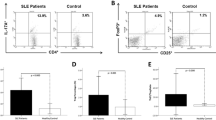
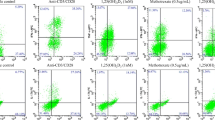
Abstract
Inflammatory T lymphocyte cytokines contribute to tissue damage in SLE patients. Vitamin D (Vit D) has a well-established immunomodulatory action, but few studies have addressed the effect of 1,25 dihydroxyvitamin D3 (1,25 (OH)2D3) on peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) in SLE patients. The aim of this study was to evaluate the immnunomodulatory effect of 1,25 (OH)2D3 on T lymphocyte-related cytokines. Blood from 27 female SLE patients was collected for PBMC isolation and anti-DNA, complement, and serum 25 (OH)D3 level measurements. PBMCs were stimulated with anti-CD3/anti-CD28 in the presence or absence of dexamethasone or various concentrations of 1,25 (OH)2D3 for 48 h. We assessed IL-17A, IL-22, IL-21, IL-9, IFN-γ, IL-4, IL-10, IL-2, IL-6, and TNF by cytometric bead assay (CBA) and enzyme immune assay (ELISA) on culture supernatant. The mean age of patients was 36.2 (± 10.5 years) and the median Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index (SLEDAI) was 4 (0–6). The addition of 1,25 (OH)2D3 in PBMC culture reduced IL-17 A, IL-22, IL-9, and IFN-γ levels at 100 nM (p ≤ 0.0001). Furthermore, the addition of 1,25 (OH)2D3 at all concentrations increased IL-4 (p ≤ 0.0006), and 0.1 and 1 nM increased IL-10 (p ≤ 0.0004) and 0.1 nM increased IL-2 levels (p ≤ 0.0001). There was no difference regarding IL-21 and TNF levels. The addition of 1,25 (OH)2D3 in PBMC culture presented an inhibitory effect on proinflammatory cytokines and increased immunoregulatory cytokines in SLE patients, suggesting the beneficial effect of this vitamin.


Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Materials
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author, upon reasonable request.
References
Lisnevskaia, L., G. Murphy, and D. Isenberg. 2014. Systemic lupus erythematosus. Lancet 384 (9957): 1878–1888.
Comte, D., M.P. Karampetsou, and G.C. Tsokos. 2015. T cells as a therapeutic target in SLE. Lupus 24 (4–5): 351–363.
Wong, C.K., C.Y. Ho, E.K. Li, and C.W. Lam. 2000. Elevation of proinflammatory cytokine (IL-18, IL-17, IL-12) and Th2 cytokine (IL-4) concentrations in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 9 (8): 589–593.
Talaat, R.M., S.F. Mohamed, I.H. Bassyouni, and A.A. Raouf. 2015. Th1/Th2/Th17/Treg cytokine imbalance in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) patients: Correlation with disease activity. Cytokine 72 (2): 146–153.
McCarthy, E.M., S. Smith, R.Z. Lee, G. Cunnane, M.F. Doran, S. Donnelly, et al. 2014. The association of cytokines with disease activity and damage scores in systemic lupus erythematosus patients. Rheumatology (Oxford) 53 (9): 1586–1594.
Singh, R.R. 2003. IL-4 and many roads to lupuslike autoimmunity. Clinical immunology 108: 73–9. United States.
Dooms, H., and A.K. Abbas. 2010. Revisiting the role of IL-2 in autoimmunity. European Journal of Immunology 40 (6): 1538–1540.
He, J., R. Zhang, M. Shao, X. Zhao, M. Miao, J. Chen, et al. 2020. Efficacy and safety of low-dose IL-2 in the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 79 (1): 141–149.
Holick, M.F. 2007. Vitamin D deficiency. New England Journal of Medicine 357 (3): 266–281.
Yamamoto, E., and T.N. Jørgensen. 2019. Immunological effects of vitamin D and their relations to autoimmunity. Journal of Autoimmunity 100: 7–16.
Schneider, L., A.S. Dos Santos, M. Santos, R.M. da Silva Chakr, and O.A. Monticielo. 2014. Vitamin D and systemic lupus erythematosus: State of the art. Clinical Rheumatology 33 (8): 1033–1038.
Petri, M., K.J. Bello, H. Fang, and L.S. Magder. 2013. Vitamin D in systemic lupus erythematosus: Modest association with disease activity and the urine protein-to-creatinine ratio. Arthritis and Rheumatism 65 (7): 1865–1871.
Lima, G.L., J. Paupitz, N.E. Aikawa, L. Takayama, E. Bonfa, and R.M. Pereira. 2016. Vitamin D supplementation in adolescents and young adults with juvenile systemic lupus erythematosus for improvement in disease activity and fatigue scores: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 68 (1): 91–98.
Aranow, C., D.L. Kamen, M. Dall’Era, E.M. Massarotti, M.C. Mackay, F. Koumpouras, et al. 2015. Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of the effect of vitamin D3 on the interferon signature in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis & Rhematology 67 (7): 1848–1857.
Piantoni, S., L. Andreoli, M. Scarsi, A. Zanola, F. Dall’Ara, C. Pizzorni, et al. 2015. Phenotype modifications of T-cells and their shift toward a Th2 response in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus supplemented with different monthly regimens of vitamin D. Lupus 24 (4–5): 490–498.
Andreoli, L., F. Dall’Ara, S. Piantoni, A. Zanola, N. Piva, M. Cutolo, et al. 2015. A 24-month prospective study on the efficacy and safety of two different monthly regimens of vitamin D supplementation in pre-menopausal women with systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 24 (4–5): 499–506.
Terrier, B., N. Costedoat-Chalumeau, M. Garrido, G. Geri, M. Rosenzwajg, L. Musset, et al. 2012. Interleukin 21 correlates with T cell and B cell subset alterations in systemic lupus erythematosus. Journal of Rheumatology 39 (9): 1819–1828.
Zheng, R., A. Gonzalez, J. Yue, X. Wu, M. Qiu, L. Gui, et al. 2019. Efficacy and safety of vitamin D supplementation in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. American Journal of the Medical Sciences 358 (2): 104–114.
Magro, R., C. Saliba, L. Camilleri, C. Scerri, and A.A. Borg. 2021. Vitamin D supplementation in systemic lupus erythematosus: Relationship to disease activity, fatigue and the interferon signature gene expression. BMC Rheumatol. 5 (1): 53.
Ben-Zvi, I., C. Aranow, M. Mackay, A. Stanevsky, D.L. Kamen, L.M. Marinescu, et al. 2010. The impact of vitamin D on dendritic cell function in patients with systemic. PLoS ONE 5 (2): e9193.
Czifra, G., B. Toth, I. Kovacs, T. Biro, Z. Griger, S. Barath, et al. 2014. The in vitro treatment with vitamin D3 is ineffective on the expression of PKC isoenzymes, but decreases further the impaired production of IL-2 in the T lymphocytes of SLE patients. Rheumatology International 34 (5): 717–720.
Wahono, C.S., H. Rusmini, D. Soelistyoningsih, R. Hakim, K. Handono, A.T. Endharti, et al. 2014. Effects of 1,25(OH)2D3 in immune response regulation of systemic lupus erithematosus (SLE) patient with hypovitamin D. International Journal of Clinical and Experimental Medicine 7 (1): 22–31.
Lerman, M., J. Burnham, and E. Behrens. 2011. 1,25 dihydroxyvitamin D3 limits monocyte maturation in lupus sera. Lupus 20 (7): 749–753.
Linker-Israeli, M., E. Elstner, J.R. Klinenberg, D.J. Wallace, and H.P. Koeffler. 2001. Vitamin D(3) and its synthetic analogs inhibit the spontaneous in vitro. Clinical Immunology 99 (1): 82–93.
Chen, S., G.P. Sims, X.X. Chen, Y.Y. Gu, and P.E. Lipsky. 2007. Modulatory effects of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 on human B cell differentiation. The Journal of Immunology 179 (3): 1634–1647.
Gladman, D.D., D. Ibanez, and M.B. Urowitz. 2002. Systemic lupus erythematosus disease activity index 2000. Journal of Rheumatology 29 (2): 288–291.
Gladman, D.D., M.B. Urowitz, C.H. Goldsmith, P. Fortin, E. Ginzler, C. Gordon, et al. 1997. The reliability of the systemic lupus international collaborating. Arthritis and Rheumatism 40 (5): 809–813.
Colin, E.M., P.S. Asmawidjaja, J.P. van Hamburg, A.M. Mus, M. van Driel, J.M. Hazes, et al. 2010. 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 modulates Th17 polarization and interleukin-22. Arthritis and Rheumatism 62 (1): 132–142.
Tian, Y., C. Wang, Z. Ye, X. Xiao, A. Kijlstra, and P. Yang. 2012. Effect of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 on Th17 and Th1 response in patients with Behcet’s disease. Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science 53 (10): 6434–6441.
Cheng, F., Z. Guo, H. Xu, D. Yan, and Q. Li. 2009. Decreased plasma IL22 levels, but not increased IL17 and IL23 levels, correlate with disease activity in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Annals of the rheumatic diseases 68: 604–6. England.
Pan, H.F., X.F. Zhao, H. Yuan, W.H. Zhang, X.P. Li, G.H. Wang, et al. 2009. Decreased serum IL-22 levels in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clinica chimica acta; international journal of clinical chemistry 401: 179–80. Netherlands.
Qin, W.Z., L.L. Chen, H.F. Pan, R.X. Leng, Z.M. Zhai, C. Wang, et al. 2011. Expressions of IL-22 in circulating CD4+/CD8+ T cells and their correlation with disease activity in SLE patients. Clinical and Experimental Medicine 11 (4): 245–250.
Noelle, R.J., and E.C. Nowak. 2010. Cellular sources and immune functions of interleukin-9. Nature Reviews Immunology 10 (10): 683–687.
Dantas, A.T., C.D. Marques, L.F. da Rocha Junior, M.B. Cavalcanti, S.M. Goncalves, P.R. Cardoso, et al. 2015. Increased serum interleukin-9 levels in rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus: Pathogenic role or just an epiphenomenon? Disease Markers 2015: 519638.
Ouyang, H., Y.B. Shi, N. Su, and L.Y. Li. 2013. Abnormality and significance of interleukin-9 and CD4(+)interleukin-9(+) T-cells in peripheral blood of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 93 (2): 99–103.
Mori, M., S.C. Morris, T. Orekhova, M. Marinaro, E. Giannini, and F.D. Finkelman. 2000. IL-4 promotes the migration of circulating B cells to the spleen and increases splenic B cell survival. The Journal of Immunology 164 (11): 5704–5712.
Erb, K.J., B. Ruger, M. von Brevern, B. Ryffel, A. Schimpl, and K. Rivett. 1997. Constitutive expression of interleukin (IL)-4 in vivo causes autoimmune-type disorders in mice. Journal of Experimental Medicine 185 (2): 329–339.
Santiago, M.L., L. Fossati, C. Jacquet, W. Muller, S. Izui, and L. Reininger. 1997. Interleukin-4 protects against a genetically linked lupus-like autoimmune syndrome. Journal of Experimental Medicine 185 (1): 65–70.
Watanabe, R., N. Ishiura, H. Nakashima, Y. Kuwano, H. Okochi, K. Tamaki, et al. 2010. Regulatory B cells (B10 cells) have a suppressive role in murine lupus: CD19 and B10 cell deficiency exacerbates systemic autoimmunity. The Journal of Immunology 184 (9): 4801–4809.
Peng, H., W. Wang, M. Zhou, R. Li, H.F. Pan, and D.Q. Ye. 2013. Role of interleukin-10 and interleukin-10 receptor in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clinical Rheumatology 32 (9): 1255–1266.
Viallard, J.F., J.L. Pellegrin, V. Ranchin, T. Schaeverbeke, J. Dehais, M. Longy-Boursier, et al. 1999. Th1 (IL-2, interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma)) and Th2 (IL-10, IL-4) cytokine production by peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Clinical and Experimental Immunology 115 (1): 189–195.
Altman, A. A.N. Theofilopoulos, R. Weiner, D.H. Katz, and F.J. Dixon. 1981. Analysis of T cell function in autoimmune murine strains. Defects in production and responsiveness to interleukin 2. The Journal of Experimental Medicine 154(3):791–808.
Alcocer-Varela, J., and D. Alarcon-Segovia. 1982. Decreased production of and response to interleukin-2 by cultured lymphocytes from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. The Journal of Clinical Investigation 69 (6): 1388–1392.
Abou-Raya, A., S. Abou-Raya, and M. Helmii. 2013. The effect of vitamin D supplementation on inflammatory and hemostatic markers and disease activity in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: A randomized placebo-controlled trial. Journal of Rheumatology 40 (3): 265–272.
Finamor, D.C., R. Sinigaglia-Coimbra, L.C. Neves, M. Gutierrez, J.J. Silva, L.D. Torres, et al. 2013. A pilot study assessing the effect of prolonged administration of high daily doses of vitamin D on the clinical course of vitiligo and psoriasis. Dermatoendocrinol. 5 (1): 222–234.
Tsokos, G.C., M.S. Lo, P. Costa Reis, and K.E. Sullivan. 2016. New insights into the immunopathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Nature Reviews Rheumatology 12 (12): 716–730.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge all participants.
Funding
This study had partial financial support by the Research Foundation of the Brazilian Rheumatology Society and a research fellowship (E.I. Sato) from the National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq) of the Brazilian Ministery of Science, Technology and Innovation (MCTI).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HM, ES, RG, and AD: study concept and design. HM and PC: data collection. HM, MR, IP, and MP: statistical analysis and data interpretation. Further data interpretation and manuscript revision were performed by all the authors. All authors gave final approval of the version to be published. HM prepared the first version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval and Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mariz, H.A., Sato, E.I., Cardoso, P.R.G. et al. Vitamin D Presented In Vitro Immunomodulatory Property on T Lymphocyte-Related Cytokines in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Inflammation 46, 730–738 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-022-01768-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-022-01768-0