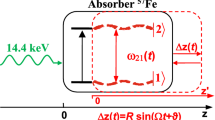
Abstract
The sub-nanometer amplitudes of the samples vibrated with high frequencies were measured by 57Fe Mössbauer spectroscopy using a nuclear Bragg monochromator and focusing optics. The Mössbauer spectra of the vibrated single-line absorber showed comb-like absorption peaks, and the amplitudes of the absorbers were determined by the sideband intensities. We used the stainless-steel foil glued on the quartz crystal or the polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) film as samples. The mean value and the variance of the amplitude in sub-nanometer order were obtained for the irradiated area of 100 μm diameter in the sample. We could obtain the sub-nanometer amplitude with almost zero variance, using the 57Fe synchrotron Mössbauer source and focusing optics for the PVDF film. The resonant absorber vibrated with high frequency and amplitude without variance is useful for the control of gamma rays. This work will advance X-ray quantum optics and quantum technology applications using a single gamma photon.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Availability of data and materials is not applicable to this study as no new data were created or analyzed in this study.
References
Adams, B.W., Buth, C., Cavaletto, S.M., Evers, J., Harman, Z., Keitel, C.H., Pálffy, A., Picón, A., Röhlsberger, R., Rostovsev, Y.: Tamasaku.: X-ray quantum optics. J. Mod. Opt. 60, 2 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1080/09500340.2012.752113
Vagizov, F., Antonov, V., Radeonyshev, Y.V., Shakhmuratov, R.N., Kocharovskaya, O.: Coherent control of the waveforms of recoilless γ-ray photons. Nature. 508, 80 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature13018
Röhlsberger, R., Wille, H.-C., Schlage, K., Sahoo, B.: Electromagnetically induced transparency with resonant nuclei in a cavity. Nature. 482, 199 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature10741
Heeg, K.P., Kaldum, A., Strohm, C., Reiser, P., Ott, C., Subramanian, T., Lentrodt, D., Haber, J., Wille, H.-C., Goerttler, S., Rüffer, T., Keitel, C.H., Röhlsberger, R., Pferifer, T., Evers, J.: Spectral narrowing of x-ray pulses for precision spectroscopy with nuclear resonances. Science. 357, 375 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aan3512
Ruby, S.L., Bolef, D.I.: Acoustically modulated γ rays from Fe57. Phys. Rev. Lett. 5, 5 (1960). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.5.5
Shakhmuratov, R.N., Vagizov., F.G.: Application of the Mössbauer effect to the study of subnanometer harmonic displacements in thin solids. Phys. Rev. B. 95, 245429 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.95.245429
Chien, C.L.: Walker.: Mössbauer sidebands from a single parent line. Phys. Rev. B. 13, 1876 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.13.1876
Cranshaw, T.E., Reivari., P.: A Mössbauer study of the hyperfine spectrum of 57Fe, using ultrasonic calibration. Proc. Phys. Soc. 90 1059. (1967). https://doi.org/10.1088/0370-1328/90/4/317
du Voorthuysen, E.H., Zhang, G.L., de Waard, H.: Test of the optical theory of Mössbauer quantum beats. Phys. Rev. A 30 2356. (1984). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.30.2356
Khairulin, I.R., Radeonychev, Y.V., Antonov, V.A., Kocharovskaya, O.: Acoustically induced transparency for synchrotron hard x-ray photons. Sci. Rep. 11, 7930 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-86555-x
Lynch, F.J., Holland, R.E., Hamermesh., M.: Time Dependence of Resonantly Filtered Gamma Rays from Fe57. Phys. Rev. 120, 513 (1960). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRev.120.513
Smirnov., G.V.: General properties of nuclear resonant scattering. Hyp Interact. 124/124, 31 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1017007520099
Perlow., G.J.: Quantum beats of recoil-free γ radiation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 40, 896 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.40.896
Pfeiffer, L., Heiman, N.D.: Walker.: Mössbauer sidebands by rf excitation of magnetic materials. Phys. Rev. B. 6, 74 (1972). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.6.74
Abragam, A.: L’effect Mössbauer, pp. 22–24. Gordon and Breach, New York (1964)
Mitsui, T., Hirao, N., Ohishi, Y., Masuda, R., Nakamura, Y., Enoki, H., Sakaki, K., Seto, M.: Development of an energy-domain 57Fe-Mössbauer spectrometer using synchrotron radiation and its application to ultrahigh-pressure studies with a diamond anvil cell. J. Synchrotron Radiat. 16(6), 723 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1107/S0909049509033615
Mkrtchyan, A.R., Arutyunyan, G.A., Arakelyan, A.R., Gabrielyan, R.G.: Modulation of Mössbauer radiation by coherent ultrasonic excitation in crystals. Phys. Stat. Sol (b). 92 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1002/pssb.2220920103
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the Accelerator Group of SPring-8 for their support, especially with the operation of electron bunch mode and the top-up injection operation. This work was supported by “Advanced Research Infrastructure for Materials and Nanotechnology in Japan (ARIM)” of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT). Proposal Nos. JPMXP1222QS0104, JPMXP1223QS0002. This work was also supported by JST, the establishment of university fellowship towards the creation of science technology innovation, Grant Number JPMJFS2123.Moreover, this work was supported by JSPS KAKENHI Grant Numbers JP21K12535, JP16K13723.
Funding
This work was supported by JST, the establishment of university fellowship towards the creation of science technology innovation, Grant Number JPMJFS2123. This work was supported by JSPS KAKENHI Grant Numbers JP21K12535, JP16K13723.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
H. Y. wrote the main manuscript text based on the advice of the other authors. All authors performed the experiments. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Ethical approval was not required for this study.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yamashita, H., Kitao, S., Kobayashi, Y. et al. Measurement of the sub-nanometer vibration amplitudes using 57Fe synchrotron Mössbauer source. Hyperfine Interact 245, 15 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10751-024-01854-9
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10751-024-01854-9