Abstract
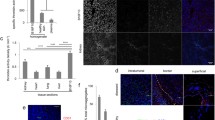
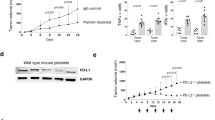
Platelet factor 4 (PF4) was the first discovered CXC chemokine and is found in platelet granules at very high concentration. Now, it is becoming increasingly evident that PF4 actively participates in inflammation and immune response. Recent paper demonstrated that PF4 limits the development and response of the Th17 cells and assisted in regulatory T cell development in transplantation. But, the immunoregulatory role of PF4 in tumor has little known and needs to be further investigated. In our current study, wild-type mice are inoculated with melanoma cell line B16-F10 (1 × 106/mouse) and treated with PF4. PF4 inhibits B16 tumor growth and decreases γδ cell infiltration. The expression of interleukin (IL)-17, IL-6, and p-signal transducer and activator of transcription-3 (Stat3) was markedly decreased with treatment of PF4 compared with control in vivo and in vitro. And, the suppressed tumor growth induced by PF4 is abolished by additional treatment of recombinant mouse IL (rmIL)-17. PF4 also induces suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 (SOCS3) upregulations, and PF4 fails to suppress expression of p-Stat3, IL-17, and IL-6 in cells transfected with SOCS3 short interfering RNA (siRNA). In conclusion, PF4 inhibits IL-17/Stat3 pathway via upregulation of SOCS3 expression and may contribute to suppressing tumor growth in murine models of melanoma.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lambert, M.P., L. Rauova, M. Bailey, M.C. Sola-Visner, M.A. Kowalska, and M. Poncz. 2007. Platelet factor 4 is a negative autocrine in vivo regulator of megakaryopoiesis: Clinical and therapeutic implications. Blood 110: 1153–1160.
Arepally, G.M., S. Kamei, K.S. Park, K. Kamei, Z.Q. Li, W. Liu, D.L. Siegel, W. Kisiel, D.B. Cines, and M. Poncz. 2000. Characterization of a murine monoclonal antibody that mimics heparin-induced thrombocytopenia antibodies. Blood 95: 1533–1540.
Ziporen, L., Z.Q. Li, K.S. Park, P. Sabnekar, W.Y. Liu, G. Arepally, Y. Shoenfeld, T. Kieber-Emmons, D.B. Cines, and M. Poncz. 1998. Defining an antigenic epitope on platelet factor 4 associated with heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Blood 92: 3250–3259.
Eslin, D.E., C. Zhang, K.J. Samuels, L. Rauova, L. Zhai, S. Niewiarowski, D.B. Cines, M. Poncz, and M.A. Kowalska. 2004. Transgenic mice studies demonstrate a role for platelet factor 4 in thrombosis: Dissociation between anticoagulant and antithrombotic effect of heparin. Blood 104: 3173–3180.
Aziz, K.A., J.C. Cawley, and M. Zuzel. 1995. Platelets prime PMN via released PF4: Mechanism of priming and synergy with GM-CSF. British Journal of Haematology 91: 846–853.
Engstad, C.S., K. Lia, O. Rekdal, J.O. Olsen, and B. Osterud. 1995. A novel biological effect of platelet factor 4 (PF4): Enhancement of LPS-induced tissue factor activity in monocytes. Journal of Leukocyte Biology 58: 575–581.
Sharpe, R.J., H.R. Byers, C.F. Scott, S.I. Bauer, and T.E. Maione. 1990. Growth inhibition of murine melanoma and human colon carcinoma by recombinant human platelet factor 4. Journal of the National Cancer Institute 82: 848–853.
Maione, T.E., G.S. Gray, A.J. Hunt, and R.J. Sharpe. 1991. Inhibition of tumor growth in mice by an analogue of platelet factor 4 that lacks affinity for heparin and retains potent angiostatic activity. Cancer Research 51: 2077–2083.
Kolber, D.L., T.L. Knisely, and T.E. Maione. 1995. Inhibition of development of murine melanoma lung metastases by systemic administration of recombinant platelet factor 4. Journal of the National Cancer Institute 87: 304–309.
Srivastava, K., I.A. Cockburn, A. Swaim, L.E. Thompson, A. Tripathi, C.A. Fletcher, E.M. Shirk, H. Sun, M.A. Kowalska, K. Fox-Talbot, et al. 2008. Platelet factor 4 mediates inflammation in experimental cerebral malaria. Cell Host & Microbe 4: 179–187.
Liu, C.Y., M. Battaglia, S.H. Lee, Q.H. Sun, R.H. Aster, and G.P. Visentin. 2005. Platelet factor 4 differentially modulates CD4 + CD25+ (regulatory) versus CD4 + CD25- (nonregulatory) T cells. Journal of Immunology 174: 2680–2686.
Shi, G., D.J. Field, K.A. Ko, S. Ture, K. Srivastava, S. Levy, M.A. Kowalska, M. Poncz, D.J. Fowell, and C.N. Morrell. 2014. Platelet factor 4 limits Th17 differentiation and cardiac allograft rejection. Journal of Clinical Investigation 124: 543–552.
Kim, H.K., H. Zhang, H. Li, T.T. Wu, S. Swisher, D. He, L. Wu, J. Xu, C.A. Elmets, M. Athar, et al. 2008. Slit2 inhibits growth and metastasis of fibrosarcoma and squamous cell carcinoma. Neoplasia 10: 1411–1420.
Liang, P., S.H. Cheng, C.K. Cheng, K.M. Lau, S.Y. Lin, E.Y. Chow, N.P. Chan, R.K. Ip, R.S. Wong, and M.H. Ng. 2013. Platelet factor 4 induces cell apoptosis by inhibition of STAT3 via up-regulation of SOCS3 expression in multiple myeloma. Haematologica 98: 288–295.
He, D., H. Li, N. Yusuf, C.A. Elmets, J. Li, J.D. Mountz, and H. Xu. 2010. IL-17 promotes tumor development through the induction of tumor promoting microenvironments at tumor sites and myeloid-derived suppressor cells. Journal of Immunology 184: 2281–2288.
Tang, Q., J. Li, H. Zhu, P. Li, Z. Zou, and Y. Xiao. 2013. Hmgb1-IL-23-IL-17-IL-6-Stat3 axis promotes tumor growth in murine models of melanoma. Mediators of Inflammation 2013: 713859.
Wormald, S., and D.J. Hilton. 2004. Inhibitors of cytokine signal transduction. Journal of Biological Chemistry 279: 821–824.
Pandey, M.K., B. Sung, and B.B. Aggarwal. 2010. Betulinic acid suppresses STAT3 activation pathway through induction of protein tyrosine phosphatase SHP-1 in human multiple myeloma cells. International Journal of Cancer 127: 282–292.
Gaffen, S.L. 2009. Structure and signalling in the IL-17 receptor family. Nature Reviews Immunology 9: 556–567.
He, D., L. Wu, H.K. Kim, H. Li, C.A. Elmets, and H. Xu. 2006. CD8+ IL-17-producing T cells are important in effector functions for the elicitation of contact hypersensitivity responses. Journal of Immunology 177: 6852–6858.
Kolls, J.K., and A. Linden. 2004. Interleukin-17 family members and inflammation. Immunity 21: 467–476.
Martin-Orozco, N., P. Muranski, Y. Chung, X.O. Yang, T. Yamazaki, S. Lu, P. Hwu, N.P. Restifo, W.W. Overwijk, and C. Dong. 2009. T helper 17 cells promote cytotoxic T cell activation in tumor immunity. Immunity 31: 787–798.
Wakita, D., K. Sumida, Y. Iwakura, H. Nishikawa, T. Ohkuri, K. Chamoto, H. Kitamura, and T. Nishimura. 2010. Tumor-infiltrating IL-17-producing gammadelta T cells support the progression of tumor by promoting angiogenesis. European Journal of Immunology 40: 1927–1937.
Jarnicki, A., T. Putoczki, and M. Ernst. 2010. Stat3: Linking inflammation to epithelial cancer—more than a “gutˮ feeling? Cell Div 5: 14.
Catlett-Falcone, R., T.H. Landowski, M.M. Oshiro, J. Turkson, A. Levitzki, R. Savino, G. Ciliberto, L. Moscinski, J.L. Fernandez-Luna, G. Nunez, et al. 1999. Constitutive activation of Stat3 signaling confers resistance to apoptosis in human U266 myeloma cells. Immunity 10: 105–115.
Rebouissou, S., M. Amessou, G. Couchy, K. Poussin, S. Imbeaud, C. Pilati, T. Izard, C. Balabaud, P. Bioulac-Sage, and J. Zucman-Rossi. 2009. Frequent in-frame somatic deletions activate gp130 in inflammatory hepatocellular tumours. Nature 457: 200–204.
Yu, H., and R. Jove. 2004. The STATs of cancer—new molecular targets come of age. Nature Reviews Cancer 4: 97–105.
Wang, L., T. Yi, M. Kortylewski, D.M. Pardoll, D. Zeng, and H. Yu. 2009. IL-17 can promote tumor growth through an IL-6-Stat3 signaling pathway. Journal of Experimental Medicine 206: 1457–1464.
Endo, T.A., M. Masuhara, M. Yokouchi, R. Suzuki, H. Sakamoto, K. Mitsui, A. Matsumoto, S. Tanimura, M. Ohtsubo, H. Misawa, et al. 1997. A new protein containing an SH2 domain that inhibits JAK kinases. Nature 387: 921–924.
Yoshimura, A., T. Naka, and M. Kubo. 2007. SOCS proteins, cytokine signalling and immune regulation. Nature Reviews Immunology 7: 454–465.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Bo Liu and Shanshan Fang contributed equally to this paper.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fang, S., Liu, B., Sun, Q. et al. Platelet Factor 4 Inhibits IL-17/Stat3 Pathway via Upregulation of SOCS3 Expression in Melanoma. Inflammation 37, 1744–1750 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-014-9903-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-014-9903-4