Abstract
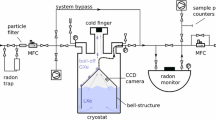
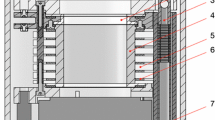
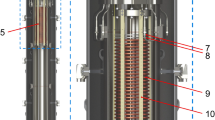
Solid xenon layers are proposed as an alternative to graphite catchers for collecting samples at on-line separators. The formation of solid xenon layers is described. Sample atoms of bismuth have been held for up to a day in such layers before being released as cold free atoms for laser spectroscopy measurement. An application to studying daughter nuclei produced by α\(\alpha\)-decay is considered. It involves a two-stage process where daughter recoils are first accumulated in the xenon layer and subsequently released into flowing helium for laser-ionization and counting.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Krönert U. et al., Appl. Phys. A 44 (1987), 339.
Le Blanc F. et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 79 (1997), 2213.
Van Duppen P. et al., Hyperfine Interact. 127 (2000), 401.
Billowes J. and Campbell P., Hyperfine Interact. 129 (2000), 289.
Helmer R. G. and Reich C. W., Phys. Rev. C 49 (1994), 1845.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ezwam, A.E., Billowes, J. A Solid Xenon Catcher for Rare Isotope Laser Spectroscopy. Hyperfine Interact 162, 189–194 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10751-005-9220-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10751-005-9220-2