Abstract
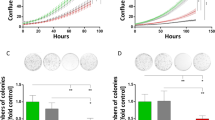
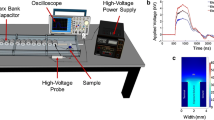
The survival of Escherichia coli bacteria and mouse glioma cells were studied under different temperatures using direct heating in water, ultrasound, and magnetic fluid hyperthermia. The survival of these microorganisms depended on whether the heating mode was continuous or discontinuous, surviving more in the former than in the discontinuous heating mode. Whereas Escherichia coli bacteria did not survive at temperatures ≥50∘C, the mouse glioma cells did not survive at temperatures ≥48∘C. The survival of both these microorganisms was independent of the presence or absence of the magnetic nanoparticles of magnetite, suggesting that these, having mean particle sizes of 9.5, 8.5 and 5, did not show any apparent cytotoxicity effect. Present results also showed that the inductive heating system which used a radiofrequency of 13.56 MHz, providing a maximum magnetic field strength of 160 A/m, the electric rather than magnetic heating predominated.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rosensweig, R.E.: Heating magnetic fluid with alternating magnetic field. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 252(2002), 370–374 (2002)
Adhikary, K., Banerjee, J.: A thermofluid analysis of the magnetic nanoparticles enhanced heating effects in tissues embedded with large blood vessel during magnetic fluid hyperthermia. J. Nanopart. 2016, 18. Article ID 6309231 (2016). doi:10.1155/2016/6309231
Chichel , A., Skowronek, J., Kubaszewska, M., Kanikowski, M.: Hyperthermia - description of a method and a review of clinical applications. Rep. Pract. Oncol Radiother 12(5), 267–275 (2007)
Gellermann, J., Hildebrandt, B., Issels, R., Ganter, H., Lodarczyk, W., Budach, V., Felix, R., Tunn, P.U., Reichardt, P., Wust, P.: Noninvasive magnetic resonance thermography of soft tissue sarcomas during regional hyperthermia. Correlation with response and direct thermometry. Cancer 107–6, 1374–1382 (2006)
Nabil, M., Decuzzi, P., Zunino, P.: Modelling mass and heat transfer in nano-based cancer hyperthermia. R Soc Open Sci 2, 150447 (2015)
Périgo, E.A., Hemery, G., Sandre, O., Ortega, D., Garaio, E., Plazaola, F., Teran, F.J.: Fundamentals and advances in magnetic hyperthermia. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2, 041302 (2015). doi:10.1063/1.4935688
Gilcrist, R.K., Medal, B., Shorey, W.D., Hanselman, R.C., Pamotrr, J.C., Bruce Taylor, C.: Selective inductive heating of lymph nodes. Annals Surg. 596–606 (1957)
Jordan, A., Wust, P., Fähling, H., Johns, W., Hinzt, A., Felix, R.: Inductive heating of ferrimagnetic particles and magnetic fluids: Physical evaluation of their potential for hyperthermia. Int. J. Hyperth. 9, 51–68 (1993)
Chan, D.C.F., Kirpotin, D.B., Bunn Jr., P.A.: Synthesis and evaluation of colloidal magnetic iron oxides for the site-specific radiofrequency-induced hyperthermia of cancer. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 122, 374–378 (1993)
Lacroix, L.M., Carrey, J., Respaud, M.: A frequency-adjustable electromagnet for hyperthermia measurements on magnetic nanoparticles. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 79, 093909 (2008)
Gutiérrez-León, D.G., Rodríguez-Méndez, B.G., López-Callejas, R., Peña-Eguiluz, R., Valencia-Alvarado, R., Mercado-Cabrera, A., Muñoz-Castro, A.E., Belman-Flores, J.M. Experimental evaluation of DBD reactor applied to bacterial inactivation in water flowing continuously. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. (2016). doi:10.1109/TPS.2016.2572640
Perez, A., Santos-Cuevas, C.L., Chairez, I., Poznyak, T., Ordaz-Rosado, D., García-becerra, R., Romero Piña, M.E.: Ozone dosage effect on C6 cell growth: in vitro and in vivo tests. Anti-Cancer Agents in Medicinal Chemistry (Formerly Current Medicinal Chemistry-Anti-Cancer Agents) 15(9), 1190–1196 (2015)
Almazán Celis, J., Olea Mejía, O.F., Cabral Prieto, A., García-Sosa, I., Escudero Derat, R., Baggio Saitovitch, E.M., Alzamora Camarena, M.: This paper form part of the proceedings of LACAME 2016, Taaken place in Panamá November 2016 (2016). doi:10.1007/s10751-017-1414-x
Mørup, S., Hansen, M.F., Frandsen, C.: Magnetic interactions between nanoparticles. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 1, 182–190 (2010)
Brok, E., Frandsen, C., Madsen, D.E., Jacobsen, H., Birk, J.O., Lefmann, K., Bendix, J., Pedersen, K.S., Boothroyd, C.B., Berhe, A.A., Simeoni, G.G., Mørup, S.: Magnetic properties of ultra-small goethite nanoparticles. J. Phys. D. Appl. Phys. 47(36), 13. Article ID 365003 (2014). doi:10.1088/0022-3727/47/36/365003
Liu, X.: Exploration of the Interaction of Electromagnetic Fields with Nanoscale Materials. Doctoral thesis, School of Electronic Engineering and Computer Science Queen Mary University of London (2012). http://qmro.qmul.ac.uk/jspui/handle/123456789/8559
Müller, P., Guggenheim, B., Attin, T., Marlinghaus, E., Schmidlin, P.R.: Potential of shock waves to remove calculus and biofilm. Clinical Oral Investigations 15(6), 959–965 (2011)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Proceedings of the 15th Latin American Conference on the Applications of the Mössbauer Effect (LACAME 2016), 13-18 November 2016, Panama City, Panama
Edited by Juan A. Jaén
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cabral–Prieto, A., López-Callejas, R., Rodríguez-Méndez, B.G. et al. Hyperthermia studies using inductive and ultrasound methods on E. coli bacteria and mouse glioma cells. Hyperfine Interact 238, 44 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10751-017-1417-7
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10751-017-1417-7