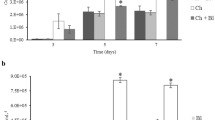
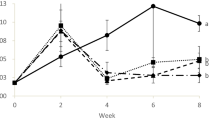
Abstract
The application of probiotics has varying effects on rotifer culture. These effects can either be directly on their growth and reproduction or indirectly by affecting the culture environment. The role played by specific probiotic candidates is still indistinct and further research is required to ascertain their significance in rotifer culture. In this study, euryhaline rotifer Brachionus rotundiformis (SS-type) was used to evaluate the effect of two commercial probiotic products on rotifer density, reproductive parameters and unionized ammonia concentration for a twelve-day culture period. To estimate these parameters, rotifers were cultured in glass bottles containing dilute sterilized sea water with the following five diet treatments: Nannochloropsis oculata (control), Igsign (PB1), Toaraze Aqua (PB2) or the combination of N. oculata with either PB1 or PB2. The rotifer density was significantly affected by the addition of probiotic. N. oculata + PB2 treatment resulted in higher rotifer density and specific growth rate compared to the control treatment. Mixis induction was unaffected by N. oculata + PB2 while it was repressed by N. oculata + PB1. Ammonia concentration was not significantly affected with the addition of probiotics. These results indicate that probiotics have synergetic effects with microalgae diet that resulted in the highest rotifer densities.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aoki, S. & A. Hino, 1996. Nitrogen flow in a chemostat culture of the rotifer Brachionus plicatilis. Fisheries Science 62: 8–14.
Araujo, A. & J. N. McNair, 2007. Individual- and population-level effects of antibiotics on the rotifers. Brachionus calyciflorus and B. plicatilis. Hydrobiologia 593: 185–199.
Benavente, G. P. & F. J. Gatesoupe, 1988. Bacteria associated with cultured rotifers and artemia are detrimental to larval turbot, Scophthalmus maximus L. Aquacultural Engineering 7: 289–293.
Burbank, D. R., S. E. Lapatra, G. Fornshell & K. D. Cain, 2012. Isolation of bacterial probiotic candidates from the gastrointestinal tract of rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum), and screening for inhibitory activity against Flavobacterium psychrophilum. Journal of Fish Diseases 35: 809–816.
Cruz, P. M., A. L. Ibáñez, O. A. M. Hermosillo & H. C. R. Saad, 2012. Use of probiotics in aquaculture. ISRN Microbiology 2012: 1–13.
de Araujo, A. B., T. W. Snell & A. Hagiwara, 2000. Effect of unionized ammonia, viscozity and protozoan contamination on the enzyme activity of the rotifer Brachionus plicalitis. Aquaculture Research 31: 359–365.
Devaraja, T. N., F. M. Yusoff & M. Shariff, 2002. Changes in bacterial populations and shrimp production in ponds treated with commercial microbial products. Aquaculture 206: 245–256.
Douillet, P. A., 2000. Bacterial additives that consistently enhance rotifer growth under synxenic culture conditions 2. Use of single and multiple bacterial probiotics. Aquaculture 182: 241–248.
FAO and WHO, 2002. WHO working group guidelines for the evaluation of probiotics in food. Guidelines for the Evaluation of Probiotics in Food, FAO, Rome, Italy.
Ferreira, M., P. Seixas, P. Coutinho, J. Fábregas & A. Otero, 2011. Effect of the nutritional status of semi-continuous microalgal cultures on the productivity and biochemical composition of Brachionus plicatilis. Marine Biotechnology 13: 1074–1085.
Gallardo, W. G., A. Hagiwara & T. W. Snell, 2000. Effect of juvenile hormone and serotonin (5-HT) on mixis induction of the rotifer Brachionus plicatilis Muller. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 252: 97–107.
Gallardo, W. G., A. Hagiwara, Y. Tomita, K. Soyano & T. W. Snell, 1997. Effect of some vertebrate and invertebrate hormones on the population growth, mictic female production, and body size of the marine rotifer Brachionus plicatilis Muller. Hydrobiologia 358: 113–120.
Geraylou, Z., M. P. M. Vanhove, C. Souffreau, E. Rurangwa, J. Buyse & F. Ollevier, 2014. In vitro selection and characterization of putative probiotics isolated from the gut of Acipenser baerii (Brandt, 1869). Aquaculture Research 45: 341–352.
Gilbert, J. J., 2010. Effect of food concentration on the production and viability of resting eggs of the rotifer Brachionus: Implications for the timing of sexual reproduction. Freshwater Biology 55: 2437–2446.
Gram, L., J. Melchiorsen, B. Spanggaard, I. Huber & T. F. Nielsen, 1999. Inhibition of Vibrio anguillarum by Pseudomonas fluorescens AH2, a possible probiotic treatment of fish. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 65: 969–973.
Hagiwara, A., A. Hino & R. Hirano, 1988a. Comparison of resting egg formation among five Japanese stocks of the rotifer Brachionus plicatilis. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 54: 577–580.
Hagiwara, A., A. Hino & R. Hirano, 1988b. Effects of temperature and chlorinity on resting egg formation in the rotifer Brachionus plicatilis. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 54: 569–575.
Hagiwara, A., K. Hamada, S. Hori & K. Hirayama, 1994. Increased sexual reproduction in Brachionus plicatilis (rotifera) with the addition of bacteria and rotifer extracts. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 181: 1–8.
Hagiwara, A., W. G. Gallardo, M. Assavaaree, T. Kotani & A. B. de Araujo, 2001. Live food production in Japan: Recent progress and future aspects. Aquaculture 200: 111–127.
Harzevili, A. R. S., H. Van Duffel, P. Dhert, J. Swings & P. Sorgeloos, 1998. Use of a potential probiotic Lactococcus lactis AR21 strain for the enhancement of growth in the rotifer Brachionus plicatilis (Muller). Aquaculture Research 29: 411–417.
Hauville, M. R., J. L. Zambonino-Infante, J. G. Bell, H. Migaud & K. L. Main, 2016. Effects of a mix of Bacillus sp. as a potential probiotic for Florida pompano, common snook and red drum larvae performances and digestive enzyme activities. Aquaculture Nutrition 22: 51–60.
Jamali, H., A. Imani, D. Abdollahi, R. Roozbehfar & A. Isari, 2015. Use of probiotic Bacillus spp. in rotifer (Brachionus plicatilis) and Artemia (Artemia urmiana) enrichment: Effects on growth and survival of Pacific white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei, larvae. Probiotics and Antimicrobial Proteins 7: 118–125.
Kagali, R. N., E. O. Ogello, Y. Sakakura & A. Hagiwara, 2018. Fish-processing wastes as an alternative diet for culturing the minute rotifer Proales similis de Beauchamp. Aquaculture Research 49: 2477–2485.
Kogane, T., A. Hagiwara & K. Imaizumi, 1997. Temperature conditions enhancing resting egg production of the euryhaline rotifer Brachionus plicatilis O. F. Müller (Kamiura strain). Hydrobiologia 358: 167–171.
Lalloo, R., G. Moonsamy, S. Ramchuran, J. Görgens & N. Gardiner, 2010. Competitive exclusion as a mode of action of a novel Bacillus cereus aquaculture biological agent. Letters in Applied Microbiology 50: 563–570.
Le, D. V., P. N. Nguyen, K. Dierckens, D. V. Nguyen, P. De Schryver, A. Hagiwara & P. Bossier, 2017. Growth performance of the very small rotifer Proales similis is more dependent on proliferating bacterial community than the bigger rotifer Brachionus rotundiformis. Aquaculture 476: 185–193.
Loo, P. L., V. C. Chong, S. Vikineswary & S. Ibrahim, 2016. Waste-grown phototrophic bacterium supports culture of the rotifer, Brachionus rotundiformis. Aquaculture Research 47: 3029–3041.
Lotka, A. J., 1913. A natural population norm. I. Journal of the Washington Academy of Sciences 3: 241–248.
Lubzens, E., Y. Wax, G. Minkoff & F. Adler, 1993. A model evaluating the contribution of environmental factors to the production of resting eggs in the rotifer Brachionus plicatilis. Hydrobiologia 255–256: 127–138.
Luo, Z., X. H. Bai & C. F. Chen, 2014. Integrated application of two different screening strategies to select potential probiotics from the gut of channel catfish Ictalurus punctatus. Fisheries Science 80: 1269–1275.
Maeda, M., A. Shibata, G. Biswas, H. Korenaga, T. Kono, T. Itami & M. Sakai, 2014. Isolation of lactic acid bacteria from Kuruma shrimp (Marsupenaeus japonicus) intestine and assessment of immunomodulatory role of a selected strain as probiotic. Marine Biotechnology 16: 181–192.
Murillo, I. & L. Villamil, 2011. Bacillus cereus and Bacillus subtilis used as probiotics in rotifer (Brachionus plicatilis) cultures. Journal of Aquaculture Research & Development. https://doi.org/10.4172/2155-9546.S1-007.
Navarrete, P. & D. Tovar-Ramrez, 2014. Use of yeasts as probiotics in fish aquaculture. In Hernandez-Vergara, M. (eds), Sustainable Aquaculture Techniques. IntechOpen: 135–172.
Nogami, K. & M. Maeda, 1992. Bacteria as biocontrol agents for rearing larvae of the crab Portunus trituberculatus. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 49: 2373–2376.
Ogello, E. O., Y. Sakakura & A. Hagiwara, 2017. Culturing Brachionus rotundiformis Tschugunoff (Rotifera) using dried foods: application of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Hydrobiologia 796: 99–110.
Ogello, E. O., S. Wullur, Y. Sakakura & A. Hagiwara, 2018. Composting fishwastes as low-cost and stable diet for culturing Brachionus rotundiformis Tschugunoff (Rotifera): Influence on water quality and microbiota. Aquaculture 486: 232–239.
Planas, M., J. A. Vázquez, J. Marqués, R. Pérez-Lomba, M. P. González & M. Murado, 2004. Enhancement of rotifer (Brachionus plicatilis) growth by using terrestrial lactic acid bacteria. Aquaculture 240: 313–329.
Qi, Z., X. H. Zhang, N. Boon & P. Bossier, 2009. Probiotics in aquaculture of China – Current state, problems and prospect. Aquaculture 290: 15–21.
Ramesh, D., A. Vinothkanna, A. K. Rai & V. S. Vignesh, 2015. Isolation of potential probiotic Bacillus spp. and assessment of their subcellular components to induce immune responses in Labeo rohita against Aeromonas hydrophila. Fish and Shellfish Immunology 45: 268–276.
Rhee, J. S., B. M. Kim, C. B. Jeong, H. G. Park, K. M. Y. Leung, Y. M. Lee & J. S. Lee, 2013. Effect of pharmaceuticals exposure on acetylcholinesterase (AchE) activity and on the expression of AchE gene in the monogonont rotifer, Brachionus koreanus. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology – C Toxicology and Pharmacology 158: 216–224.
Rombaut, G., P. Dhert, J. Vandenberghe, L. Verschuere, P. Sorgeloos & W. Verstraete, 1999. Selection of bacteria enhancing the growth rate of axenically hatched rotifers (Brachionus plicatilis). Aquaculture 176: 195–207.
Snell, T. W., 2017. Analysis of proteins in conditioned medium that trigger monogonont rotifer mictic reproduction. Hydrobiologia 796: 245–253.
Snell, T. W. & E. M. Boyer, 1988. Thresholds for mictic female production in the rotifer Brachionus plicatilis (Muller). Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 124: 73–85.
Snell, T. W. & F. H. Hoff, 1985. The effect of environmental factors on resting egg production in the rotifer Brachionus plicatilis. Journal of the World Mariculture Society 16: 484–497.
Spencer, M., N. Colegrave & S. S. Schwartz, 2001. Hatching fraction and timing of resting stage production in seasonal environments: Effects of density dependence and uncertain season length. Journal of Evolutionary Biology 14: 357–367.
Suga, K., N. Oshiyama, Y. Tanaka, Y. Sakakura & A. Hagiwara, 2011a. Isolation of mixis-related genes from the rotifer Brachionus plicatilis using subtractive hybridization. Hydrobiologia 662: 83–88.
Suga, K., Y. Tanaka, Y. Sakakura & A. Hagiwara, 2011b. Axenic culture of Brachionus plicatilis using antibiotics. Hydrobiologia 662: 113–119.
Sun, Y.-Z., H.-L. Yang, Z.-C. Ling & J.-D. Ye, 2015. Microbial communities associated with early stages of intensively reared orange-spotted grouper (Epinephelus coioides). Aquaculture Research 46: 131–140.
Sun, Y. Z., H. L. Yang, R. L. Ma & W. Y. Lin, 2010. Probiotic applications of two dominant gut Bacillus strains with antagonistic activity improved the growth performance and immune responses of grouper Epinephelus coioides. Fish and Shellfish Immunology 29: 803–809.
Talpur, A. D., M. Ikhwanuddin, M. D. D. Abdullah & A. M. A. Bolong, 2013. Indigenous Lactobacillus plantarum as probiotic for larviculture of blue swimming crab, Portunus pelagicus (Linnaeus, 1758): Effects on survival, digestive enzyme activities and water quality. Aquaculture 416–417: 173–178.
Watanabe, K., K. Sezaki, K. Yazawa & A. Hino, 1992. Nutritive fortification of the rotifer Brachionus plicatilis with eicosapentaenoic acid-producing bacteria. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 58: 271–276.
Xiang, X. L., Y. L. Zhu, Q. L. Xu, L. Y. Zhu & Y. L. Xi, 2017. Comprehensive effects of tetracycline hydrochloride concentration on life history traits of Brachionus calyciflorus under different food densities. Shengtai Xuebao/Acta Ecologica Sinica 37: 7718–7728.
Yoshimura, K., K. Usuki, T. Yoshimatsu, C. Kitajima & A. Hagiwara, 1997. Recent development of a high density mass culture system for the rotifer Brachionus rotundiformis Tschugunoff. Hydrobiologia 358: 139–144.
Yu, J.-P. & K. Hirayama, 1986. Study on the unexpected sudden decrease and suppressed growth of the rotifer population in mass culture – I The effect of un-ionized ammonia on the population growth of the rotifer in mass culture. Bulletin of the Japanese Society of Scientific Fisheries 52: 1509–1513.
Yu, J.-P., A. Hino, M. Ushiro & M. Maeda, 1989. Function of bacteria as vitamin B12 producers during mass culture of the rotifer Brachionus plicatilis. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 55: 1799–1806.
Yu, J.-P., K. Hirayama & A. Hino, 1994. The role of bacteria in mass culture of rotifer Brachionus plicatilis. Bulletin of National Research Institute of Aquaculture, Supplement 1: 67–70.
Acknowledgements
This research was partly supported by Japanese Society for Promotion of Sciences (JSPS) KAKENHI Grant number JP17H038662 to Atsushi Hagiwara as well as Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA) which provided Ph.D. fellowship to Robert N. Kagali under the JKUAT/PAUSTI/AU Network project_Nagasaki University (J1610573). The commercial probiotic products used in this research were provided by Toa pharmaceutical company Limited, Tokyo, Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Guest editors: Steven A. J. Declerck, Diego Fontaneto, Rick Hochberg & Terry W. Snell / Crossing Disciplinary Borders in Rotifer Research
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kagali, R.N., Kim, HJ., Koga, T. et al. Effect of two commercial probiotic products on population growth of rotifer Brachionus rotundiformis Tschugunoff. Hydrobiologia 844, 173–182 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-018-3852-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-018-3852-0