Abstract
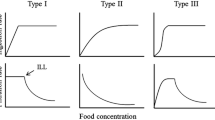
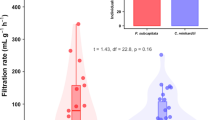
Assessing the environmental variables that influence freshwater bivalve filtration activity is key to better understand the functioning of stream ecosystems. In the present study, the effects of light (0 ± 0 µmol m−2 s−1 and 19 ± 2 µmol m−2 s−1) and temperature (10, 15, 20 and 25°C) on the clearance rates of two bivalve species: the Asian clam Corbicula fluminea (Cyrenidae) and pocketbook Lampsilis ovata (Unionidae) were assessed under controlled laboratory conditions at two different concentrations of algal food (i.e., 10,000 cells ml−1 and 100,000 cells ml−1). Clearance rates for C. fluminea varied from 0 to 491 ml g−1 h−1, while the observed range for L. ovata was 0 to 905 ml g−1 h−1. We found that the relative contribution of the tested variables was species-dependent. While temperature plays a major role in the clearance rates of C. fluminea, food concentration was the most significant variable in the clearance rate of L. ovata. Our results confirm the complex interactions between abiotic and biotic factors in freshwater bivalve filtration activity. Overall, clearance rates are highly variable especially in C. fluminea and presumably regulated by other untested factors suggesting high plasticity in filtration.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data are available upon personal request.
References
Ackerman, J. D., 1999. Effect of velocity on the filter feeding of dreissenid mussels (Dreissena polymorpha and Dreissena bugensis): implications for trophic dynamics. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 56: 1551–1561.
Aldridge, D. W., B. S. Payne & A. C. Miller, 1995. Oxygen consumption, nitrogenous excretion, and filtration rates of Dreissena polymorpha at acclimation temperatures between 20 and 32 °C. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 52: 1761–1767.
Anthony, J. L., D. H. Kesler, W. L. Downing, & J. A. Downing, 2001. Length-specific growth rates in freshwater mussels (Bivalvia: Unionidae): extreme longevity or generalized growth cessation? Freshwater Biology 46(10): 1349–1359.
Baker, S. M. & D. J. Hornbach, 2001. seasonal metabolism and biochemical composition of two unionid mussels, Actinonaias ligamentina and Amblema plicata. Journal of Molluscan Studies 67: 407–416.
Bianchi, V. A., J. M. Castro, I. Rocchetta, F. Bieczynski & C. M. Luquet, 2014. Health status and bioremediation capacity of wild freshwater mussels (Diplodon chilensis) exposed to sewage water pollution in a glacial Patagonian lake. Fish & Shellfish Immunology 37: 268–277.
Block, J. E., G. W. Gerald & T. D. Levine, 2013. Temperature effects on burrowing behaviors and performance in a freshwater mussel. Journal of Freshwater Ecology 28(3): 375–384.
Boltovskoy, D., I. Izaguirre & N. Correa, 1995. Feeding selectivity of Corbicula fluminea (Bivalvia) on natural phytoplankton. Hydrobiologia 312: 171–182.
Burlakova, L. E., B. L. Tulumello, A. Y. Karatayev, R. A. Krebs, D. W. Schloesser, W. L. Paterson, T. A. Griffith, M. W. Scott, T. Crail & D. T. Zanatta, 2014. Competitive replacement of invasive congeners may relax impact on native species: Interactions among zebra, quagga, and native Unionid mussels. PLOS ONE 9(12): e114926.
Coughlan, J., 1969. The estimation of filtering rate from clearance of suspensions. Marine Biology 2: 356–358.
Domingues, A., I. C. Rosa, J. Pinto da Costa, T. A. P. Rocha-Santos, F. J. M. Gonçalves, R. Pereira & J. L. Pereira, 2020. Potential of the bivalve Corbicula fluminea for the remediation of olive oil wastewaters. Journal of Cleaner Production 252: 119773.
Duchini, D., D. Boltovskoy & F. Sylvester, 2015. Detachment, displacement and reattachment activity in a freshwater byssate mussel (Limnoperna fortunei): the effects of light, temperature and substratum orientation. Biofouling 31: 599–611.
Ferreira-Rodríguez, N., R. Sousa & I. Pardo, 2018. Negative effects of Corbicula fluminea over native freshwater mussels. Hydrobiologia 810(1): 85–95.
Galbraith, H. S., S. E. Frazier, B. Allison & C. C. Vaughn, 2009. Comparison of gill surface morphology across a guild of suspension-feeding unionid bivalves. Journal of Molluscan Studie 75(2): 103–107.
Gatenby, C. M., D. Kreeger, M. Patterson, M. Marini & R. Neves, 2013. Clearance rates of Villosa iris (Bivalvia: Unionidae) fed different rations of the alga Neochloris oleoabundans. Freshwater Mollusk Biology and Conservation 16: 9–20.
Gatenby, C. M., R. J. Neves & B. C. Parker, 1996. Influence of sediment and algal food on cultured juvenile freshwater mussels. Journal of the North American Benthological Society 15: 597–609.
Groemping, U., 2007. Relative importance for linear regression in R: the package relaimpo. Journal of Statistical Software 17: 1–27.
Guillard, R. R., 1975. Culture of phytoplankton for feeding marine invertebrates. In Chanley, M. H., H. Matoira & L. Walter (eds), Culture of Marine Invertebrate Animals. Springer, Boston: 29–60.
Haag, W. R., 2012. North American Freshwater Mussels: Natural History, Ecology, and Conservation. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, New York.
Hills, A., S. Pouil, D. Hua & T. J. Mathews, 2020. Effects of light on the clearance rates of freshwater bivalves: the exotic Corbicula fluminea and the native Utterbackia imbecillis. Aquatic Ecology. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10452-020-09793-7.
Hornbach, D. J., C. Way, T. E. Wissing & A. J. Burky, 1984. Effects of particle concentration and season on the filtration rates of the freshwater clam, Sphaerium striatinum Lamarck (Bivalvia: Pisidiidae). Hydrobiologia 108: 83–96.
Howard, J. K. & K. M. Cuffey, 2006. The functional role of native freshwater mussels in the fluvial benthic environment. Freshwater Biology 51: 460–474.
Kobak, J. & P. Nowacki, 2007. Light-related behaviour of the zebra mussel (Dreissena polymorpha, Bivalvia). Fundamental and Applied Limnology 169: 341–352.
Kryger, J. & H. U. Riisgård, 1988. Filtration rate capacities in 6 species of European freshwater bivalves. Oecologia 77: 34–38.
Lim, K.-H., H.-C. Shin & J.-S. Yang, 2005. The influence of water temperature and food concentration on the filtration rates of the Asiatic clam, Corbicula fluminea. The Korean Journal of Malacology 21: 19–24.
Loayza-Muro, R. & R. Elias-Letts, 2007. Responses of the mussel Anodontites trapesialis (Unionidae) to environmental stressors: Effect of pH, temperature and metals on filtration rate. Environmental Pollution 149: 209–215.
Malish, M. C. & D. A. Woolnough, 2019. Varied physiological responses of Amblema plicata and Lampsilis cardium exposed to rising temperatures. Freshwater Science 38: 842–855.
Marescaux, J., E. Falisse, J. Lorquet, K. Van Doninck, J.-N. Beisel & J.-P. Descy, 2016. Assessing filtration rates of exotic bivalves: dependence on algae concentration and seasonal factors. Hydrobiologia 777: 67–78.
McMahon, R. F., 2002. Evolutionary and physiological adaptations of aquatic invasive animals: r selection versus resistance. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 59: 1235–1244.
Mistry, R. & J. D. Ackerman, 2017. Algal flux affects the clearance rates of recently metamorphosed freshwater mussels. Aquatic Sciences 79: 139–148.
Mistry, R. & J. D. Ackerman, 2018. Flow, flux, and feeding in freshwater mussels. Water Resources Research 54: 7619–7630.
Mukherjee, A., S. Das, T. Bhattacharya, M. De, T. Maiti & T. De Kumar, 2014. Optimization of phytoplankton preservative concentrations to reduce damage during long-term storage. Biopreservation and Biobanking 12: 139–147.
Nichols, S. J., H. Silverman, T. H. Dietz, J. W. Lynn & D. L. Garling, 2005. Pathways of food uptake in native (Unionidae) and introduced (Corbiculidae and Dreissenidae) freshwater bivalves. Journal of Great Lakes Research 31: 87–96.
Ortmann, C. & M. K. Grieshaber, 2003. Energy metabolism and valve closure behaviour in the Asian clam Corbicula fluminea. Journal of Experimental Biology 206: 4167–4178.
Payne, B. S. & A. Miller, 1995. Palp to gill area ratio of bivalves: a sensitive indicator of elevated suspended solids. Regulated Rivers Research & Management 11: 193–200.
Pickhardt, P. C. & N. S. Fisher, 2007. Accumulation of inorganic and methylmercury by freshwater phytoplankton in two contrasting water bodies. Environmental Science & Technology 41(1): 125–131.
Pigneur, L.-M., E. Falisse, K. Roland, E. Everbecq, J.-F. Deliège, J. S. Smitz, K. Van Doninck & J.-P. Descy, 2014. Impact of invasive Asian clams, Corbicula spp., on a large river ecosystem. Freshwater Biology 59: 573–583.
R Development Core Team, 2020. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna.
Riisgård, H. U., 2001. On measurement of filtration rates in bivalves—the stony road to reliable data: Review and interpretation. Marine Ecology Progress Series 211: 275–291.
Rodland, D. L., B. R. Schöne, S. Baier, Z. Zhang, W. Dreyer & N. A. Page, 2008. Changes in gape frequency, siphon activity and thermal response in the freshwater bivalves Anodonta cygnea and Margaritifera falcata. Journal of Molluscan Studies 75: 51–57.
Roper, D. S. & C. W. Hickey, 1995. Effects of food and silt on filtration, respiration and condition of the freshwater mussel Hyridella menziesi (Unionacea: Hyriidae): implications for bioaccumulation. Hydrobiologia 312: 17–25.
Rosa, I. C., R. Costa, F. Goncalves & J. L. Pereira, 2014. Bioremediation of metal-rich effluents: Could the invasive bivalve Corbicula fluminea work as a biofilter? Journal of Environmental Quality 43: 1536–1545.
Salerno, J., P. L. Gillis, C. J. Bennett, P. K. Sibley & R. S. Prosser, 2018. Investigation of clearance rate as an endpoint in toxicity testing with freshwater mussels (Unionidae). Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety 163: 165–171.
Sprung, M. & U. Rose, 1988. Influence of food size and food quantity on the feeding of the mussel Dreissena polymorpha. Oecologia 77: 526–532.
Strayer, D. L. & H. M. Malcom, 2018. Long-term responses of native bivalves (Unionidae and Sphaeriidae) to a Dreissena invasion. Freshwater Science 37(4): 697–711.
Strayer, D. L. & H. M. Malcom, 2007. Effects of zebra mussels (Dreissena polymorpha) on native bivalves: the beginning of the end or the end of the beginning? Journal of the North American Benthological Society 26: 111–122.
Tankersley, R. A., 1996. Multipurpose gills: effect of larval brooding on the feeding physiology of freshwater unionid mussels. Invertebrate Biology 115: 243–255.
Tankersley, R. A. & R. V. Dimock Jr., 1993. The effect of larval brooding on the filtration rate and particle-retention efficiency of Pyganodon cataracta (Bivalvia: Unionidae). Canadian Journal of Zoology 71: 1934–1944.
Tuttle-Raycraft, S. & J. D. Ackerman, 2018. Does size matter? Particle size vs. quality in bivalve suspension feeding. Freshwater Biology 63: 1560–1568.
Tuttle-Raycraft, S. & J. D. Ackerman, 2019. Living the high turbidity life: the effects of total suspended solids, flow, and gill morphology on mussel feeding. Limnology and Oceanography 64: 2526–2537.
Vanderploeg, H. A., J. R. Liebig & T. F. Nalepa, 1995. From picoplankton to microplankton: temperature-driven filtration by the unionid bivalve Lampsilis radiata siliquoidea in Lake St. Clair. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 52: 63–74.
Vaughn, C. C., 2018. Ecosystem services provided by freshwater mussels. Hydrobiologia 810: 15–27.
Vidal, M. L., A. Basseres & J. F. Narbonne, 2002. Influence of temperature, pH, oxygenation, water-type and substrate on biomarker responses in the freshwater clam Corbicula fluminea (Muller). Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology C-Toxicology & Pharmacology 132: 93–104.
Viergutz, C., C. Linn & M. Weitere, 2012. Intra- and interannual variability surpasses direct temperature effects on the clearance rates of the invasive clam Corbicula fluminea. Marine Biology 159: 2379–2387.
Vohmann, A., J. Borcherding, A. Kureck, A. Bij de Vaate, H. Arndt & M. Weitere, 2010. Strong body mass decrease of the invasive clam Corbicula fluminea during summer. Biological Invasions 12(1): 53–64.
Zarauz, L. & X. Irigoien, 2008. Effects of Lugol’s fixation on the size structure of natural nano–microplankton samples, analyzed by means of an automatic counting method. Journal of Plankton Research 30: 1297–1303.
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by the US Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge Office of Environmental Management (ORO-DOE) and URS CH2M Oak Ridge LLC (UCOR) and is a product of ORNL’s Mercury Remediation Technology Development Program. Authors acknowledge Dr. Dan Hua, Senior Scientist at TWRA’s C-RAC, and her team who reared and provided the juveniles Lampsilis ovata used in this study. Special thanks to Allison Fortner, Michael Jones, Trent Jett, and Nikki Jones and Louise Stevenson (ORNL) for assistance with field collections of Corbicula fluminea and/or their constructive comments on the manuscript. This manuscript has been authored by UT-Battelle, LLC under Contract No. DE-AC05-00OR22725 with the U.S. Department of Energy. The United States Government retains and the publisher, by accepting the article for publication, acknowledges that the United States Government retains a non-exclusive, paid-up, irrevocable, worldwide license to publish or reproduce the published form of this manuscript, or allow others to do so, for United States Government purposes. The Department of Energy will provide public access to these results of federally sponsored research in accordance with the DOE Public Access Plan (http://energy.gov/downloads/doe-public-access-plan).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
S.P. and A.H. designed and performed the experiments and analyzed samples. S.P. performed statistical analyses, interpreted the results and wrote the first draft of the paper. T.J.M. supervised the experiments. T.J.M. and A.H. corrected and improved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Handling editor: Manuel Lopes Lima.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pouil, S., Hills, A. & Mathews, T.J. The effects of food quantity, light, and temperature on clearance rates in freshwater bivalves (Cyrenidae and Unionidae). Hydrobiologia 848, 675–689 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-020-04472-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-020-04472-y