Abstract
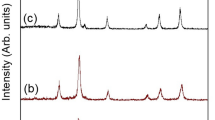
Microwave–hydrothermal (MH) route was employed to synthesize various iron oxide phases in ultra-fine crystalline powders by using ferrous sulphate and sodium hydroxide as starting chemicals. All chemical reactions were carried out under identical MH conditions, namely, at 190°C, 154 psi, 30 min, by varying the molar ratio (MR) of FeSO4/NaOH in the aqueous solutions. The variation of MR has a dramatic effect on the crystallization behavior of various phases of iron oxides under MH processing conditions. For example, spherical agglomerates of Fe3O4 powder were obtained if MR equal to 0.133 (pH > 10 sample A). On the other hand non-stoichiometric Fe3O4 powders (Sample B) were obtained for all higher MR of FeSO4/NaOH between 0.133 and 4.00 (6.6 < pH < 10). However, when MR was equal to 4.0 (pH ≅ 6.6) a varied distribution of shapes and sizes of agglomerates of -Fe2O3 powders (sample C) were produced. Fe57 Mössbauer spectra were recorded for all the three sets of samples at room temperature. In the case of sample B, temperature dependent Mössbauer spectra were recorded in the range of 77–300 K to understand the non-stoichiometric nature of Fe3O4 powders. All these results are discussed in the present paper.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ichinose, N., Ozaki, Y., Kashu, S.: Superfine Particle Technology. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York (1992)
Gleiter, H.: Prog. Mater. Sci. 33, 223 (1989, and references therein)
Matijevic, P.E.: In: Hench, L.L., Ulrich, D.B. (eds.) Colloid Science of Composites System, Science of Ceramic Chemical Processing, pp. 463. Wiley, New York (1986)
Osterhout, V.: In: Craik, D.S. (ed.) Magnetic Oxides, pp. 700. Wiley, New York (1975)
Khollam, Y.B., Dhage, S.R., Potdar, H.S., Deshpande, S.B., Bakare, P.P., Kulkarni, S.D., Date, S.K.: Mater. Lett. 56, 571 (2002)
Dhage, S.R., Khollam, Y.B., Potdar, H.S., Deshpande, S.B., Bakare, P.P., Sainkar, S.R., Date, S.K.: Mater. Lett. 57, 457 (2002)
JCPDS card nos. Fe3O4 [19–629] and -Fe2O3 [16–653]
Simmons, G.W., Leidheiser, H., Jr.: In: Cohen, R.L. (ed.) Application of Mössbauer Spectroscopy, vol. 1, pp. 106. Academic, New York (1976)
Visalakski, G., Venkateswaran, G., Kulshreshtha, S.K., Moorthy, P.H.: Mater. Res. Bull. 28, 829 (1993)
Wang, S., Xin, H., Qian, Y.: Mater. Lett. 33, 113 (1997)
Coey, J.M.D., Morrish, A.H., Sawatzky, G.A.: J. Phys. 32, C1–C271 (1971)
Balasubramanian, C., Khollam, Y.B., Banerjee, I., Bakare, P.P., Date, S.K., Das, A.K., Bhoraskar, S.V.: Mater. Lett. 58, 3958 (2004)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bakare, P.P., Date, S.K., Khollam, Y.B. et al. Mössbauer effect studies on the formation of iron oxide phases synthesized via microwave–hydrothermal route. Hyperfine Interact 168, 1127–1132 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10751-006-9458-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10751-006-9458-3