Abstract
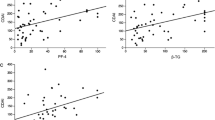
The predictors for the development of cardiovascular diseases and peripheral arterial diseases in patients with systemic sclerosis (SSc) were not clearly established, and there is no specific study conducted to investigate the mean platelet volume (MPV) levels in SSc patients. Therefore, this study evaluates the MPV levels in SSc and possible relationship between SSc, its clinical features and activity/severity scores, and MPV. In total, 76 SSc patients (67 women and 9 men, mean age 50.44 ± 13.21 years) diagnosed according to the classification criteria of the American College of Rheumatology and 45 healthy volunteers were enrolled into study. Data relating to anamnesis, physical examination, MPV, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, C-reactive protein levels, electrocardiography, echocardiography, high-resolution computerized tomography findings, complaints, and treatment processes were recorded into the database. Of the total cases, 17 had (22.3 %) cardiac involvement, 45 had gastrointestinal involvement (59.2 %), 47 had (61.8 %) lung involvement, 31 (32 %) had finger flexion deformity, and 27 (35.5 %) had digital ulcers at the fingertips. The mean MPV levels of SSc patients were significantly higher than those of the control group (p = 0.008). The mean MPV levels of SSc patients with cardiac involvement, digital ulcers, and gangrene presence were significantly high, and lower in Ilomedin-receiving patients than in the Ilomedin naives (p < 0.05). A negative relationship was discovered between the mean MPV levels, Valentini score, and Disease Severity Index of the patients with systemic sclerosis (p = 0.006, r = −0.310; p = 0.047, r = −0.229). MPV levels were significantly elevated in SSc patients and they were negatively correlated with disease activity scores. Increased MPV levels would be a predictive marker in the diagnosis of macrovascular and microvascular disease involvement in SSc patients.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
LeRoy, E.C. 1996. Systemic sclerosis. A vascular perspective. Rheumatic Diseases Clinics of North America 22: 675–694.
Kahaleh, M.B., and E.C. Leroy. 1999. Autoimmunity and vascular involvement in systemic sclerosis (SSc). Autoimmunity 31: 195–214.
Kahaleh, M.B. 2004. Vascular involvement in systemic sclerosis (SSc). Clinical and Experimental Rheumatology 22: 19–23.
Gear, A.R., and D. Camerini. 2003. Platelet chemokines and chemokine receptors: Linking hemostasis, inflammation, and host defense. Microcirculation 10: 335–350.
Weyrich, A.S., S. Lindemann, and G.A. Zimmerman. 2003. The evolving role of platelets in inflammation. Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis 1: 1897–1905.
Martin, J.F., T. Shaw, J. Heggie, and D.G. Penington. 1983. Measurement of the density of human platelets and its relationship to volume. British Journal of Haematology 54: 337–352.
Martin, J.F., P.M.W. Bath, and M.L. Burr. 1991. Influence of platelet size on outcome after myocardial infarction. Lancet 338: 1409–1411.
Berger, J.S., L.H. Eraso, D. Xie, D. Sha, and E.R. Mohler 3rd. 2010. Mean platelet volume and prevalence of peripheral artery disease, the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 1999–2004. Atherosclerosis 213(2): 586–591.
Pattanaik, D., M. Brown, and A.E. Postlethwaite. 2011. Vascular involvement in systemic sclerosis (scleroderma). Journal of Inflammation Research 4: 105–125.
Friedhoff, L.T., J.R. Seibold, H.C. Kim, and K.S. Simester. 1984. Serotonin induced platelet aggregation in systemic sclerosis. Clinical and Experimental Rheumatology 2: 119–123.
Postlethwaite, A.E., and T.M. Chiang. 2007. Platelet contributions to the pathogenesis of systemic sclerosis. Current Opinion in Rheumatology 19: 574–579.
Masi, A.T., T.A. Medsger, G.P. Rodnan, et al. 1980. Preliminary criteria for the classification of systemic sclerosis. Arthritis and Rheumatism 23: 581–590.
Clements, P., P. Lachenbruch, J. Seibold, et al. 1995. Inter and intraobserver variability of total skin thickness score (modified Rodnan TSS) in systemic sclerosis. Journal of Rheumatology 22: 1281–1285.
Valentini, G., A. Della Rossa, S. Bombardieri, et al. 2001. European multicentre study to define disease activity criteria for systemic sclerosis. II. Identification of disease activity variables and development of preliminary activity indexes. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 60: 592–598.
Medsger Jr., T.A., A.J. Silman, V.D. Steen, et al. 1999. A disease severity scale for systemic sclerosis: Development and testing. Journal of Rheumatology 26: 2159–2167.
Gawaz, M. 2004. Role of platelets in coronary thrombosis and reperfusion of ischemic myocardium. Cardiovascular Research 61: 498–511.
Anitua, E., I. Andia, B. Ardanza, P. Nurden, and A.T. Nurden. 2004. Autologous platelets as a source of proteins for healing and tissue regeneration. Thrombosis and Haemostasis 91: 4–15.
Villeneuve, J., A. Block, M.C. Le Bousse-Kerdiles, S. Lepreux, P. Nurden, J. Ripoche, et al. 2009. Tissue inhibitors of matrix metalloproteinases in platelets and megakaryocytes: A novel organization for these secreted proteins. Experimental Hematology 37: 849–856.
Yanaba, K., K. Takehara, and S. Sato. 2004. Serum concentrations of soluble P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1 are increased in patients with systemic sclerosis: Association with lower frequency of pulmonary fibrosis. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 63: 583–587.
Frenette, P.S., C.V. Denis, L. Weiss, K. Jurk, S. Subbarao, B. Kehrel, et al. 2000. P-Selectin glycoprotein ligand 1 (PSGL-1) is expressed on platelets and can mediate platelet-endothelial interactions in vivo. Journal of Experimental Medicine 191: 1413–1422.
Kasper, B., and F. Petersen. 2011. Molecular pathways of platelet factor 4/CXCL4 signaling. European Journal of Cell Biology 90: 521–526.
Maeda, M., H. Kachi, and S. Mori. 1998. Ultrastructural observation of platelets from patients with progressive systemic sclerosis (PSS). Journal of Dermatology 25: 222–230.
Allanore, Y., D. Borderie, C. Meune, H. Lemarechal, S. Weber, O.G. Ekindjian, et al. 2005. Increased plasma soluble CD40 ligand concentrations in systemic sclerosis and association with pulmonary arterial hypertension and digital ulcers. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 64: 481–483.
Komura, K., S. Sato, M. Hasegawa, M. Fujimoto, and K. Takehara. 2004. Elevated circulating CD40L concentrations in patients with systemic sclerosis. Journal of Rheumatology 31: 514–519.
Herrick, A.L., K. Illingworth, A. Blann, C.R. Hay, S. Hollis, and M.I. Jayson. 1996. Von Willebrand factor, thrombomodulin, thromboxane, beta-thromboglobulin and markers of fibrinolysis in primary Raynaud's phenomenon and systemic sclerosis. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 55: 122–127.
Guiducci, S., J.H. Distler, A. Jungel, D. Huscher, L.C. Huber, B.A. Michel, et al. 2008. The relationship between plasma microparticles and disease manifestations in patients with systemic sclerosis. Arthritis and Rheumatism 58: 2845–2853.
Fonseca, C., D. Abraham, and M. Ponticos. 2009. Neuronal regulators and vascular dysfunction in Raynaud's phenomenon and systemic sclerosis. Current Vascular Pharmacology 7: 34–39.
Silveri, F., R. De Angelis, A. Poggi, S. Muti, G. Bonapace, F. Argentati, et al. 2001. Relative roles of endothelial cell damage and platelet activation in primary Raynaud's phenomenon (RP) and RP secondary to systemic sclerosis. Scandinavian Journal of Rheumatology 30: 290–296.
Polidoro, L., R. Barnabei, P. Giorgini, L. Petrazzi, C. Ferri, and G. Properzi. 2012. Platelet activation in patients with the Raynaud's Phenomenon. Internal Medicine Journal 42: 531–535.
Zaldivar, M.M., K. Pauels, P. von Hundelshausen, M.L. Berres, P. Schmitz, J. Bornemann, et al. 2010. CXC chemokine ligand 4 (Cxcl4) is a platelet-derived mediator of experimental liver fibrosis. Hepatology 51: 1345–1353.
Dees, C., A. Akhmetshina, P. Zerr, N. Reich, K. Palumbo, A. Horn, et al. 2011. Platelet-derived serotonin links vascular disease and tissue fibrosis. Journal of Experimental Medicine 208: 961–972.
Abou-Raya, A., S. Abou-Raya, and M. Helmii. 2008. Statins: Potentially useful in therapy of systemic sclerosis-related Raynaud's phenomenon and digital ulcers. Journal of Rheumatology 35: 1801–1808.
Matucci-Cerinic, M., and J.R. Seibold. 2008. Digital ulcers and outcomes assessment in scleroderma. Rheumatology (Oxford, England) 47: 46–47.
Hak, A.E., E.W. Karlson, D. Feskanich, M.J. Stampfer, and K.H. Costenbader. 2009. Systemic lupus erythematosus and the risk of cardiovascular disease: Results from the nurses' health study. Arthritis and Rheumatism 61: 1396–1402.
Balbaloglu O, Korkmaz M, Yolcu S, Karaaslan F, Beceren NG. 2013. Evaluation of mean platelet volume (MPV) levels in patients with synovitis associated with knee osteoarthritis. Platelets. doi:10.3109/09537104.2013.776162
Kisacik, B., A. Tufan, U. Kalyoncu, O. Karadag, A. Akdogan, M.A. Ozturk, S. Kiraz, I. Ertenli, and M. Calguneri. 2008. Mean platelet volume (MPV) as an inflammatory marker in ankylosing spondylitis and rheumatoid arthritis. Joint, Bone, Spine 75: 291–294.
Gasparyan, A.Y., A. Sandoo, A. Stavropoulos-Kalinoglou, and G.D. Kitas. 2010. Mean platelet volume in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: The effect of anti-TNF-α therapy. Rheumatology International 30: 1125–1129.
Stürzebecher, C.S. 1987. Effects of iloprost on platelet activation in vitro. In Prostacyclin and its stable analogue iloprost, ed. R.J. Gryglewski and G. Stock, 39–45. Berlin: Springer.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Soydinc, S., Turkbeyler, I.H., Pehlivan, Y. et al. Mean Platelet Volume Seems To Be a Valuable Marker in Patients with Systemic Sclerosis. Inflammation 37, 100–106 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-013-9716-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-013-9716-x