Abstract
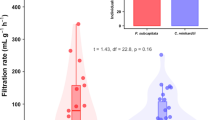
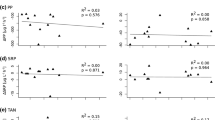
Eutrophic shallow lakes have a high content of organic matter in the sediment that may be frequently resuspended. Whilst it is generally accepted that inorganic suspended matter has a negative effect on filtering-feeding bivalves in streams, it is unclear whether resuspended sediment in lakes with a high organic content will inhibit or support bivalve growth, the latter reflecting that resuspended sediment can increase food availability for Asian clams directly but also through release of nutrients, promoting the growth of phytoplankton. We conducted two experiments assessing the impact of different concentrations of total suspended solids (TSS) on the growth and feeding behaviour of Asian clams. We found that the growth rates in the low, medium and high treatments increased 12%, 36% and 53% respectively, when compared with the control with no sediment added. The effect on clearance rates of Asian clams differed amongst suspended fractions, and the clams showed significant preference for diatoms over other algae at high TSS. We conclude that an increase in TSS stimulated rather than reduced the growth of Asian clams, suggesting that eutrophication in shallow lakes provides more favourable conditions for the population expansion of Asian clams, an invasive species in many water bodies outside Asia.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
APHA, 2012. Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, American Public Health Association, Washington, DC.
Argente, F. A. T., S. A. Cesar & D. T. Dy, 2014. High turbidity affects filtration rate and pseudofaeces production of the mud clam Polymesoda erosa (Solander 1786) (Bivalvia: Corbiculidae). Biotropia 21(2): 71–81.
Asmus, R. M. & H. Asmus, 1991. Mussel beds: limiting or promoting phytoplankton? Journal of Experimental Marine Biology & Ecology 148(2): 215–232.
Bartsch, M. R., L. A. Bartsch, W. B. Richardson, J. M. Vallazza & B. Moraska Lafrancois, 2017. Effects of food resources on the fatty acid composition, growth and survival of freshwater mussels. PLoS ONE 12(3): e0173419.
Bolam, B. A., G. Rollwagen-Bollens & S. M. Bollens, 2019. Feeding rates and prey selection of the invasive Asian clam, Corbicula fluminea, on microplankton in the Columbia River, USA. Hydrobiologia 833(1): 107–123.
Bolker, B. M., M. E. Brooks, C. J. Clark, S. W. Geange, J. R. Poulsen, M. H. H. Stevens & J. S. S. White, 2009. Generalized linear mixed models: a practical guide for ecology and evolution. Trends in Ecology & Evolution 24(3): 127–135.
Brooks, M. E., K. Kristensen, K. J. van Benthem, A. Magnusson, C. W. Berg, A. Nielsen, H. J. Skaug, M. Machler & B. M. Bolker, 2017. glmmTMB balances speed and flexibility among packages for zero-inflated generalized linear mixed modeling. R Journal 9(2): 378–400.
Cai, Y., Y. Lu & Z. Gong, 2015. Changes in macrozoobenthic assemblages in a shallow subtropical lake (Lake Taihu, China): 1987–1988 vs. 2007. Journal of Freshwater Ecology 30(1): 157–168.
Chen, M., S. Ding, X. Chen, Q. Sun, X. Fan, J. Lin, M. Ren, L. Yang & C. Zhang, 2018. Mechanisms driving phosphorus release during algal blooms based on hourly changes in iron and phosphorus concentrations in sediments. Water Research 133: 153–164.
Coughlan, J., 1969. The estimation of filtering rate from the clearance of suspensions. Marine Biology 2(4): 356–358.
Counts, C. L., 1986. The zoogeography and history of the invasion of the United States by Corbicula fluminea (Bivalvia: Corbiculidae). American Malacological Bulletin Special Edition 2: 7–39.
Cranford, P., J. Ward & S. Shumway, 2011. Bivalve filter feeding: variability and limits of the aquaculture biofilter. In Shumway, S. E. (ed), Shellfish Aquaculture and the Environment John Wiley & Sons Inc., Chichester, West Sussex, UK: 81–124.
Deng, J., X. Lu, W. Hu & Z. Xu, 2022. Nutrients and organic matter in the surface sediment of a submerged macrophyte zone in a eutrophic lake: implications for lake management. International Journal of Sediment Research 37(3): 307–316.
Dutertre, M., P. G. Beninger, L. Barillé, M. Papin, P. Rosa, A.-L. Barillé & J. Haure, 2009. Temperature and seston quantity and quality effects on field reproduction of farmed oysters, Crassostrea gigas, in Bourgneuf Bay, France. Aquatic Living Resources 22(3): 319–329.
Ferreira-Rodríguez, N., Y. B. Akiyama, O. V. Aksenova, R. Araujo, M. Christopher Barnhart, Y. V. Bespalaya, A. E. Bogan, I. N. Bolotov, P. B. Budha, C. Clavijo, S. J. Clearwater, G. Darrigran, V. T. Do, K. Douda, E. Froufe, C. Gumpinger, L. Henrikson, C. L. Humphrey, N. A. Johnson, O. Klishko, M. W. Klunzinger, S. Kovitvadhi, U. Kovitvadhi, J. Lajtner, M. Lopes-Lima, E. A. Moorkens, S. Nagayama, K.-O. Nagel, M. Nakano, J. N. Negishi, P. Ondina, P. Oulasvirta, V. Prié, N. Riccardi, M. Rudzīte, F. Sheldon, R. Sousa, D. L. Strayer, M. Takeuchi, J. Taskinen, A. Teixeira, J. S. Tiemann, M. Urbańska, S. Varandas, M. V. Vinarski, B. J. Wicklow, T. Zając & C. C. Vaughn, 2019. Research priorities for freshwater mussel conservation assessment. Biological Conservation 231: 77–87.
Ferreira-Rodríguez, N., R. Sousa & I. Pardo, 2018. Negative effects of Corbicula fluminea over native freshwater mussels. Hydrobiologia 810(1): 85–95.
Foe, C. & A. Knight, 1985. The effect of phytoplankton and suspended sediment on the growth of Corbicula fluminea (Bivalvia). Hydrobiologia 127(2): 105–115.
Hatton, S., B. J. Hayden & M. R. James, 2005. The effects of food concentration and quality on the feeding rates of three size classes of the GreenshellTM mussel, Perna canaliculus. Hydrobiologia 548(1): 23–32.
Jin, H., C. H. A. van Leeuwen, D. B. Van de Waal & E. S. Bakker, 2022. Impacts of sediment resuspension on phytoplankton biomass production and trophic transfer: implications for shallow lake restoration. Science of the Total Environment 808: 152156.
Kasai, A. & A. Nakata, 2005. Utilization of terrestrial organic matter by the bivalve Corbicula japonica estimated from stable isotope analysis. Fisheries Science 71(1): 151–158.
Kiørboe, T., F. Møhlenberg & O. Nøhr, 1981. Effect of suspended bottom material on growth and energetics in Mytilus edulis. Marine Biology 61(4): 283–288.
Kristensen, P., M. Søndergaard & E. Jeppesen, 1992. Resuspension in a shallow eutrophic lake. Hydrobiologia 228(1): 101–109.
Lin, Y., W. Cao, W. Luo, D. Guo, A. Zheng & C. Huang, 2003. Experimental studies on filtration rates in four species of suspension feeding bivalves. Acta Oceanologica Sinica 25(1): 86–92 ((in Chinese with English abstract)).
Lindeque, P. K., A. Dimond, R. A. Harmer, H. E. Parry, K. L. Pemberton & E. S. Fileman, 2015. Feeding selectivity of bivalve larvae on natural plankton assemblages in the Western English Channel. Marine Biology 162(2): 291–308.
Lucy, F. E., A. Y. Karatayev & L. E. Burlakova, 2012. Predictions for the spread, population density, and impacts of Corbicula fluminea in Ireland. Aquatic Invasions 7(4): 465–474.
Marescaux, J., E. Falisse, J. Lorquet, K. Van Doninck, J.-N. Beisel & J.-P. Descy, 2016. Assessing filtration rates of exotic bivalves: dependence on algae concentration and seasonal factors. Hydrobiologia 777(1): 67–78.
Mario, N.-S., R. Luis Fernando-Bucle, P.-V. Pablo, M.-J. Maria, M.-B. Anselmo, M.-C. Luis & L.-E. Jose, 2013. Combined effect of temperature and food concentration on the filtration and clarification rates and assimilation efficiency of Atrina tuberculosa Sowerby, 1835 (Mollusca: Bivalvia) under laboratory conditions. Archives of Biological Sciences 65(1): 99–106.
Martin-Creuzburg, D., E. V. Elert & K. H. Hoffmann, 2008. Nutritional constraints at the cyanobacteria – Daphnia magna interface: the role of sterols. Limnology and Oceanography 53(2): 456–468.
Mistry, R. & J. D. Ackerman, 2018. Flow, Flux, and feeding in freshwater mussels. Water Resources Research 54(10): 7619–7630.
Møhlenberg, F. & H. U. Riisgård, 1979. Filtration rate, using a new indirect technique, in thirteen species of suspension-feeding bivalves. Marine Biology 54(2): 143–147.
Morais, P., J. Teodósio, J. Reis, M. A. Chicharo & L. Chicharo, 2009. The Asian clam Corbicula fluminea (Müller, 1774) in the Guadiana River Basin (southwestern Iberian Peninsula): setting the record straight. Aquatic Invasions 4(4): 681–684.
Mouthon, J., 2001. Life cycle and population dynamics of the Asian clam Corbicula fluminea (Bivalvia: Corbiculidae) in the Saone River at Lyon (France). Hydrobiologia 452(1): 109–119.
Naddafi, R., K. Pettersson & P. EklÖV, 2007. The effect of seasonal variation in selective feeding by zebra mussels (Dreissena polymorpha) on phytoplankton community composition. Freshwater Biology 52(5): 823–842.
Ortmann, C. & M. K. Grieshaber, 2003. Energy metabolism and valve closure behaviour in the Asian clam Corbicula fluminea. Journal of Experimental Biology 206(22): 4167–4178.
Payne, B. S., A. C. Miller, E. D. Hubertz & J. Lei, 1995. Adaptive variation in palp and gill size of the zebra mussel (Dreissena polymorpha) and Asian clam (Corbicula fluminea). Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 52(5): 1130–1134.
Qin, B., G. Zhu, G. Gao, Y. Zhang, W. Li, H. W. Paerl & W. W. Carmichael, 2010. A drinking water crisis in lake Taihu, China: linkage to climatic variability and lake management. Environmental Management 45(1): 105–112.
Rueda, J. L. & A. C. Smaal, 2002. Physiological response of Spisula subtruncata (da Costa, 1778) to different seston quantity and quality. Hydrobiologia 475/476(1): 505–511.
Sousa, R., C. Antunes & L. Guilhermino, 2008a. Ecology of the invasive Asian clam Corbicula fluminea (Müller, 1774) in aquatic ecosystems: an overview. Annales De Limnologie-International Journal of Limnology 44(2): 85–94.
Sousa, R., A. J. A. Nogueira, M. B. Gaspar, C. Antunes & L. Guilhermino, 2008b. Growth and extremely high production of non-indigenous invasive species Corbicula fluminea (Müller, 1774): possible implications for ecosystem functioning. Estuarine Coastal & Shelf Science 80(2): 289–295.
Summons, R. E., A. S. Bradley, L. L. Jahnke & J. R. Waldbauer, 2006. Steroids, triterpenoids and molecular oxygen. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society b: Biological Sciences 361(1470): 951–968.
Tang, H., H. A. Vanderploeg, T. H. Johengen & J. R. Liebig, 2014. Quagga mussel ( Dreissena rostriformis bugensis ) selective feeding of phytoplankton in Saginaw Bay. Journal of Great Lakes Research 40(S1): 83–94.
Tang, C., Y. Li, C. He & K. Acharya, 2020. Dynamic behavior of sediment resuspension and nutrients release in the shallow and wind-exposed Meiliang Bay of Lake Taihu. Science of the Total Environment 708: 135131.
Tuttle-Raycraft, S. & J. D. Ackerman, 2018. Does size matter? Particle size vs. quality in bivalve suspension feeding. Freshwater Biology 63(12): 1560–1568.
Tuttle-Raycraft, S. & J. D. Ackerman, 2019. Living the high turbidity life: the effects of total suspended solids, flow, and gill morphology on mussel feeding. Limnology and Oceanography 64(6): 2526–2537.
Tuttle-Raycraft, S., T. Morris & J. Ackerman, 2017. Suspended solid concentration reduces feeding in freshwater mussels. Science of the Total Environment 598: 1160–1168.
Vaughn, C. C. & C. C. Hakenkamp, 2001. The functional role of burrowing bivalves in freshwater ecosystems. Freshwater Biology 46(11): 1431–1446.
Vaughn, C. C. & T. J. Hoellein, 2018. Bivalve Impacts in Freshwater and Marine Ecosystems. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics 49(1): 183–208.
Widdows, J., P. Fieth & C. M. Worrall, 1979. Relationships between seston, available food and feeding activity in the common mussel Mytilus edulis. Marine Biology 50(3): 195–207.
Wu, Q., Y. Chen & Z. Liu, 2005. Filtering capacity of Anodonta woodiana and its feeding selectivity on phytoplankton. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology 16(12): 2423–2427 ((in Chinese with English abstract)).
Xia, Z., H. J. MacIsaac, R. E. Hecky, D. C. Depew, G. D. Haffner & R. P. Weidman, 2021. Multiple factors regulate filtration by invasive mussels: Implications for whole-lake ecosystems. Science of the Total Environment 765: 144435.
Xu, H., M. J. McCarthy, H. W. Paerl, J. D. Brookes, G. Zhu, N. S. Hall, B. Qin, Y. Zhang, M. Zhu, J. J. Hampel, S. E. Newell & W. S. Gardner, 2021. Contributions of external nutrient loading and internal cycling to cyanobacterial bloom dynamics in Lake Taihu, China: Implications for nutrient management. Limnology and Oceanography 66(4): 1492–1509.
Zhang, Y. L., B. Q. Qin, W. M. Chen & L. C. Luo, 2004. A study on total suspended matter in Lake Taihu. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin. 13(3): 266–71 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zieritz, A., F. N. Mahadzir, W. N. Chan & S. McGowan, 2019. Effects of mussels on nutrient cycling and bioseston in two contrasting tropical freshwater habitats. Hydrobiologia 835(1): 179–191.
Acknowledgements
We would like to express our gratefulness to Anne Mette Poulsen for linguistic assistance, and to Hu He for the help of analysis methods. We also thank the Taihu Laboratory for Lake Ecosystem Research for providing the experimental site for this study. This study was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant 32001156; 31770509; 32001154), Introducing Talent Starting Project of NIGLAS (NIGLAS2019QD02), the Belt and Road Special Foundation of the State Key Laboratory of Hydrology-Water Resources and Hydraulic Engineering (2021491711) and the TÛBITAK BIDEB2232 program (Project 118C250).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YZ and KL: conceptualization, methodology, funding acquisition. YZ, WL, YH and JG: data curation, formal analysis. YZ and LC: writing—original draft, software. EJ and KL: writing—reviewing and editing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We declare that there is no conflict of interest associated with any of the decisions made or components of this study.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Manuel Lopes-Lima
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Cheng, L., Li, W. et al. Growth and clearance rate of Corbicula fluminea in relation to fine sediment resuspension in eutrophic shallow lakes. Hydrobiologia 850, 1045–1058 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-022-05105-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-022-05105-2