Abstract
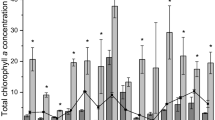
Tidal freshwater zones (TFZs) can significantly affect nutrient transport from watersheds to estuaries through biogeochemical cycling. Phytoplankton, pivotal in nutrient cycling, have been relatively understudied within TFZs. Employing accessory pigment analysis, this study assessed the contribution of diverse phytoplankton groups to chlorophyll a (chl a) biomass over an annual cycle under baseflow conditions. Spatial and temporal patterns in chl a concentrations and community structure as inferred from accessory pigment analysis were evaluated in relation to temperature, dissolved inorganic nitrogen (DIN), soluble reactive phosphorus (SRP), and DIN/SRP ratios. Downstream phytoplankton transport and seasonal succession within the TFZ, driven by nutrient levels and temperature, lead to variations in chl a concentration and community composition. Overall chl a levels were higher in the TFZ than in the upstream river and downstream estuary, with cyanobacteria prominently contributing to chl a biomass, especially in the lower TFZ sections. This study underscores the role of prolonged residence times and nutrient enrichment in TFZs, resulting in elevated chl a concentrations and shaping phytoplankton community composition, with implications for downstream estuaries.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available in the Mendeley Data repository, https://doi.org/10.17632/97sxgbzvfv.2.
References
Andersen, R. A., R. R. Bidigare, M. D. Keller & M. Latasa, 1996. A comparison of HPLC pigment signatures and electron microscopic observations for oligotrophic waters of the North Atlantic and Pacific Oceans. Deep Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography 43: 517–537. https://doi.org/10.1016/0967-0645(95)00095-x.
Anderson, G. F., 1986. Silica, diatoms and a freshwater productivity maximum in Atlantic Coastal Plain estuaries, Chesapeake Bay. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 22: 183–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/0272-7714(86)90112-5.
APHA (2012) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 22nd edition. American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association, Water Environment Federation
Arndt, S., G. G. Lacroix, N. Gypens, et al., 2011. Nutrient dynamics and phytoplankton development along an estuary-coastal zone continuum: A model study. Journal of Marine Systems 84: 49–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmarsys.2010.08.005.
Basen, T., K.-O. Rothhaupt & D. Martin-Creuzburg, 2012. Absence of sterols constrains food quality of cyanobacteria for an invasive freshwater bivalve. Oecologia 170: 57–64. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-012-2294-z.
Brett, M. & D. Müller-Navarra, 1997. The role of highly unsaturated fatty acids in aquatic foodweb processes. Freshwater Biology 38: 483–499. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2427.1997.00220.x.
Brett, M. T., D. C. Müller-Navarra & P. Sang-Kyu, 2000. Empirical analysis of the effect of phosphorus limitation on algal food quality for freshwater zooplankton. Limnology and Oceanography 45: 1564–1575. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.2000.45.7.1564.
Brett, M. T., M. J. Kainz, S. J. Taipale & H. Seshan, 2009. Phytoplankton, not allochthonous carbon, sustains herbivorous zooplankton production. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 106: 21197–21201. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0904129106.
Bruesewitz, D. A., W. S. S. Gardner, R. F. Mooney, et al., 2013. Estuarine ecosystem function response to flood and drought in a shallow, semiarid estuary: nitrogen cycling and ecosystem metabolism. Limnology and Oceanography 58: 2293–2309. https://doi.org/10.4319/10.2013.58.6.2293.
Bukaveckas, P. A. & W. N. Isenberg, 2013. Loading, transformation, and retention of nitrogen and phosphorus in the tidal freshwater James River (Virginia). Estuaries and Coasts 36: 1219–1236. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12237-013-9644-x.
Bukaveckas, P. A., L. E. Barry, M. J. Beckwith, et al., 2011. Factors determining the location of the chlorophyll maximum and the fate of algal production within the tidal freshwater James River. Estuaries and Coasts 34: 569–582. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12237-010-9372-4.
Burford, M. A. A., A. T. B. Revill, D. W. C. Palmer, et al., 2011. River regulation alters drivers of primary productivity along a tropical river-estuary system. Marine and Freshwater Research 62: 141. https://doi.org/10.1071/MF10224.
Cole, J. J., N. F. Caraco & B. L. Peierls, 1992. Can phytoplankton maintaina positive carbon balance in a turbid, freshwater, tidal estuary? Limnology and Oceanography 37: 1608–1617. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.1992.37.8.1608.
Coles, J. F., R. C. Jones & M. Lemmer-, 2000. Effect of temperature on photosynthesis-light response and growth of four phytoplankton species isolated from a tidal freshwater river. Journal of Phycology 36: 7–16. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1529-8817.2000.98219.x.
Conner, W. H., T. W. Doyle & K. W. Krauss, 2007. Ecology of tidal freshwater forested wetlands of the southeastern United States, Springer, Netherlands, Dordrecht:
de Sève, M. A., 1993. Diatom bloom in the tidal freshwater zone of a turbid and shallow estuary, Rupert Bay (James Bay, Canada). Hydrobiologia 269–270: 225–233. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00028021.
Domingues, R. B., T. P. Anselmo, A. B. Barbosa, et al., 2010. Tidal variability of phytoplankton and environmental drivers in the freshwater reaches of the Guadiana Estuary (SW Iberia). International Review of Hydrobiology 95: 352–369. https://doi.org/10.1002/iroh.201011230.
Domingues, R. B., T. P. Anselmo, A. B. Barbosa, et al., 2011. Nutrient limitation of phytoplankton growth in the freshwater tidal zone of a turbid, Mediterranean estuary. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 91: 282–297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2010.10.033.
Douglas, S., J. Xue, A. Hardison & Z. Liu, 2023. Phytoplankton community response to a drought-to-wet climate transition in a subtropical estuary. Limnology and Oceanography. https://doi.org/10.1002/lno.12348.
Edwards, K. F., M. K. Thomas, C. A. Klausmeier & E. Litchman, 2016. Phytoplankton growth and the interaction of light and temperature: a synthesis at the species and community level. Limnology and Oceanography 61: 1232–1244. https://doi.org/10.1002/lno.10282.
Elser, J. J., M. E. S. Bracken, E. E. Cleland, et al., 2007. Global analysis of nitrogen and phosphorus limitation of primary producers in freshwater, marine and terrestrial ecosystems. Ecology Letters 10: 1135–1142. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1461-0248.2007.01113.x.
Ensign, S. H. & G. B. Noe, 2018. Tidal extension and sea-level rise: recommendations for a research agenda. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment 16: 37–43. https://doi.org/10.1002/fee.1745.
Ensign, S. H., M. W. Doyle, M. F. Piehler, et al., 2012. Tidal geomorphology affects phytoplankton at the transition from forested streams to tidal rivers. Freshwater Biology 57: 2141–2155. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2427.2012.02856.x.
Ensign, S. H., M. W. Doyle, M. F. Piehler, et al., 2013. The effect of tide on the hydrology and morphology of a freshwater river. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms 38: 655–660. https://doi.org/10.1002/esp.3392.
Evans A., K. Madden, & S. Palmer, 2012. The ecology and sociology of the Mission-Aransas estuary: an estuarine and watershed profile.
Gao, Y., J. M. O’Neil, D. K. Stoecker & J. C. Cornwell, 2014. Photosynthesis and nitrogen fixation during cyanobacteria blooms in an oligohaline and tidal freshwater estuary. Aquatic Microbial Ecology 72: 127–142. https://doi.org/10.3354/ame01692.
Ger, K. A., P. Urrutia-Cordero, P. C. Frost, et al., 2016. The interaction between cyanobacteria and zooplankton in a more eutrophic world. Harmful Algae 54: 128–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hal.2015.12.005.
Havens, K. E., 2008. Cyanobacteria blooms: effects on aquatic ecosystems. In Hudnell, H. K. (ed), Cyanobacterial harmful algal blooms: state of the science and research needs Springer, New York: 733–747.
Hitchcock, G. L. & T. J. Smayda, 1977. The importance of light in the initiation of the 1972–1973 winter-spring diatom bloom in Narragansett Bay. Limnology and Oceanography 22: 126–131. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.1977.22.1.0126.
Howarth, R. W., R. Schneider & D. Swaney, 1996. Metabolism and organic carbon fluxes in the tidal freshwater Hudson River. Estuaries 19: 848. https://doi.org/10.2307/1352302.
Hubble, D. S. & D. M. Harper, 2002. Phytoplankton community structure and succession in the water column of Lake Naivasha, Kenya: a shallow tropical lake. Hydrobiologia 488: 89–98. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023314128188.
Johnson, S.L., 2009. A general method for modeling coastal water pollutant loadings. The University of Texas at Austin.
Jones, R. C., 1998. Seasonal and spatial patterns in phytoplankton photosynthetic parameters in a tidal freshwater river. Hydrobiologia 364: 199–208. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1003107306421.
Jones, R. C., D. P. Kelso & E. Schaeffer, 2008. Spatial and seasonal patterns in water quality in an embayment-mainstem reach of the tidal freshwater Potomac River, USA: a multiyear study. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment 147: 351–375. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-007-0126-0.
Jones, A. E., B. R. Hodges, J. W. McClelland, et al., 2017. Residence-time-based classification of surface water systems. Water Resources Research 53: 5567–5584. https://doi.org/10.1002/2016WR019928.
Jones, A. E., A. K. Hardison, B. R. Hodges, et al., 2019. An expanded rating curve model to estimate river discharge during tidal influences across the progressive-mixed-standing wave systems. PLoS One 14: e0225758. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0225758.
Jones, A. E., A. K. Hardison, B. R. Hodges, et al., 2020. Defining a riverine tidal freshwater zone and its spatiotemporal dynamics. Water Resource Research. https://doi.org/10.1029/2019WR026619.
Kassambara. A, 2021 rstatix: Pipe-Friendly Framework for Basic Statistical Tests. R package version 0.7.0. https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=rstatix
Kiss, K. T. & S. I. Genkal, 1993. Winter blooms of centric diatoms in the River Danube and in its side-arms near Budapest (Hungary). In van Dam, H. (ed), Twelfth international diatom symposium Springer, Netherlands, Dordrecht: 317–325.
Konopka, A. & T. D. Brock, 1978. Effect of temperature on blue-green algae (cyanobacteria) in lake mendota. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 36: 572–576.
Lampman, G. G., N. F. Caraco & J. J. Cole, 1999. Spatial and temporal patterns of nutrient concentration and export in the tidal Hudson River. Estuaries 22: 285. https://doi.org/10.2307/1352984.
Lapierre, J. & J. Frenette, 2008. Advection of freshwater phytoplankton in the St. Lawrence River estuarine turbidity maximum as revealed by sulfur-stable isotopes. Marine Ecology Progress Series 372: 19–29. https://doi.org/10.3354/meps07685.
Lauridsen, T. L., L. Schlüter & L. S. Johansson, 2011. Determining algal assemblages in oligotrophic lakes and streams: comparing information from newly developed pigment/chlorophyll a ratios with direct microscopy. Freshwater Biology 56: 1638–1651. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2427.2011.02588.x.
Lebreton, B., J. Beseres Pollack, B. Blomberg, et al., 2016. Origin, composition and quality of suspended particulate organic matter in relation to freshwater inflow in a South Texas estuary. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 170: 70–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2015.12.024.
Legendre, P. & L. F. J. Legendre, 2012. Numerical ecology, Elsevier, Amsterdam:
Lehman, P. W., G. Boyer, C. Hall, et al., 2005. Distribution and toxicity of a new colonial Microcystis aeruginosa bloom in the San Francisco Bay Estuary, California. Hydrobiologia 541: 87–99. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-004-4670-0.
Lehman, P. W., W. Resources & E. Studies, 2007. The influence of phytoplankton community composition on primary productivity along the riverine to freshwater tidal continuum in the San Joaquin River, California. Estuaries and Coasts 30: 82–93. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02782969.
Letelier, R. M., R. R. Bidigare, D. V. Hebel, et al., 1993. Temporal variability of phytoplankton community structure based on pigment analysis. Limnology and Oceanography 38: 1420–1437. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.1993.38.7.1420.
Litchman, E. & C. A. Klausmeier, 2008. Trait-based community ecology of phytoplankton. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics 39: 615–639.
Litchman, E., Pinto P. de Tezanos, K. F. Edwards, et al., 2015. Global biogeochemical impacts of phytoplankton: a trait-based perspective. Journal of Ecology 103: 1384–1396. https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2745.12438.
Lucas, L., J. Koseff, J. Cloern, et al., 1999. Processes governing phytoplankton blooms in estuaries. I: the local production-loss balance. Marine Ecology Progress Series 187: 1–15. https://doi.org/10.3354/meps187001.
Lürling, M., F. Eshetu, E. J. Faassen, et al., 2013. Comparison of cyanobacterial and green algal growth rates at different temperatures. Freshw Biol 58: 552–559. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2427.2012.02866.x.
Lürling, M., M. M. E. Mello, F. van Oosterhout, et al., 2018. Response of natural cyanobacteria and algae assemblages to a nutrient pulse and elevated temperature. Front Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.01851.
Mackey, M., D. Mackey, H. Higgins & S. Wright, 1996. CHEMTAX - a program for estimating class abundances from chemical markers:application to HPLC measurements of phytoplankton. Marine Ecology Progress Series 144: 265–283. https://doi.org/10.3354/meps144265.
Mallin, A. & W. Paerl, 1991. Seasonal phytoplankton composition, productivity and biomass in the Neuse River Estuary, North Carolina. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 32: 609–623.
McTigue, N. D., P. Bucolo, Z. Liu & K. H. Dunton, 2015. Pelagic-benthic coupling, food webs, and organic matter degradation in the Chukchi Sea: Insights from sedimentary pigments and stable carbon isotopes. Limnology and Oceanography 60: 429–445. https://doi.org/10.1002/lno.10038.
Megonigal, J. P. & S. C. Neubauer, 2019. Biogeochemistry of tidal freshwater wetlands. In Perillo, G. M. E., E. Wolanski, D. Cahoon & C. Hopkinson (eds), Coastal Wetlands 2nd ed. Elsevier: 641–683.
Mitrovic, S. M., J. N. Hitchcock, A. W. Davie & D. A. Ryan, 2010. Growth responses of Cyclotella meneghiniana (Bacillariophyceae) to various temperatures. Journal of Plankton Research 32: 1217–1221. https://doi.org/10.1093/plankt/fbq038.
Mooney, R. F. & J. W. McClelland, 2012. Watershed export events and ecosystem responses in the mission-aransas national estuarine research reserve, South Texas. Estuaries and Coasts 35: 1468–1485. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12237-012-9537-4.
Muylaert, K., M. Tackx & W. Vyverman, 2005. Phytoplankton growth rates in the freshwater tidal reaches of the Schelde estuary (Belgium) estimated using a simple light-limited primary production model. Hydrobiologia 540: 127–140. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-004-7128-5.
Muylaert, K., K. Sabbe & W. Vyverman, 2009. Changes in phytoplankton diversity and community composition along the salinity gradient of the Schelde estuary (Belgium/The Netherlands). Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 82: 335–340. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2009.01.024.
Niu, L., P. H. A. J. M. van Gelder & J. K. Vrijling, 2017. Physical limitation of phytoplankton dynamics in coastal waters. Journal of Coastal Research 331: 88–95. https://doi.org/10.2112/JCOASTRES-D-15-00136.1.
Oksanen, J., F. G. Blanchet, R. Kindt, et al., 2013. Package ‘vegan.’ Community Ecology Package, Version 2: 1–295.
Paerl, H. W., R. S. Fulton, P. H. Moisander & J. Dyble, 2001. Harmful freshwater algal blooms, with an emphasis on cyanobacteria. The Scientific World JOURNAL 1: 76–113. https://doi.org/10.1100/tsw.2001.16.
Phlips, E. J., S. Badylak, J. Hart, et al., 2012. Climatic influences on autochthonous and allochthonous phytoplankton blooms in a subtropical estuary, St. Lucie Estuary, Florida, USA. Estuaries and Coasts 35: 335–352. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12237-011-9442-2.
Popovich, C. A., C. V. Spetter, J. E. Marcovecchio & R. H. Freije, 2008. Dissolved nutrient availability during winter diatom bloom in a turbid and shallow estuary (Bahía Blanca, Argentina). J Coast Res 241: 95–102. https://doi.org/10.2112/06-0656.1.
Pratt, D. M., 1965. The winter-spring diatom flowering in Narragansett Bay. Limnology and Oceanography 10: 173–184. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.1965.10.2.0173.
Preece, E. P., F. J. Hardy, B. C. Moore & M. Bryan, 2017. A review of microcystin detections in estuarine and marine waters: environmental implications and human health risk. Harmful Algae 61: 31–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hal.2016.11.006.
Qian, Y., A. E. Jochens, M. C. Kennicutt II. & D. C. Biggs, 2003. Spatial and temporal variability of phytoplankton biomass and community structure over the continental margin of the northeast Gulf of Mexico based on pigment analysis. Continental Shelf Research 23: 1–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0278-4343(02)00173-5.
Qin, Q. & J. Shen, 2017. The contribution of local and transport processes to phytoplankton biomass variability over different timescales in the Upper James River, Virginia. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 196: 123–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2017.06.037.
Relexans, J. C., M. Meybeck, G. Billen, et al., 1988. Algal and microbial processes involved in particulate organic matter dynamics in the Loire estuary. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 27: 625–644. https://doi.org/10.1016/0272-7714(88)90072-8.
Reyna, N. E., A. K. Hardison & Z. Liu, 2017. Influence of major storm events on the quantity and composition of particulate organic matter and the phytoplankton community in a subtropical estuary, Texas. Frontiers in Marine Science 4: 43. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2017.00043.
Reynolds, C. S., 2006. The ecology of phytoplankton, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge:
Reynolds, C. S., V. Huszar, C. Kruk, et al., 2002. Towards a functional classification of the freshwater phytoplankton. Journal of Plankton Research 24: 417–428. https://doi.org/10.1093/plankt/24.5.417.
Riebesell, U., 1989. Comparison of sinking and sedimentation rate measurements in a diatom winter/spring bloom. Marine Ecology Progress Series 54: 109–119. https://doi.org/10.3354/meps054109.
Schlüter, L., T. L. Lauridsen, G. Krogh & T. Jorgensen, 2006. Identification and quantification of phytoplankton groups in lakes using new pigment ratios—a comparison between pigment analysis by HPLC and microscopy. Freshwater Biology 51: 1474–1485. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2427.2006.01582.x.
Schmidt, K. & S. Jónasdóttir, 1997. Nutritional quality of two cyanobacteria: How rich is “poor” food? Marine Ecology Progress Series 151: 1–10. https://doi.org/10.3354/meps151001.
Schuchardt, B. & M. Schirmer, 1991. Phytoplankton maxima in the tidal freshwater reaches of two coastal plain estuaries. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 32: 187–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/0272-7714(91)90014-3.
Schuchardt, B., U. Haesloop & M. Schirmer, 1993. The tidal freshwater reach of the Weser estuary: Riverine or estuarine? Netherlands Journal of Aquatic Ecology 27: 215–226. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02334785.
Sharp, J. H., K. Yoshiyama, A. E. Parker, et al., 2009. A biogeochemical view of estuarine eutrophication: Seasonal and spatial trends and correlations in the Delaware Estuary. Estuaries and Coasts 32: 1023–1043. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12237-009-9210-8.
Sin, Y., E. Lee, Y. Lee & K. Shin, 2015. The river–estuarine continuum of nutrients and phytoplankton communities in an estuary physically divided by a sea dike. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 163: 279–289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2014.12.028.
Smith, V. H., 2003. Eutrophication of freshwater and coastal marine ecosystems a global problem. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 10: 126–139. https://doi.org/10.1065/espr2002.12.142.
Solis, R. S. & G. L. Powell, 1999. Hydrography, mixing characteristics, and residence times of Gulf of Mexico estuaries. In Bianchi, T. S., J. R. Pennock & R. R. Twilley (eds), Biogeochemistry of Gulf of Mexico estuaries Wiley, New York: 29–59.
Sommer, U., 1988. Growth and survival strategies of planktonic diatoms. In Sandgren, C. D. (ed), Growth and reproductive strategies of freshwater phytoplankton Cambridge University Press, Cambridge: 227–260.
Spetter, C. V., C. A. Popovich, A. Arias, et al., 2015. Role of nutrients in phytoplankton development during a winter diatom bloom in a eutrophic South American Estuary (Bahía Blanca, Argentina). Journal of Coastal Research 31: 76. https://doi.org/10.2112/JCOASTRES-D-12-00251.1.
Sthapit, E., C. A. Ochs & P. V. Zimba, 2008. Spatial and temporal variation in phytoplankton community structure in a southeastern U.S. reservoir determined by HPLC and light microscopy. Hydrobiologia 600: 215–228. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-007-9234-7.
Ward, George H, 1997. Processes and trends of circulation within the Corpus Christi Bay National Estuary Program study area. Texas Natural Resource Conservation Commission
Wei, H., X. Xu, A. E. Jones, et al., 2022. Tidal freshwater zones modify the forms and timing of nitrogen export from rivers to estuaries. Estuaries and Coasts 45: 2414–2427. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12237-022-01112-7.
Wilson, A. E., O. Sarnelle & A. R. Tillmanns, 2006. Effects of cyanobacterial toxicity and morphology on the population growth of freshwater zooplankton: Meta-analyses of laboratory experiments. Limnology and Oceanography 51: 1915–1924. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.2006.51.4.1915.
Wood, J. D., R. B. Franklin, G. Garman, et al., 2014. Exposure to the cyanotoxin microcystin arising from interspecific differences in feeding habits among fish and shellfish in the James River Estuary, Virginia. Environ Sci Technol 48: 5194–5202. https://doi.org/10.1021/es403491k.
Wright, S. W. & R. L. Van den Enden, 2000. Phytoplankton community structure and stocks in the East Antarctic marginal ice zone (BROKE survey, January-March 1996) determined by CHEMTAX analysis of HPLC pigment signatures. Deep Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography 47: 2363–2400.
Xu, X., H. Wei, G. Barker, et al., 2021. Tidal freshwater zones as hotspots for biogeochemical cycling: sediment organic matter decomposition in the lower reaches of two south Texas rivers. Estuaries and Coasts 44: 722–733. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12237-020-00791-4.
Yu, X., J. R. Yang, J. Chen, et al., 2021. On the use of chemotaxonomy, a phytoplankton identification and quantification method based on pigment for quick surveys of subtropical reservoirs. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 28: 3544–3555. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10704-4.
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Science Foundation (#1417433). We thank the REUisME program (NSF #1358890) led by Dr. Deana Erdner and the University of Texas at Austin Semester-by-the-Sea program. We also thank Dr. Ryan Hladyniuk and Patricia Garlough for analyzing the particulate organic nutrient samples, and Drs. Zhanfei Liu and Jianhong Xue for their help with the HPLC analysis. This work would not have been possible without their help.
Funding
National Science Foundation (1417433), Natural Science Research of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions of China (22KJB170013).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors certify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest or non-financial interest in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript.
Additional information
Handling editor: Judit Padisak
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, H., Xu, X., Savoie, A. et al. Seasonal and nutrient controls on phytoplankton in the Aransas River tidal freshwater zone, Texas, USA. Hydrobiologia 851, 1275–1290 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-023-05388-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-023-05388-z