Abstract
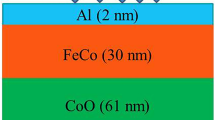
FeCoB/MgO bilayer is prepared to study the interface magnetism and its role in azimuthal angle-dependent magnetic properties. As observed in magneto-optic Kerr effect measurements, unusual hysteresis loops are understood precisely through interface resolved grazing incident nuclear resonance scattering (GINRS) measurements under x-ray standing wave (XSW) conditions. To excite XSW modes, the bilayer is deposited between a Pt waveguide structure, where the position of the anti-nodes is varied by changing incident angles. As GINRS is an isotope sensitive technique, the FeCoB layer is enriched with 57Fe isotope during deposition. The formation of a high-density 57FeCoB layer at the 57FeCoB/MgO interface with a hyperfine field ~34.25 T is found and attributed to the increasing volume of FeCo at the interface. Boron diffusion from 57FeCoB to the MgO layer is found to be responsible for FeCo rich FeCoB layer near the interface. The azimuthal angle-dependent unusual shape of hysteresis loops is described in terms of coupled magnetization reversal between the bulk and interface parts of FeCoB layer. In contrast to some studies in literature, no evidence of the formation of an oxide layer is observed at the interface.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wolf, S.A., Awschalom, D.D., Buhrman, R.A., Daughton, J.M., Von Molnár, S., Roukes, M.L., Chtchelkanova, A.Y., Treger, D.M.: Spintronics: A spin-based electronics vision for the future. Science 294, 1488 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1065389
Reiss, G., Meyners, D.: Reliability of field programmable magnetic logic gate arrays. Appl. Phys. Lett. 88, 1–3 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2167609
Löhndorf, M., Duenas, T., Tewes, M., Quandt, E., Rührig, M., Wecker, J.: Highly sensitive strain sensors based on magnetic tunneling junctions. Appl. Phys. Lett. 81, 313–315 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1483123
Djayaprawira, D.D., Tsunekawa, K., Nagai, M., Maehara, H., Yamagata, S., Watanabe, N., Yuasa, S., Suzuki, Y., Ando, K.: 230% room-temperature magnetoresistance in CoFeBMgOCoFeB magnetic tunnel junctions. Appl. Phys. Lett. 86, 1–3 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1871344
Lee, Y.M., Hayakawa, J., Ikeda, S., Matsukura, F., Ohno, H.: Effect of electrode composition on the tunnel magnetoresistance of pseudo-spin-valve magnetic tunnel junction with a MgO tunnel barrier. Appl. Phys. Lett. 90, 2005–2008 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2742576
Ikeda, S., Miura, K., Yamamoto, H., Mizunuma, K., Gan, H.D., Endo, M., Kanai, S., Hayakawa, J., Matsukura, F., Ohno, H.: A perpendicular-anisotropy CoFeB-MgO magnetic tunnel junction. Nat. Mater. 9, 721–724 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat2804
Gellert, R., Geiss, O., Klingelhöfer, G., Ladstätter, H., Stahl, B., Walter, G., Kankeleit, E.: Depth selective CEMS in the energy range 0 to 20 keV. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. Atoms. 76, 381–382 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1016/0168-583X(93)95246-2
Couet, S., Schlage, K., Diederich, T., Rüffer, R., Theis-Bröhl, K., Toperverg, B.P., Zhernenkov, K., Zabel, H., Röhlsberger, R.: The magnetic structure of coupled Fe/FeO multilayers revealed by nuclear resonant and neutron scattering methods. New J. Phys. 11, 13038 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1088/1367-2630/11/1/013038
Oko, M., Harada, I., Okada, K.: Theory of XAS and XMCD for the field-controlled valence mixed state in RE compounds. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 190, 012016 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/190/1/012016
Khanderao, A.G., Sergueev, I., Wille, H.C., Kumar, D.: Interface resolved magnetism at metal-organic (Fe/Alq3) interfaces under x-ray standing wave condition. Appl. Phys. Lett. 116, (2020). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5135361
Parratt, L.G.: Surface studies of solids by total reflection of x-rays. Phys. Rev. 95, 359–369 (1954). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRev.95.359
Singh, S., Kumar, D., Gupta, M., Lalla, N.P.: Study of interface induced anisotropic exchange coupling in amorphous FeCoB/MgO bilayer. J. Alloys Compd. 789, 330–335 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JALLCOM.2019.03.025
Gupta, A., Kumar, D., Phatak, V.: Asymmetric diffusion at the interfaces in Fe/Si multilayers. Phys. Rev. B. 81, 155402 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.81.155402
Gupta, A., Kumar, D., Meneghini, C.: Interface structure in magnetic multilayers using x-ray standing waves. Phys. Rev. B. 75, 064424 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.75.064424
Klein, H.-P., Ghafari, M., Ackermann, M., Gonser, U., Wagner, H.-G.: Crystallization of amorphous metals. Nucl. Inst. Methods. 199(159–162), (1982)
Ghafari, M., Peng, G., Wang, D., Imai, Y., Kamali, S.: Occurrence of two amorphous phases in an Fe40Co40B20 alloy. Mater. Lett. 164, 535–538 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MATLET.2015.10.098
Spurgeon, S.R., Sloppy, J.D., Tao, R., Klie, R.F., Lofland, S.E., Baldwin, J.K., Misra, A., Taheri, M.L.: A study of the effect of iron island morphology and interface oxidation on the magnetic hysteresis of Fe-MgO (001) thin film composites. J. Appl. Phys. 112, (2012). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4730630
Greer, A.A., Gray, A.X., Kanai, S., Kaiser, A.M., Ueda, S., Yamashita, Y., Bordel, C., Palsson, G., Maejima, N., Yang, S.-H., Conti, G., Kobayashi, K., Ikeda, S., Matsukura, F., Ohno, H., Schneider, C.M., Kortright, J.B., Hellman, F., Fadley, C.S.: Observation of boron diffusion in an annealed ta/CoFeB/MgO magnetic tunnel junction with standing-wave hard x-ray photoemission. Appl. Phys. Lett. 101, 202402 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4766351
Wang, Z., Saito, M., Mckenna, K.P., Fukami, S., Sato, H., Ikeda, S., Ohno, H., Ikuhara, Y.: 1530−1536 downloaded via UGC DAE INDORE on. Nano Lett. 16, 17 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.nanolett.5b03627
Harnchana, V., Hindmarch, A.T., Sarahan, M.C., Marrows, C.H., Brown, A.P., Brydson, R.M.D.: Evidence for boron diffusion into sub-stoichiometric MgO (001) barriers in CoFeB/MgO-based magnetic tunnel junctions. J. Appl. Phys. 113, (2013). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4802692
Cha, J.J., Read, J.C., Buhrman, R.A., Muller, D.A.: Spatially resolved electron energy-loss spectroscopy of electron-beam grown and sputtered CoFeBMgOCoFeB magnetic tunnel junctions. Appl. Phys. Lett. 91, (2007). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2769753
Acknowledgements
Portions of this research work were carried out at the synchrotron light source PETRA III of DESY beamline P01. We would like to thank Olaf Leupold and Rene Steinbruegge for their assistance at beamline P01, PETRA III. Financial support provided by the Department of Science and Technology (DST) Government of India (Proposal No. I-20180885) within the framework of the India@DESY collaboration is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Proceedings of the International Conference on Hyperfine Interactions (HYPERFINE 2021), 5-10 September 2021, Brasov, Romania
Edited by Ovidiu Crisan
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jamal, M.S., Kumar, Y., Gupta, M. et al. Study of interface and its role in an unusual magnetization reversal in 57FeCoB/MgO bilayer. Hyperfine Interact 242, 17 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10751-021-01736-4
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10751-021-01736-4