Abstract
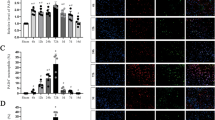
Brain death (BD) can induce inflammation and injury of organs. Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress is associated with a variety of diseases. However, little is known about how ER stress is implicated in brain death (BD)-induced lung injury. In this study, a stable BD rat model was constructed to investigate the role of ER stress on BD-induced lung injury. H&E staining demonstrated that BD can induce lung injury in rats. The results of Western blot and immunohistochemistry showed that apoptosis was observed in the lung tissues of BD rats. And the level of GRP78, p-PERK, p-eIF2α, CHOP, and Caspase-12 was highly expressed in BD rats compared with the control group. Inhibition of ER stress with salubrinal reduced the BD-induced lung inflammation. Moreover, BD-induced increase of NF-κB activity was lowered by inhibition of ER stress. These results suggested that inhibition of ER stress alleviates BD-induced lung inflammation by regulating NF-κB signaling pathway.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kotloff, R.M., and G. Thabut. 2011. Lung transplantation. American journal of respiratory and critical care medicine 184: 159–171.
Adrie, C., M. Monchi, J.P. Fulgencio, et al. 2010. Immune status and apoptosis activation during brain death. Shock 33: 353–362.
Bugge, J.F. 2009. Brain death and its implications for management of the potential organ donor. Acta anaesthesiologica scandinavica 53: 1239–1250.
Cao, S., T. Wang, B. Yan, et al. 2014. Protective effects of SP600125 in brain death-induced liver injury. Clinics and research in hepatology and gastroenterology 38: 577–582.
Cao, S., B. Yan, Y. Lu, et al. 2015. C/EBP homologous protein-mediated endoplasmic reticulum stress-related renal apoptosis is involved in rats with brain death. Transplantation proceedings 47: 354–358.
Fang, H., S. Zhang, W. Guo, et al. 2015. Cobalt protoporphyrin protects the liver against apoptosis in rats of brain death. Clinics and research in hepatology and gastroenterology 39: 475–481.
Guo, W., S. Cao, B. Yan, et al. 2016. Myocardial protective effects of a c-Jun N-terminal kinase inhibitor in rats with brain death. Journal of cellular and molecular medicine 20: 1214–1218.
Wang, T., S.J. Zhang, S.L. Cao, et al. 2015. Protective effects of salubrinal on liver injury in rat models of brain death. Chinese medical journal 128: 1523–1528.
Ron, D., and P. Walter. 2007. Signal integration in the endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response. Nature reviews molecular cell biology 8: 519–529.
Mihailidou, C., C. Panagiotou, H. Kiaris, et al. 2016. Crosstalk between C/EBP homologous protein (CHOP) and glucocorticoid receptor in lung cancer. Molecular and cellular endocrinology 436: 211–223.
Hosoi, T., and K. Ozawa. 2010. Endoplasmic reticulum stress in disease: mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities. Clinical science (London, England) 118: 19–29.
Hotamisligil, G.S. 2010. Endoplasmic reticulum stress and the inflammatory basis of metabolic disease. Cell 140: 900–917.
Zhang, K., and R.J. Kaufman. 2008. From endoplasmic-reticulum stress to the inflammatory response. Nature 454: 455–462.
Zhang, S., S. Cao, T. Wang, et al. 2014. Modified brain death model for rats. Experimental and clinical transplantation 12: 469–473.
Avlonitis, V.S., C.H. Wigfield, J.A. Kirby, and J.H. Dark. 2005. The hemodynamic mechanisms of lung injury and systemic inflammatory response following brain death in the transplant donor. American journal of transplantation 5: 684–693.
Zweers, N., A.H. Petersen, J.A. van der Hoeven, et al. 2004. Donor brain death aggravates chronic rejection after lung transplantation in rats. Transplantation 78: 1251–1258.
Avlonitis, V.S., A.J. Fisher, J.A. Kirby, and J.H. Dark. 2003. Pulmonary transplantation: the role of brain death in donor lung injury. Transplantation 75: 1928–1933.
Clarke, H.J., J.E. Chambers, E. Liniker, and S.J. Marciniak. 2014. Endoplasmic reticulum stress in malignancy. Cancer Cell 25: 563–573.
Cnop, M., F. Foufelle, and L.A. Velloso. 2012. Endoplasmic reticulum stress, obesity and diabetes. Trends in molecular medicine 18: 59–68.
Doyle, K.M., D. Kennedy, A.M. Gorman, et al. 2011. Unfolded proteins and endoplasmic reticulum stress in neurodegenerative disorders. Journal of cellular and molecular medicine 15: 2025–2039.
Malhotra, D., R. Thimmulappa, N. Vij, et al. 2009. Heightened endoplasmic reticulum stress in the lungs of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: the role of Nrf2-regulated proteasomal activity. American journal of respiratory and critical care medicine 180: 1196–1207.
Korfei, M., C. Ruppert, P. Mahavadi, et al. 2008. Epithelial endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis in sporadic idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. American journal of respiratory and critical care medicine 178: 838–846.
Boyce, M., K.F. Bryant, C. Jousse, et al. 2005. A selective inhibitor of eIF2α dephosphorylation protects cells from ER stress. Science 307: 935–939.
Methippara, M., B. Mitrani, F.X. Schrader, et al. 2012. Salubrinal, an endoplasmic reticulum stress blocker, modulates sleep homeostasis and activation of sleep- and wake-regulatory neurons. Neuroscience 209: 108–118.
Engin, F., and G.S. Hotamisligil. 2010. Restoring endoplasmic reticulum function by chemical chaperones: An emerging therapeutic approach for metabolic diseases. Diabetes, obesity and metabolism 12 (Suppl 2): 108–115.
Kim, H.J., J.S. Jeong, S.R. Kim, et al. 2013. Inhibition of endoplasmic reticulum stress alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced lung inflammation through modulation of NF-kappaB/HIF-1α signaling pathway. Scientific Reports 3: 1142.
Mizukami, T., K. Orihashi, B. Herlambang, et al. 2010. Sodium 4-phenylbutyrate protects against spinal cord ischemia by inhibition of endoplasmic reticulum stress. Journal of vascular surgery 52: 1580–1586.
Srinivasan, K., and S.S. Sharma. 2011. Sodium phenylbutyrate ameliorates focal cerebral ischemic/reperfusion injury associated with comorbid type 2 diabetes by reducing endoplasmic reticulum stress and DNA fragmentation. Behavioural brain research 225: 110–116.
Hayden, M.S., A.P. West, and S. Ghosh. 2006. NF-kappaB and the immune response. Oncogene 25: 6758–6780.
Baldwin, A.S. Jr. 1996. The NF-κB and IκB proteins: new discoveries and insights. Annual review of immunology 14: 649–683.
Cahill, C.M., W. Zhu, E. Oziolor, et al. 2016. Differential expression of the activator protein 1 transcription factor regulates interleukin-1ss induction of interleukin 6 in the developing enterocyte. PloS One 11: e0145184.
Schmidt, D., B. Textor, O.T. Pein, et al. 2007. Critical role for NF-κB-induced JunB in VEGF regulation and tumor angiogenesis. The EMBO journal 26: 710–719.
Libermann, T.A., and D. Baltimore. 1990. Activation of interleukin-6 gene expression through the NF-kappa B transcription factor. Molecular and cellular biology 10: 2327–2334.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no.81571947) and the Scientific Research Fund of Henan Education Department (grant No. 16A320055).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, H., Zhang, J., Cao, S. et al. Inhibition of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Alleviates Lung Injury Induced by Brain Death. Inflammation 40, 1664–1671 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-017-0606-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-017-0606-5