Abstract
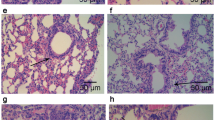
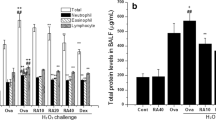
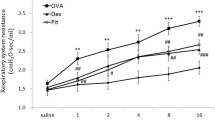
Statins could be of potential therapeutic effect in asthma due to their pleiotropic effects on inflammation process. This study aimed to examine the possible interaction of serum lipids, and evaluate the effect of rosuvastatin treatment on asthma. Seven groups of rats, namely control (C), asthmatic (A), hyperlipidemic (H), asthmatic-hyperlipidemic (AH), rosuvastatin (40 mg/kg)-treated asthmatic (AR), rosuvastatin-treated hyperlipidemic (HR), and rosuvastatin-treated hyperlipidemic-asthmatic (AHR) groups, were studied. Total and differential WBC counts, serum oxidative stress markers, and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) levels of IL-6 and IL-10 were evaluated. In the A and AH groups, total and differential WBC counts, and IL-6 and IL-10 levels were higher than in the C group (p<0.05 to p<0.001). An increase in nitrite and malondialdehyde concentrations and a decrease in total thiol content and superoxide dismutase and catalase activities were observed in the A, H, and AH groups compared to the C group (p<0.05 to p<0.001). Beyond lipid lowering, rosuvastatin treatment reduced total and differential WBC counts in the A and AH groups (p<0.05 to p<0.001), IL-6 level in the AH group (p<0.05), and IL-10 level in all treated groups (p<0.05). Rosuvastatin reduced oxidative stress by decreasing nitrite and malondialdehyde concentrations, and increasing total thiol content in all treated groups as well as superoxide dismutase and catalase activities in the H and AH groups (p<0.05 to p<0.01). Rosuvastatin reduced airway inflammation and oxidation through regulating NOS and reducing pro-inflammatory cytokine and inflammatory cells, which indicate a novel insight into the pleiotropic effects of rosuvastatin in treatment of asthma.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
de Groot, Linsey E.S., Yanaika S. Sabogal Piñeros, Suzanne M. Bal, Marianne A. Van De Pol, Jörg Hamann, Peter J. Sterk, Wim Kulik, and René Lutter. 2019. Do eosinophils contribute to oxidative stress in mild asthma? Clinical and Experimental Allergy 49 (6): 929–931.
Desai, D., and C. Brightling. 2009. Cytokine and anti-cytokine therapy in asthma: ready for the clinic? Clinical and Experimental Immunology 158 (1): 10–19.
Al-Shawwa, Baha, Nidal Al-Huniti, Gregory Titus, and Mutasim Abu-Hasan. 2006. Hypercholesterolemia is a potential risk factor for asthma. The Journal of Asthma 43 (3): 231–233. https://doi.org/10.1080/02770900600567056.
Shore, Stephanie A. 2008. Obesity and asthma: possible mechanisms. The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 121 (5): 1087–1093.
Chen, Yang Ching, Kuan Yen Tung, Ching Hui Tsai, Su Ming Wei, Pei Chuan Wang, Chien Han Chen, and Yungling Leo Lee. 2013. Lipid profiles in children with and without asthma: interaction of asthma and obesity on hyperlipidemia. Diabetes and Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research and Reviews 7 (1): 20–25.
Bradbury, Peta, Daniela Traini, Alaina J. Ammit, Paul M. Young, and Hui Xin Ong. 2018. Repurposing of statins via inhalation to treat lung inflammatory conditions. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews 133: 93–106.
Capra, Valérie, and G. Enrico Rovati. 2014. Rosuvastatin inhibits human airway smooth muscle cells mitogenic response to eicosanoid contractile agents. Pulmonary Pharmacology & Therapeutics 27 (1): 10–16.
Yildizeli, Olgun, Derya Kocakaya Sehnaz, Baran Balcan, Aygun Ikinci, Rengin Ahiskali, and Berrin Ceyhan. 2017. Influence of rosuvastatin treatment on airway inflammatory markers and health related quality of life domains in asthmatic patients. Marmara Medical Journal 30 (2): 73–81.
Alwahsh, Salamah Mohammad, Min Xu, Frank Christian Schultze, Jörg Wilting, Sabine Mihm, Dirk Raddatz, and Giuliano Ramadori. 2014. Combination of alcohol and fructose exacerbates metabolic imbalance in terms of hepatic damage, dyslipidemia, and insulin resistance in rats. PLoS One 9 (8): e104220.
Saadat, Saeideh, Amin Mokhtari-Zaer, and Mohammad Hossein Boskabady. 2019. Rosuvastatin affects tracheal responsiveness, bronchoalveolar lavage inflammatory cells, and oxidative stress markers in hyperlipidemic and asthmatic rats. Iranian Journal of Allergy, Asthma, and Immunology: 624–638.
Saadat, Saeideh, Nema Mohamadian Roshan, Mohammad Reza Aslani, and Mohammad Hossein Boskabady. 2020. Rosuvastatin suppresses cytokine production and lung inflammation in asthmatic, hyperlipidemic and asthmatic-hyperlipidemic rat models. Cytokine 128: 154993.
Saadat, Saeideh, Mostafa Mohammadi, Maryam Fallahi, and Mohammad Reza Aslani. 2015. The protective effect of α-hederin, the active constituent of Nigella sativa, on tracheal responsiveness and lung inflammation in ovalbumin-sensitized guinea pigs. The Journal of Physiological Sciences 65 (3): 285–292.
Saadat, Saeideh, Farimah Beheshti, Vahid Reza Askari, Mahmoud Hosseini, Nema Mohamadian Roshan, and Mohammad Hossein Boskabady. 2019. Aminoguanidine affects systemic and lung inflammation induced by lipopolysaccharide in rats. Respiratory Research 20 (1): 96.
Keyhanmanesh, Rana, Saeideh Saadat, Mostafa Mohammadi, Amir-Ali Shahbazfar, and Maryam Fallahi. 2015. The protective effect of α-hederin, the active constituent of nigella sativa, on lung inflammation and blood cytokines in ovalbumin sensitized guinea pigs. Phytotherapy Research 29 (11): 1761–1767.
Shakeri, Farzaneh, and Mohammad Hossein Boskabady. 2017. Anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and immunomodulatory effects of curcumin in ovalbumin-sensitized rat. BioFactors 43 (4): 567–576. https://doi.org/10.1002/biof.1364.
Shakeri, Farzaneh, Nama Mohamadian Roshan, Mahsa Kaveh, Naeima Eftekhar, and Mohammad Hossein Boskabady. 2018. Curcumin affects tracheal responsiveness and lung pathology in asthmatic rats. Pharmacological Reports 70 (5): 981–987.
Peters, Michael C., Kelly Wong McGrath, Gregory A. Hawkins, Annette T. Hastie, Bruce D. Levy, Elliot Israel, Brenda R. Phillips, David T. Mauger, Suzy A. Comhair, and Serpil C. Erzurum. 2016. Plasma interleukin-6 concentrations, metabolic dysfunction, and asthma severity: a cross-sectional analysis of two cohorts. The Lancet Respiratory Medicine 4 (7): 574–584.
Aslani, Mohammad Reza, Rana Keyhanmanesh, and Mohammad Reza Alipour. 2017. Increased visfatin expression is associated with nuclear factor-κB in obese ovalbumin-sensitized male Wistar rat tracheae. Medical Principles and Practice 26 (4): 351–358.
Xu, Lan, Xing-wei Dong, Liang-liang Shen, Fen-fen Li, Jun-xia Jiang, Rui Cao, Hong-yi Yao, Hui-juan Shen, Yun Sun, and Qiang-min Xie. 2012. Simvastatin delivery via inhalation attenuates airway inflammation in a murine model of asthma. International Immunopharmacology 12 (4): 556–564.
Tao, Z.H.U., Wei Zhang, Dao-xin Wang, Huang Ni-wen, B.O. Hong, D.E.N.G. Wang, and D.E.N.G. Jia. 2012. Rosuvastatin attenuates mucus secretion in a murine model of chronic asthma by inhibiting the gamma-aminobutyric acid type A receptor. Chinese Medical Journal 125 (8): 1457–1464.
Huang, Kuo-Chin, Ching-Wen Chen, Jui-Ching Chen, and Wan-Wan Lin. 2003. HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors inhibit inducible nitric oxide synthase gene expression in macrophages. Journal of Biomedical Science 10 (4): 396–405.
Kırzıoğlu, F.Y., Ö. Özmen, B. Doğan, M.T. Bulut, Ö. Fentoğlu, and M. Özdem. 2018. Effects of rosuvastatin on inducible nitric oxide synthase in rats with hyperlipidaemia and periodontitis. Journal of Periodontal Research 53 (2): 258–266.
Ferreira, Thiago Santos, Manuella Lanzetti, Marina Valente Barroso, Carlos Romualdo Rueff-Barroso, Cláudia Farias Benjamim, Lycia de Brito-Gitirana, Luís Cristóvão Porto, and Samuel Santos Valença. 2014. Oxidative stress and inflammation are differentially affected by atorvastatin, pravastatin, rosuvastatin, and simvastatin on lungs from mice exposed to cigarette smoke. Inflammation 37 (5): 1355–1365.
Bast, Aalt, Antje R. Weseler, Guido R.M.M. Haenen, and Gertjan J.M. den Hartog. 2010. Oxidative stress and antioxidants in interstitial lung disease. Current Opinion in Pulmonary Medicine 16 (5): 516–520.
Availability of Data and Materials
The data of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
Funding
This work was supported by a grant from Research Council of Mashhad University of Medical Sciences (Grant Number: 940997).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SS carried out the experimental work, performed statistical analysis, prepared figures, and drafted the first version of the manuscript. MHB designed and supervised the study, helped in statistical analysis, and corrected the manuscript. Both authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Mashhad University of Medical Sciences for Animal Experiments (Approval No. 940997).
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saadat, S., Boskabady, M.H. Anti-inflammatory and Antioxidant Effects of Rosuvastatin on Asthmatic, Hyperlipidemic, and Asthmatic-Hyperlipidemic Rat Models. Inflammation 44, 2279–2290 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-021-01499-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-021-01499-8