Abstract
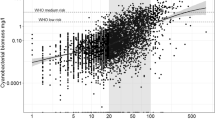
In 2000, a total maximum daily load (TMDL) total phosphorus (TP) goal of 40 µg/L was established for Lake Okeechobee, Florida. The goal was selected to reduce the “imbalance to flora and fauna” caused by excessive phosphorus loading in the lake. We recalculate the TMDL TP goal using a water quality data series of TP and chlorophyll-a concentrations from 1986 to 2018 for the original 30 in-lake stations plus an additional 29 stations. Using the cross-tabulation approach used to generate the original TMDL TP goal, we determined a new goal of 42 µg/L, nominally different from the original. We also reevaluate the goal’s ability to maintain an implicit goal of 11.5% bloom frequency. We conclude substantial changes in the frequency and scope of the water quality sampling scheme prevent a determination on the effectiveness of the TMDL TP goal. The implementation, however, appears to have failed as the median TP concentration has increased by 93 µg/L to 133 µg/L and bloom frequency, after correcting for the declining sampling frequency, has increased from 1986 to 2018. An increased sampling frequency of TP and chlorophyll-a sampling is needed, or else tracking responses of chlorophyll-a to future TP reductions will be virtually impossible.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aldridge, F. J., E. J. Phlips & C. L. Schelske, 1995. The use of nutrient enrichment bioassays to test for spatial and temporal distribution of limiting factors affecting phytoplankton dynamics in Lake Okeechobee, Florida. Archiv für Hydrobiologie, Advances in Limnology 45: 177–190.
Aumen, N. G. & R. G. Wetzel, 1995. Ecological studies on the littoral and pelagic systems of Lake Okeechobee, Florida (USA). Archiv für Hydrobiologie Special Issues Archiv fur Hydrobiologie Beihefte: Ergebnisse der Limnologie 163: 225–239.
Carlson, R. E., 1977. A trophic state index for lakes. Limnology and Oceanography 22(2): 361–369.
Dillon, P. J. & F. H. Rigler, 1974. The phosphorus-chlorophyll relationship in lakes. Limnology and Oceanography 19(5): 767–773.
Engstrom, D. R., S. P. Schottler, P. R. Leavitt & K. E. Havens, 2006. A reevaluation of the cultural eutrophication of Lake Okeechobee using multiproxy sediment records. Ecological Applications 16: 1194–1206.
Flaig, E. G. & K. E. Havens, 1995. Historical trends in the Lake Okeechobee ecosystem. 1. Land use and nutrient loading. Archiv für Hydrobiologie Supplement 107(1): 1–24.
Havens, K. E., 2003. Submerged aquatic vegetation correlations with depth and light attenuating materials in a shallow subtropical lake. Hydrobiologia 493(1–3): 173–186.
Havens, K. E. & D. E. Gawlik, 2005. Lake Okeechobee conceptual ecological model. Wetlands 25(4): 908–925.
Havens, K. E. & W. W. Walker Jr., 2002. Development of a total phosphorus concentration goal in the TMDL process for Lake Okeechobee, Florida (USA). Lake and Reservoir Management 18(3): 227–238.
Havens, K. E., E. J. Phlips, M. F. Cichra & B. L. Li, 1998. Light availability as a possible regulator of cyanobacteria species composition in a shallow subtropical lake. Freshwater Biology 39(3): 547–556.
Havens, K. E., K. R. Jin, N. Iricanin & R. T. James, 2007. Phosphorus dynamics at multiple time scales in the pelagic zone of a large shallow lake in Florida, USA. Hydrobiologia 581(1): 25–42.
Havens, K. E., H. Paerl, E. J. Phlips, M. Zhu, J. R. Beaver & A. Srifa, 2016. Extreme weather events and climate variability provide a lens to how shallow lakes may respond to climate change. Water 8(6): 229.
Havens, K. E., G. Ji, J. R. Beaver, R. S. Fulton & C. E. Teacher, 2019. Dynamics of cyanobacteria blooms are linked to the hydrology of shallow Florida lakes and provide insight into possible impacts of climate change. Hydrobiologia 829: 43–59.
Heiskary, S. A. & W. W. Walker Jr., 1988. Developing phosphorus criteria for Minnesota lakes. Lake and Reservoir Management 4(1): 1–9.
James, R. T. & V. J. Bierman, 1995. A preliminary modeling analysis of water quality in Lake Okeechobee, Florida: calibration results. Water Research 29(12): 2755–2766.
James, T. R., M. J. Chimney, B. Sharfstein, D. R. Engstrom, S. P. Schottler, T. East & K. R. Jin, 2008. Hurricane effects on a shallow lake ecosystem, Lake Okeechobee, Florida (USA). Archiv für Hydrobiologie 172(4): 273–287.
Jeppesen, E., M. Sondergaard, J. P. Jensen, K. E. Havens, O. Anneville, L. Carvalho, M. F. Coveney, R. Deneke, M. T. Dokulil, B. Foy, D. Gerdeaux, S. E. Hampton, S. Hilt, K. Kangur, J. Kohler, E. H. H. R. Lammens, T. L. Lauridsen, M. Manca, M. R. Miracle, B. Moss, P. Noges, G. Persson, G. Phillips, R. Portielje, S. Romo, C. L. Schelske, D. Straile, I. Tatrai, E. Willen & M. Winder, 2005. Lake responses to reduced nutrient loading – an analysis of contemporary long-term data from 35 case studies. Freshwater Biology 50: 1747–1771.
Ji, Z.-G. & K.-R. Jin, 2014. Impacts of wind waves on sediment transport in a large, shallow lake. Lakes & Reservoirs: Science, Policy and Management for Sustainable Use 19: 118–129.
Johnson, K. G., M. S. Allen & K. E. Havens, 2007. A review of littoral vegetation, fisheries, and wildlife responses to hydrologic variation at Lake Okeechobee. Wetlands 27(1): 110–126.
Kramer, B. J., T. W. Davis, K. A. Meyer, B. H. Rosen, J. A. Goleski, G. J. Dick, G. Oh & C. J. Gobler, 2018. Nitrogen limitation, toxin synthesis potential, and toxicity of cyanobacterial populations in Lake Okeechobee and the St. Lucie River Estuary, Florida, during the 2016 state of emergency event. PLoS ONE 13: e0196278.
National Academies of Sciences, Engineering and Medicine, 2016. Progress Toward Restoring the Everglades: The Sixth Biennial Review – 2016. National Academies Press, Washington, D.C.
O’Reilly, C. M., S. Sharma, D. K. Gray, S. E. Hampton, J. S. Read, R. J. Rowley, P. Schneider, J. D. Lenters, P. B. McIntyre, B. M. Kraemer, G. A. Weyhenmeyer, D. Straile, B. Dong, R. Adrian, M. G. Allan, O. Anneville, L. Arvola, J. Austin, J. L. Bailey, J. S. Baron, J. D. Brookes, E. de Eyto, M. T. Dokulil, D. P. Hamilton, K. Havens, A. L. Hetherington, S. N. Higgins, S. Hook, L. R. Izmesteva, K. D. Joehnk, K. Kangur, P. Kasprzak, M. Kumagai, E. Kuusisto, G. Leshkevich, D. M. Livingstone, S. MacIntyre, L. May, J. M. Melack, D. C. Mueller-Navarra, M. Naumenko, P. Noges, T. Noges, R. P. North, P.-D. Plisnier, A. Rigosi, A. Rimmer, M. Rogora, L. G. Rudstam, J. A. Rusak, N. Salmaso, N. R. Samal, D. E. Schindler, S. G. Schladow, M. Schmid, S. R. Schmidt, E. Silow, M. E. Soylu, K. Teubner, P. Verburg, A. Voutilainen, A. Watkinson, C. E. Williamson & G. Zhang, 2015. Rapid and highly variable warming of lake surface waters around the globe: Global Lake Surface Warming. Geophysical Research Letters 42: 10773–10781.
Paerl, H. W., E. Karl, Nathan Havens, S. Hall, T. G. Otten, M. Zhu, H. Xu, G. Zhu & B. Qin, 2020. Mitigating a global expansion of toxic cyanobacterial blooms: confounding effects and challenges posed by climate change. Marine & Freshwater Research 71: 579.
Phlips, E. J., F. J. Aldridge, P. Hansen, P. V. Zimba, J. Ihnat, M. Conroy & P. Ritter, 1993. Spatial and temporal variability of trophic state parameters in a shallow subtropical lake (Lake Okeechobee, Florida, USA). Archiv für Hydrobiologie 128(4): 437–458.
Qin, B., G. Zhu, G. Gao, Y. Zhang, W. Li, H. W. Paerl & W. W. Carmichael, 2010. A drinking water crisis in lake Taihu, China: Linkage to climatic variability and lake management. Environmental Management 45: 105–112.
R Core Team, 2019. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria.
Redfield, G. W., 2000. Ecological research for aquatic science and environmental restoration in south Florida. Ecological Applications 10(4): 990–1005.
Richardson, J., C. Miller, S. C. Maberly, P. Taylor, L. Globevnik, P. Hunter, E. Jeppesen, U. Mischke, S. J. Moe, A. Pasztaleniec, M. Søndergaard & L. Carvalho, 2018. Effects of multiple stressors on cyanobacteria abundance vary with lake type. Global Change Biology 24: 5044–5055.
Siders, Z., 2020. Revisiting the Total Maximum Daily Load Total Phosphorus Goal in Lake Okeechobee. OSF, http://osf.io/5kqdp.
[SFWMD] South Florida Water Management District, 1993. Surface Water Improvement and Management (SWIM) Plan Update for Lake Okeechobee. SFWMD, West Palm Beach, FL.
Søndergaard, M., R. Bjerring & E. Jeppesen, 2013. Persistent internal phosphorus loading during summer in shallow eutrophic lakes. Hydrobiologia 710: 95–107.
Steinman, A. D., K. E. Havens, H. J. Carrick & R. VanZee, 2002. The past, present, and future hydrology and ecology of Lake Okeechobee and its watersheds. In Porter, J. W. & K. G. Porter (eds), The Everglades, Florida Bay, and Coral Reefs of the Florida Keys. CRC Press, Boca Raton (FL): 19–37.
[USACE] United States Army Corps of Engineers. 2008. Central and southern Florida Project Water Control Plan for Lake Okeechobee and Everglades Agricultural Area, Section 7.07.a. USACE, Jacksonville, FL.
Walker, W. W. Jr., 1987. Cross-tabulation as a tool for analyzing large monitoring data bases. Monitoring, Modeling, and Mediating Water Quality. Proceedings of American Water Resources Association Conference, Syracuse (NY).
Walker Jr., W. W. & K. E. Havens, 1995. Relating algal bloom frequencies to phosphorus concentrations in Lake Okeechobee. Lake and Reservoir Management 11(1): 77–83.
Zan, F., S. Huo, B. Xi, C. Zhu, H. Liao, J. Zhang & K. M. Yeager, 2012. A 100-year sedimentary record of natural and anthropogenic impacts on a shallow eutrophic lake, Lake Chaohu, China. Journal of Environmental Monitoring 14: 804.
Zhang, J., P. Burke, N. Iricanin, S. Hill, S. Gray & R. Budell, 2011. Long-term water quality trends in the Lake Okeechobee Watershed, Florida. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology 41: 548–575.
Acknowledgments
This manuscript would not have been possible without the data collected by the South Florida Water Management District and disseminated by Tom James.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling editor: Alex Elliott
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Siders, Z.A., Havens, K.E. Revisiting the total maximum daily load total phosphorus goal in Lake Okeechobee. Hydrobiologia 847, 4221–4232 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-020-04406-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-020-04406-8