Abstract
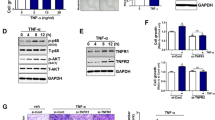
The role of Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) in immune cells is well characterized, but its biological properties in bladder epithelial cells (BECs), especially reciprocal crosstalk between mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase pathway and signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT)3-mediated signal transduction elicited by TLR4 have not been demonstrated so far. The present studies were to demonstrate the signal transduction and inflammatory cytokine response elicited through activation of TLR4 in BECs with a special focus on the crosstalk between the MAPK-pathway and STAT3-mediated signals and its regulatory relevance for the inflammatory response towards lipopolysaccharide (LPS). We selected human bladder cancer T24 cell line in the present study and examined its expression of TLR4 by reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and immunohistochemistry. The expression of p38, extracellular signal regulated kinase (ERK), c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase (JNK), and STAT3 were performed by RT-PCR, quantitative PCR, and Western blotting. Signal transduction was analyzed by Western blotting. Interleukin-6 (IL-6) and interleukin-10 (IL-10) secretion in culture supernatants were tested by human enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kit. BECs of rat infection in vivo model and patients with cystitis glandularis (CG) were analyzed as described above. Our study demonstrated that TLR4 was significantly upregulated following LPS treatment, with the maximum mRNA expression occurring at 4 h after stimulation. Activation of TLR4 signaling by LPS resulted in phosphorylation of MAPK and STAT pathways and upregulation of IL-10 in dose- and time-dependent manners in T24 cells. Pretreatment of cells with SB203580 (inhibitor of p38) and SP600125 (inhibitor of JNK) attenuated LPS-induced IL-10 expression, whereas it markedly inhibited the STAT3 expression. IL-10 mRNA expression was increased in inflamed lesions compared to noninflamed tissue in rats and patients with CG disease. Our results demonstrate that activation of TLR4 signaling in BECs induces IL-10 expression via activation of p38 and JNK, and the activation of STAT-3 was upregulated. Our data indicated that the reciprocal crosstalk between the MAPK pathway and STAT3-mediated signal transduction forms a critical axis successively activated by LPS in BECs.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BEC:
-
Bladder epithelial cell
- BSA:
-
Bovine serum albumin
- CG:
-
Cystitis glandularis
- ERK:
-
Extracellular signal-regulated kinase
- ELISA:
-
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
- GAPDH:
-
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase
- IL:
-
Interleukin
- JNK:
-
c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase
- LPS:
-
Lipopolysaccharide
- MAP kinase:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase
- NF-κB:
-
Nuclear factor-κB
- PCR:
-
Polymerase chain reaction
- STAT:
-
Signal transducer and activator of transcription
- TLR:
-
Toll-like receptor
References
Akira, S., S. Uematsu, and O. Takeuchi. 2006. Pathogen recognition and innate immunity [J]. Cell 124(4): 783–801.
Kawai, T., and S. Akira. 2006. TLR signaling [J]. Cell Death and Differentiation 13(5): 816–825.
Cavalli, V., F. Vilbois, M. Corti, et al. 2001. The stress-induced MAP kinase p38 regulates endocytic trafficking via the GDI:Rab5 complex [J]. Molecular Cell 7(2): 421–432.
Bhattacharya, M., N. Ojha, S. Solanki, et al. 2006. IL-6 and IL-12 specifically regulate the expression of Rab5 and Rab7 via distinct signaling pathways [J]. EMBO Journal 25(12): 2878–2888.
Bode, J.G., J. Schweigart, J. Kehrmann, et al. 2003. TNF-alpha induces tyrosine phosphorylation and recruitment of the Src homology protein-tyrosine phosphatase 2 to the gp130 signal-transducing subunit of the IL-6 receptor complex [J]. Journal of Immunology 171(1): 257–266.
Schilling, J.D., S.M. Martin, D.A. Hunstad, et al. 2003. CD14- and Toll-like receptor-dependent activation of bladder epithelial cells by lipopolysaccharide and type 1 piliated Escherichia coli [J]. Infection and Immunity 71(3): 1470–1480.
Otto, G., J. Braconier, A. Andreasson, et al. 1999. Interleukin-6 and disease severity in patients with bacteremic and nonbacteremic febrile urinary tract infection [J]. Journal of Infectious Diseases 179(1): 172–179.
Huang, B., J. Zhao, H. Li, et al. 2005. Toll-like receptors on tumor cells facilitate evasion of immune surveillance [J]. Cancer Research 65(12): 5009–5014.
Song, J., M.J. Duncan, G. Li, et al. 2007. A novel TLR4-mediated signaling pathway leading to IL-6 responses in human bladder epithelial cells [J]. PLoS Pathogens 3(4): e60.
Poltorak, A., P. Ricciardi-Castagnoli, S. Citterio, et al. 2000. Physical contact between lipopolysaccharide and toll-like receptor 4 revealed by genetic complementation [J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97(5): 2163–2167.
Bryan, R.T., J.H. Nicholls, R.F. Harrison, et al. 2003. The role of beta-catenin signaling in the malignant potential of cystitis glandularis [J]. Journal of Urology 170(5): 1892–1896.
Lin, H.Y., W.J. Wu, M.Y. Jang, et al. 2001. Cystitis glandularis mimics bladder cancer—three case reports and literature review [J]. The Kaohsiung Journal of Medical Sciences 17(2): 102–106.
Liang, F.X., M.C. Bosland, H. Huang, et al. 2005. Cellular basis of urothelial squamous metaplasia: roles of lineage heterogeneity and cell replacement [J]. The Journal of Cell Biology 171(5): 835–844.
Qian, Y., J. Deng, L. Geng, et al. 2008. TLR4 signaling induces B7-H1 expression through MAPK pathways in bladder cancer cells [J]. Cancer Investigation 26(8): 816–821.
Qian, Y., J. Deng, H. Xie, et al. 2009. Regulation of TLR4-induced IL-6 response in bladder cancer cells by opposing actions of MAPK and PI3K signaling [J]. Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology 135(3): 379–386.
Kacar, F., I. Meteoğlu, H. Yasa, et al. 2007. Helicobacter pylori-induced changes in the gastric mucosa are associated with mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) activation [J]. Applied Immunohistochemistry & Molecular Morphology 15(2): 224–228.
Chen, C.L., L. Cen, J. Kohout, et al. 2008. Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 activation is associated with bladder cancer cell growth and survival [J]. Molecular Cancer 7: 78.
Verstrepen, L., T. Bekaert, T.L. Chau, et al. 2008. TLR-4, IL-1R and TNF-R signaling to NF-kappaB: variations on a common theme [J]. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences 65(19): 2964–2978.
Bode, J.G., C. Ehlting, and D. Häussinger. 2012. The macrophage response towards LPS and its control through the p38(MAPK)–STAT3 axis [J]. Cellular Signalling 24(6): 1185–1194.
Lang, R., D. Patel, J.J. Morris, et al. 2002. Shaping gene expression in activated and resting primary macrophages by IL-10 [J]. Journal of Immunology 169(5): 2253–2263.
Chang, E.Y., B. Guo, S.E. Doyle, et al. 2007. Cutting edge: involvement of the type I IFN production and signaling pathway in lipopolysaccharide-induced IL-10 production [J]. Journal of Immunology 178(11): 6705–6709.
Miggin, S.M., E. Pålsson-McDermott, A. Dunne, et al. 2007. NF-kappaB activation by the Toll-IL-1 receptor domain protein MyD88 adapter-like is regulated by caspase-1 [J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104(9): 3372–3377.
Wen, Z., Z. Zhong, and J.E. Darnell Jr. 1995. Maximal activation of transcription by Stat1 and Stat3 requires both tyrosine and serine phosphorylation [J]. Cell 82(2): 241–250.
David, M., E. Petricoin 3rd, C. Benjamin, et al. 1995. Requirement for MAP kinase (ERK2) activity in interferon alpha- and interferon beta-stimulated gene expression through STAT proteins [J]. Science 269(5231): 1721–1723.
Kodama, H., K. Fukuda, J. Pan, et al. 2000. Significance of ERK cascade compared with JAK/STAT and PI3-K pathway in gp130-mediated cardiac hypertrophy [J]. American Journal of Physiology - Heart and Circulatory Physiology 279(4): H1635–H1644.
Beutler, B., K. Hoebe, X. Du, et al. 2003. How we detect microbes and respond to them: the Toll-like receptors and their transducers [J]. Journal of Leukocyte Biology 74(4): 479–485.
Medvedev, A.E., I. Sabroe, J.D. Hasday, et al. 2006. Tolerance to microbial TLR ligands: molecular mechanisms and relevance to disease [J]. Journal of Endotoxin Research 12(3): 133–150.
Acknowledgments
This project was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (30900368) and by the Ministry of Education research fund for the doctoral program of China (20092104120011).
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ying, H., Da, L., Yu-xiu, S. et al. TLR4 Mediates MAPK–STAT3 Axis Activation in Bladder Epithelial Cells. Inflammation 36, 1064–1074 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-013-9638-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-013-9638-7