Abstract
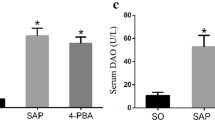
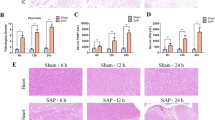
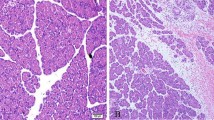
This study aimed to investigate the protective effect of emodin on endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress in rats with severe acute pancreatitis (SAP) and the underlying molecular mechanism. Sprague–Dawley male rats were randomly divided into sham operation group, SAP model group, and emodin treatment group. SAP was constructed through injecting sodium taurocholate into pancreatic and biliary duct in rats. Half an hour before establishing the animal model, emodin or sodium carboxymethylcellulose was intragastrically administrated to the rats in respective group. Rats were killed at 3, 6, and 12 h postdisease induction. The amylase, tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) levels in serum, pancreatic histopathology, acinar ER ultrastructure, protein expression of Bip, IRE1α,TRAF2, ASK1, p-JNK, and p-p38 MAPK in pancreas were examined. Sodium taurocholate induced pancreatic injury and ER lumen dilated in exocrine pancreas in rats at 3-, 6-, and 12-h time points. ER stress transducers Bip, IRE1α, and their downstream molecules TRAF2, ASK1 in pancreatitis were upregulated. Furthermore, phosphorylation of JNK and p38MAPK in pancreas was increased, which induced high expression level of inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α and IL-6. Treatment with emodin obviously ameliorated pancreatic injury and decreased the release of amylase and inflammatory cytokines. Further studies showed that emodin significantly decreased the expression of Bip, IRE1α, TRAF2, and ASK1, inhibited phosphorylation of JNK and p38 MAPK in pancreas in rats at all time points. Emodin could reduce pancreatic injury and restrain inflammatory reaction in SAP rats partly via inhibiting ER stress transducers IRE1α and its downstream molecules.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papachristou, G.I. 2008. Prediction of severe acute pancreatitis: current knowledge and novel insights. World Journal of Gastroenterology 14(41): 6273–6275 [ PMID:19009638].
Morrow, L.E., V. Gogineni, and M.A. Malesker. 2012. Probiotic, prebiotic, and synbiotic use in critically ill patients. Current Opinion in Critical Care 18(2): 186–91.
Talukdar, R., and Vege S. Swaroop. 2011. Early management of severe acute pancreatitis. Current Gastroenterology Reports 13(2): 123–130.
Kylanpaa, M.L., H. Repo, and P.A. Puolakkainen. 2010. Inflammation and immunosuppression in severe acute pancreatitis. World Journal of Gastroenterology 16(23): 2867–2872.
Gorelick, F.S., and E. Thrower. 2009. The acinar cell and early pancreatitis responses. Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology 7(11): S10–4.
Kubisch, C.H., and C.D. Logsdon. 2008. Endoplasmic reticulum stress and the pancreatic acinar cell. Expert Review of Gastroenterology & Hepatology 2(2): 249–260.
Zeng Y, Wang X, Zhang W, Wu K, Ma J. 2012. Hypertriglyceridemia aggravates ERS and pathogenesis of acute pancreatitis. Hepatogastroenterology 59(119). [PMID:22389298]
Gerasimenko, J., P. Ferdek, L. Fischer, A.S. Gukovskaya, and S.J. Pandol. 2010. Inhibitors of Bcl-2 protein family deplete ER Ca2+ stores in pancreatic acinar cells. Pflügers Archiv 460(5): 891–900.
Pavitt GD, Ron D. 201.2 New insights into translational regulation in the endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 4(6). [PMID:22535228]
Sendler M, Dummer A, Weiss FU, Krüger B, Wartmann T, Scharffetter-Kochanek K, van Rooijen N, Malla SR, Aghdassi A, Halangk W, Lerch MM, Mayerle J. 2013. Tumour necrosis factor a secretion induces protease activation and acinar cell necrosis in acute experimental pancreatitis in mice. Gut 62:430–439 [PMID:22490516]
Leppa, S., and D. Bohmann. 1999. Diverse functions of JNK signaling and c-Jun in stress response and apoptosis. Oncogene 18(45): 6158–6162.
Maguire, J.A., S. Mulugeta, and M.F. Beers. 2011. Endoplasmic reticulum stress induced by surfactant protein C Brichos mutants promotes proinflammatory signaling by epithelial cells. American Journal of Respiratory Cell and Molecular Biology 44(3): 404–414.
Kim, S.M., M.J. Chung, T.J. Ha, H.N. Choi, S.J. Jang, S.O. Kim, M.H. Chun, S.I. Do, Y.K. Choo, and Y.I. Park. 2012. Neuroprotective effects of black soybean anthocyanins via inactivation of ASK1–JNK/p38 pathways and mobilization of cellular sialic acids. Life Sciences 90(21): 874–882.
Wang, G., B. Sun, Y. Gao, Q.H. Meng, and H.C. Jiang. 2007. The effect of emodin-assisted early enteral nutrition on severe acute pancreatitis and secondary hepatic injury. Mediators of Inflammation 16: 1–9.
Li, Z., X. Xia, S. Zhang, A. Zhang, W. Bo, and R. Zhou. 2009. Up-regulation of Toll-like receptor 4 was suppressed by emodin and baicalin in the setting of acute pancreatitis. Biomedicine and Pharmacotherapy 63(2): 120–128.
Xia, X.M., B.K. Li, S.M. Xing, and H.L. Ruan. 2012. Emodin promoted pancreatic claudin-5 and occluding expression in experimental acute pancreatitis rats. World Journal of Gastroenterology 18(17): 2132–2139.
Zhang, X.P., Z.F. Li, X.G. Liu, et al. 2005. Effects of emodin and baicalein on rats with severe acute pancreatitis. World Journal of Gastroenterology 11(14): 2095–2100 [ PMID:15810074].
Chen, H., W.T. Wei, Y.F. Guo, and A. Liu. 2011. Enhanced effect of gemcitabine by emodin against pancreatic cancer in vivo via cytochrome C-regulated apoptosis. Oncology Reports 25(5): 1253–1261.
Chen, P., L. Huang, Y. Zhang, M. Qiao, and Y. Yuan. 2010. SiRNA-mediated PIAS1 silencing promotes inflammatory response and leads to injury of cerulein-stimulated pancreatic acinar cells via regulation of the P38MAPK signaling pathway. International Journal of Molecular Medicine 26(4): 619–626.
Liu, M., L. Shi, M. Chen, S. Chen, and X. Zou. 2012. Effects of c-Jun N-terminal kinase signaling pathway on severe acute pancreatitis-associated lung injury. Pancreas 41(3): 358–366.
Paran, H., A. Mayo, D. Kidron, G. Sivak, T. Reshef, T. Vider, O. Ziv, and U. Freun. 2000. Experimental acute necrotising pancreatitis: evaluation and characterisation of a model of intraparenchymal injection of sodium taurocholate in rats. European Journal of Surgery 166(11): 894–898.
Kusske, A.M., A.J. Rongione, S.W. Ashley, D.W. McFadden, and H.A. Reber. 1996. Interleukin-10 prevents death in lethal necrotizing pancreatitis in mice. Surgery 120(2): 284–288.
Kubisch, M., H. Constanze, and M.D. Sans. 2006. Early activation of endoplasmic reticulum stress is associated with arginine-induced acute pancreatitis. American Journal of Physiology - Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology 291(2): 238–245.
Kubisch, C.H., and C.D. Logsdon. 2007. Secretagogues differentially activate endoplasmic reticulum stress responses in pancreatic acinar cells. American Journal of Physiology - Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology 292(6): G1804–12.
Seyhun, E., A. Malo, C. Schafer, C.A. Moskaluk, R.T. Hoffmann, B. Goke, and C.H. Kubisch. 2011. Tauroursodeoxycholic acid reduces endoplasmic reticulum stress, acinar cell damage, and systemic inflammation in acute pancreatitis. American Journal of Physiology—Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology 301(5): G773–82.
Szmola, R., and M. Sahin-Toth. 2010. Pancreatitis-associated chymotrypsinogen C (CTRC) mutant elicits endoplasmic reticulum stress in pancreatic acinar cells. Gut 59(3): 365–72.
Malo, A., B. Kruger, E. Seyhun, C. Schafer, R.T. Hoffmann, B. Goke, and C.H. Kubisch. 2010. Tauroursodeoxycholic acid reduces endoplasmic reticulum stress, trypsin activation, and acinar cell apoptosis while increasing secretion in rat pancreatic acini. American Journal of Physiology - Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology 299(4): G877–86.
Ye, R., O.A. Mareninova, and E. Barron. 2010. Grp78 heterozygosity regulates chaperone balance in exocrine pancreas with differential response to cerulein-induced acute pancreatitis. American Journal of Pathology 177(6): 2827–2836.
Hetz, C., and L.H. Glimcher. 2009. Fine-tuning of the unfolded protein response: assembling the IRE1αalpha interactome. Molecular Cell 35(5): 551–561.
Liu, C.Y., M. Schroder, and R.J. Kaufman. 2000. Ligand-independent dimerization activates the stress response kinases IRE1 and PERK in the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum. Journal of Biological Chemistry 275(32): 24881–24885.
Urano, F., X. Wang, A. Bertolotti, Y. Zhang, P. Chung, H.P. Harding, and D. Ron. 2000. Coupling of stress in the ER to activation of JNK protein kinases by transmembrane protein kinase IRE1. Science 287(5453): 664–666.
Nishitoh, H., A. Matsuzawa, K. Tobiume, K. Saegusa, K. Takeda, K. Inoue, S. Hori, A. Kakizuka, and H. Ichijo. 2002. ASK1 is essential for endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced neuronal cell death triggered by expanded polyglutamine repeats. Genes & Development 16(11): 1345–1355.
Nguyen, D.T., S. Kebache, A. Fazel, H.N. Wong, S. Jenna, A. Emadali, E.H. Lee, J.J. Bergeron, R.J. Kaufman, L. Larose, and E. Chevet. 2004. Nck-dependent activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase-1 and regulation of cell survival during endoplasmic reticulum stress. Molecular Biology of the Cell 15(9): 4248–4260.
Hu, P., Z. Han, A.D. Couvillon, R.J. Kaufman, and J.H. Exton. 2006. Autocrine tumor necrosis factor alpha links endoplasmic reticulum stress to the membrane death receptor pathway through IRE1alphamediated NF-kappaB activation and down-regulation of TRAF2 expression. Molecular and Cellular Biology 26(1): 3071–3084.
Kanda, H., and M. Miura. 2004. Regulatory roles of JNK in programmed cell death. J Biochem (Tokyo). 136(8): 1–6.
Mauro, C., E. Crescenzi, R. De Mattia, F. Pacifico, S. Mellone, S. Salzano, C. de Luca, L. D’Adamio, G. Palumbo, S. Formisano, P. Vito, and A. Leonardi. 2006. Central role of the scaffold protein tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 2 in regulating endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis. Journal of Biological Chemistry 281(5): 2631–2638.
Kim, I., C.W. Shu, W. Xu, C.W. Shiau, D. Grant, S. Vasile, N.D. Cosford, and J.C. Reed. 2009. Chemical biology investigation of cell death pathways activated by endoplasmic reticulum stress reveals cytoprotective modulators of ASK1. Journal of Biological Chemistry 284(3): 1593–1603.
Williard, D.E., E. Twait, Z. Yuan, et al. 2010. Nuclear factor kappa B-dependent gene transcription in cholecystokinin- and tumor necrosis factor-alpha-stimulated isolated acinar cells is regulated by p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase. American Journal of Surgery 200(2): 283–290.
Twait, E., D.E. Williard, and I. Samuel. 2010. Dominant negative p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase expression inhibits NF-kappaB activation in AR42J cells. Pancreatology 10(2): 119–128.
Yun, S.W., G.S. Bae, M.S. Kim, K.C. Park, B.S. Koo, B.J. Kim, T.H. Kim, S.W. Seo, Y.K. Shin, S.H. Lee, H.J. Song, and S.J. Park. 2011. Melittin inhibits cerulein-induced acute pancreatitis via inhibition of the JNK pathway. International Immunopharmacology 11(12): 2062–2072.
Murr, M.M., J. Yang, A. Fier, S.F. Gallagher, G. Carter, W.R. Gower Jr., and J.G. Norman. 2003. Regulation of Kupffer cell TNF gene expression during experimental acute pancreatitis: the role of p38-MAPK, ERK1/2, SAPK/JNK, and NF-kappaB. Journal of Gastrointestinal Surgery 7(1): 20–25.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Open Project of National First-Class Key Discipline for Science of Chinese Materia Medica, Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine (2011ZYX4-006), National Natural Science Foundation of China (81073022 and 81270514), and Science and Technology Foundation of Jiangsu Traditional Chinese Medicine Administration (LZ11190).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, L., Cai, B., Zheng, S. et al. Effect of Emodin on Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Rats with Severe Acute Pancreatitis. Inflammation 36, 1020–1029 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-013-9634-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-013-9634-y