Abstract
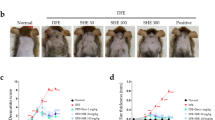
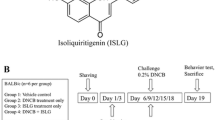
Scutellaria baicalensis has long been used in Asian traditional medicine to prevent and treat suppurative dermatitis, allergic diseases, inflammation, hyperlipemia, and arteriosclerosis. Oroxylin A is a flavone present in Scutellaria baicalensis. Because the root extracts of Scutellaria baicalensis have been shown to have anti-dermatitis effects, the authors investigated the effects of oroxylin A on chemically induced atopic dermatitis (AD) in an in vivo AD model induced by 1-chloro-2,4-dinitrobenzene (CDNB) in BALB/c mice. CDNB-induced skin hypertrophy and accumulation of mast cells in the epidermis and dermis were significantly decreased by oroxylin A. Increased serum levels of immunoglobulin E, as well as pro-inflammatory chemokines and cytokines in the skin and lymph nodes, were significantly decreased by oroxylin A. Suppression of immune responses in the skin and lymph nodes by oroxylin A decreased the symptoms of AD. Thus, these results proved that oroxylin A is an effective component of Scutellaria baicalensis for treating the symptoms of AD.







Similar content being viewed by others
AVAILABILITY OF DATA AND MATERIALS
Not applicable.
References
Kim, C.-J., and S.K. Cho. 1991. Pharmacological activities of flavonoids (III) structure-activity relationships of flavonoids in immunosuppression. Archives of Pharmacal Research 14: 147–159.
Shah, R., C. Mehta, and T. Wheeler. 1936. 131. The constitution of oroxylin-A, a yellow colouring matter from the root-bark of Oroxylum indicum, vent. Journal of the Chemical Society (Resumed):591–593.
Li, H.-B., Y. Jiang, and F. Chen. 2004. Separation methods used for Scutellaria baicalensis active components. Journal of chromatography B 812: 277–290.
Lu, L., Q. Guo, and L. Zhao. 2016. Overview of oroxylin A: A promising flavonoid compound. Phytotherapy Research 30: 1765–1774.
Yang, X., F. Zhang, Y. Wang, M. Cai, Q. Wang, Q. Guo, et al. 2013. Oroxylin A inhibits colitis-associated carcinogenesis through modulating the IL-6/STAT3 signaling pathway. Inflammatory bowel diseases 19: 1990–2000.
Chen, Y.-C., L.-L. Yang, and T.J. Lee. 2000. Oroxylin A inhibition of lipopolysaccharide-induced iNOS and COX-2 gene expression via suppression of nuclear factor-κB activation. Biochemical pharmacology 59: 1445–1457.
Ye, M., Q. Wang, W. Zhang, Z. Li, Y. Wang, and R. Hu. 2014. Oroxylin A exerts anti-inflammatory activity on lipopolysaccharide-induced mouse macrophage via Nrf2/ARE activation. Biochemistry and Cell Biology 92: 337–348.
Lee, A.-Y., S. Kang, S.-J. Park, J. Huang, and D.-S. Im. 2016. Anti-Allergic effect of oroxylin A from oroxylum indicum using in vivo and in vitro experiments. Biomolecules & Therapeutics 24: 283.
Zhou, D.-G., B.-Z. Diao, W. Zhou, and J.-L. Feng. 2016. Oroxylin A inhibits allergic airway inflammation in ovalbumin (OVA)-induced asthma murine model. Inflammation 39: 867–872.
Kang, J., and D.S. Im. 2020. FFA2 Activation ameliorates 2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene-induced atopic dermatitis in mice. Biomolecules and Therapeutics (Seoul) 28: 267–271.
Kang, J., J.H. Lee, and D.S. Im. 2020. Topical Application of S1P(2) Antagonist JTE-013 attenuates 2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene-induced atopic dermatitis in mice. Biomol Ther (Seoul) 28: 537–541.
Park, S.J., and D.S. Im. 2020. Blockage of sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 2 attenuates 2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene-induced atopic dermatitis in mice. Acta Pharmacologica Sinica 41: 1487–1496.
Son, S.E., S.J. Park, J.M. Koh, and D.S. Im. 2020. Free fatty acid receptor 4 (FFA4) activation ameliorates 2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene-induced atopic dermatitis by increasing regulatory T cells in mice. Acta Pharmacologica Sinica 41: 1337–1347.
Su, C., T. Yang, Z. Wu, J. Zhong, Y. Huang, T. Huang, et al. 2017. Differentiation of T-helper cells in distinct phases of atopic dermatitis involves Th1/Th2 and Th17/Treg. European Journal of Inflammation 15: 46–52.
Lee, J.-H., and D.-S. Im. 2022. Honokiol suppresses 2, 6-dinitrochlorobenzene-induced atopic dermatitis in mice. Journal of Ethnopharmacology p. 115023.
Kezic, S., M.A. McAleer, I. Jakasa, S.M. Goorden, K. Ghauharali‐van der Vlugt, F.S. Beers‐Stet, et al. 2022. Children with atopic dermatitis show increased activity of β‐glucocerebrosidase and stratum corneum levels of glucosylcholesterol that are strongly related to local cytokine milieu. British Journal of Dermatology.
Montero-Vilchez, T., C. Cuenca-Barrales, J.-A. Rodriguez-Pozo, P. Diaz-Calvillo, J. Tercedor-Sanchez, A. Martinez-Lopez, et al. 2022. Epidermal barrier function and skin homeostasis in atopic dermatitis: The impact of age. Life 12: 132.
Salimian, J., Z. Salehi, A. Ahmadi, A. Emamvirdizadeh, S.M. Davoudi, M. Karimi, et al. 2022. Atopic dermatitis: Molecular, cellular, and clinical aspects. Molecular Biology Reports p. 1–16.
Zhao, Z., W. Qin, T. Liu, Y. Yang, Z. Wang, H. Ma, et al. 2022. The nanostructured lipid carrier gel of Oroxylin A reduced UV-induced skin oxidative stress damage. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces p. 112578.
Yun, M.-Y., J.-H. Yang, D.-K. Kim, K.-J. Cheong, H.-H. Song, D.-H. Kim, et al. 2010. Therapeutic effects of Baicalein on atopic dermatitis-like skin lesions of NC/Nga mice induced by dermatophagoides pteronyssinus. International Immunopharmacology 10: 1142–1148.
Hung, C.-H., C.-N. Wang, H.-H. Cheng, J.-W. Liao, Y.-T. Chen, Y.-W. Chao, et al. 2018. Baicalin ameliorates imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like inflammation in mice. Planta medica 84: 1110–1117.
Wu, J., H. Li, and M. Li. 2015. Effects of baicalin cream in two mouse models: 2, 4-dinitrofluorobenzene-induced contact hypersensitivity and mouse tail test for psoriasis. International journal of clinical and experimental medicine 8: 2128.
Wang, L., Y.-F. Xian, S.K.F. Loo, S.P. Ip, W. Yang, W.Y. Chan, et al. 2022. Baicalin ameliorates 2, 4-dinitrochlorobenzene-induced atopic dermatitis-like skin lesions in mice through modulating skin barrier function, gut microbiota and JAK/STAT pathway. Bioorganic Chemistry 119: 105538.
Lim, H., H. Park, and H.P. Kim. 2004. Inhibition of contact dermatitis in animal models and suppression of proinflammatory gene expression by topically applied flavonoid, wogonin. Archives of Pharmacal Research 27: 442–448.
Park, B.K., M.Y. Heo, H. Park, and H.P. Kim. 2001. Inhibition of TPA-induced cyclooxygenase-2 expression and skin inflammation in mice by wogonin, a plant flavone from Scutellaria radix. European Journal of Pharmacology 425: 153–157.
Chi, Y.S., H. Lim, H. Park, and H.P. Kim. 2003. Effects of wogonin, a plant flavone from Scutellaria radix, on skin inflammation: In vivo regulation of inflammation-associated gene expression. Biochemical pharmacology 66: 1271–1278.
Li, H.-J., N.-L. Wu, C.-M. Pu, C.-Y. Hsiao, D.-C. Chang, and C.-F. Hung. 2020. Chrysin alleviates imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like skin inflammation and reduces the release of CCL20 and antimicrobial peptides. Scientific Reports 10: 1–13.
Trinh, H.-t, E.-h Joh, H.-y Kwak, N.-i Baek, and D.-h Kim. 2010. Anti-pruritic effect of baicalin and its metabolites, baicalein and oroxylin A, in mice. Acta Pharmacologica Sinica 31: 718–724.
Wang, Y.-l, J.-m Gao, and L.-z Xing. 2016. Therapeutic potential of oroxylin A in rheumatoid arthritis. International Immunopharmacology 40: 294–299.
Funding
This research was supported by the Basic Research Laboratory Program (BRL) and the Basic Science Research Program of the Korean National Research Foundation funded by the Korean Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning (NRF-2020R1A4A1016142 and NRF-2019R1A2C1005523).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YJ Lee and DS Im designed the experiments. YJ Lee performed the experiments and analyzed the data. YJ Lee and DS Im wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, YJ., Im, DS. Inhibitory Effect of Oroxylin A in a Mouse Model of Atopic Dermatitis. Inflammation 46, 679–687 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-022-01764-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-022-01764-4