptosis in Septic Myocardial Injury. Inflammation 46, 2416–2432 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-023-01889-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-023-01889-0