Abstract
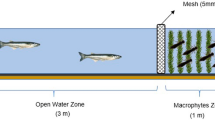
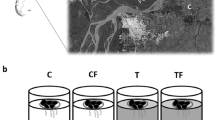
Whether macrophytes offer an effective refuge for zooplankton in all shallow lakes is subject to debate. To explore potential constraints between different predator threats and the related habitat choice by zooplankton, we conducted a mesocosm experiment in 12 large-sized pools mimicking the nearshore environment with part of its length being covered by submersed macrophytes (Egeria densa) and holding a mixed zooplankton community. Four treatments were used: (i) young zooplanktivorous fish (3 silverside, Odontesthes bonariensis) in the “open-water” zone; (ii) macroinvertebrate predator (31 grass shrimp, Palaemonetes argentinus) in the vegetated zone; (iii) both, fish in the open-water and shrimp in the vegetated zones; and (iv) control with no predators. Our results show specific effects of each predator on the abundance, composition, and size of cladocerans. Regarding distribution, in control and shrimp mesocosms, no differences were found between the two zones, while cladocerans were clearly more abundant in the vegetated side in the presence of fish. When both fish and shrimp were present, cladocerans preferred the vegetated zone too, but in a smaller proportion, and their abundance was less. The presence of predatory macroinvertebrates in vegetated littoral zone reduces the refuge value of this habitat, at least for cladocerans.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balseiro, E. G., 1992. The role of pelagic water mites in the control of cladoceran population in a temperate lake of the southern Andes. Journal of Plankton Research 14: 1267–1277.
Boveri M., 2009. Interacciones tróficas en el ecosistema de las lagunas pampeanas: estudios experimentales en mesocosmos. Tesis de doctorado, Escuela para graduados, Facultad de Agronomía, Universidad de Buenos Aires.
Boveri, M. & R. Quirós, 2003. Trophic interactions in pampean shallow lakes: evaluation of silverside predatory effects in mesocosm experiments. Internationale Vereinigung fur Theoretische und Angewandte Limnologie Verhandlungen 28: 1274–1278.
Boveri, M. & R. Quirós, 2007. Cascading trophic effects in pampean shallow lakes: results of a mesocosm experiment using two coexisting fish species with different feed strategies. Hydrobiologia 584: 215–222.
Boveri, M. B. & P. M. Binder, 2015. Fish as links between pelagic and littoral zones: feeding strategy of “Sabalito”(Cyphocharax voga) in a mesocosm experiment. Pan-American Journal of Aquatic Sciences 10: 297–308.
Brooks, J. L. & S. I. Dodson, 1965. Predation, body size, and composition of plankton. Science 150: 28–35.
Burks, R. L., E. Jeppesen & D. M. Lodge, 2001. Littoral zone structures as Daphnia refugia against fish predators. Limnology and Oceanography 46: 230–237.
Burks, R. L., D. M. Lodge, E. Jeppesen & T. L. Lauridsen, 2002. Diel horizontal migration of zooplankton: costs and benefits of inhabiting the littoral. Freshwater Biology 47: 343–365.
Canfield, D. E., J. V. Shireman, D. E. Colle, W. T. Haller, C. E. Watkins & M. J. Maceina, 1984. Prediction of chlorophyll a concentrations in Florida Lakes – importance of aquatic macrophytes. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 41: 497–501.
Carpenter, S., J. F. Kitchell & J. R. Hodgson, 1985. Cascading trophic interactions and lake productivity. Bioscience 35: 634–639.
Collins, P., 1995. Variaciones diarias de la actividad trófica en una población de Palaemonetes argentinus (Crustacea Decapoda). Revista de la Asociación de Ciencias Naturales del Litoral 26: 57–66.
Collins, P. A., 1999. Feeding of Palaemonetes argentinus (Decapoda: Palaemonidae) from an Oxbow Lake of the Paraná River, Argentina. Journal of Crustacean Biology 19: 485–492.
Collins, P. A. & J. C. Paggi, 1998. Feeding ecology of Macrobrachium borellii (Nobili) (Decapoda: Palaemonidae) in flood valley of river Parana Argentina. Hidrobiologia 362: 21–30.
Descalzo, M., 2015. Estudio del efecto de la presencia de Madrecita (Cnesterodon decemmaculatus) sobre los hábitos alimentarios de Pejerrey (Odontesthes bonariensis) y sus impactos derivados en el sistema: una experiencia en mesocosmos. Tesis de grado, Facultad de Agronomía, Universidad de Buenos Aires.
Edmondson, W. T. & G. G. Winberg, 1971. A Manual on Methods for the Assessment of Secondary Productivity in Fresh Waters. IBP Handbook N° 17. Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford.
Estlander, S., J. Horppila, M. Olin & L. Nurminen, 2017. Should I stay or should I go? The diurnal behaviour of plant-attached zooplankton in lakes with different water transparency. Journal of Limnology 76: 253–260.
Fontanarrosa, M., G. Chaparro, P. de Tezanos Pinto, P. Rodríguez & I. O’Farrell, 2010. Zooplankton response to shading effects of free-floating plants in shallow warm temperate lakes: a field mesocosm experiment. Hydrobiologia 646: 231–242.
Gilbert, J. J. & S. E. Hampton, 2001. Diel vertical migrations of zooplankton in shallow, fishless pond: a possible avoidance-response cascade induced by notonectids. Freshwater Biology 46: 611–621.
Giri, F. & P. Collins, 2004. Eficiencia de captura del camarón dulceacuícola Palaemonetes argentinus (Nobili 1901) sobre larvas de mosquito Culex pipiens sl (Linnaeus 1758). Hidrobiológica 14: 85–90.
González Sagrario, M. A. & E. Balseiro, 2003. Indirect enhancement of large zooplankton by consumption of predacious macroinvertebrates by littoral fish. Archiv für Hydrobiologie 158: 551–574.
González Sagrario, M. A. & E. Balseiro, 2010. The role of macroinvertebrates and fish in regulating the provision by macrophytes of refugia for zooplankton in a warm temperate shallow lake. Freshwater Biology 55: 2153–2166.
González Sagrario, M. A., E. Balseiro, R. Ituarte & E. Spivak, 2009. Macrophytes as refuge or risky area for zooplankton: a balance set by littoral predacious macroinvertebrates. Freshwater Biology 54: 1042–1053.
Hampton, S. E., J. J. Gilbert & C. W. Burns, 2000. Direct and indirect effects of juvenile Buenoa macrotibialis (Hemiptera: Notonectidae) on the zooplankton of a shallow pond. Limnology and Oceanography 45: 1006–1012.
Herwig, B. R. & D. E. Schindler, 1996. Effects of aquatic insect predators on zooplankton in fishless ponds. Hydrobiologia 324: 141–147.
Haney, J. F. & D. J. Hall, 1973. Sugar-coated Daphnia: a preservation technique for Cladocerans. Limnology and Oceanography 18: 331–333.
Hindley, J. P. R., 1975. The detection, location and recognition of food by juvenile banana prawns, Penaeus marguiensis. Marine Behavioural Physiology 3: 193–210.
Hirvonen, H., 1999. Shifts in foraging tactics of larval damselflies: effects of prey density. Oikos 86: 443–452.
Hurlbert, S. H. & M. S. Mulla, 1981. Impacts of mosquitofish (Gambusia affinis) predation on plankton communities. Hydrobiologia 83: 125–151.
Hrbacek, J., M. Dvorakova, V. Korinek & L. Prochazkova, 1961. Demonstration of the effect of fish stock on the species composition of zooplankton and the intensity of metabolism of the whole plankton association. Internationale Vereinigung fur Theoretische und Angewandte Limnologie Verhandlungen 14: 192–195.
Iglesias, C., G. Goyenola, N. Mazzeo, M. Meerhoff, E. Rodó & E. Jeppesen, 2007. Horizontal dynamics of zooplankton in subtropical Lake Blanca (Uruguay) hosting multiple zooplankton predators and aquatic plant refuges. Hydrobiologia 584: 179–189.
Iglesias, C., N. Mazzeo, G. Goyenola, C. Fosalba, F. Teixeira de Mello, S. García & E. Jeppesen, 2008. Field and experimental evidence of the effect of Jenynsia multidentata, a small omnivorous–planktivorous fish, on the size distribution of zooplankton in subtropical lakes. Freshwater Biology 53: 1797–1807.
Iglesias, C., E. Jeppesen, N. Mazzeo, J. P. Pacheco, F. T. D. Mello, F. Landkildehus, C. Fosalba, J. M. Clemente & M. Meerhoff, 2017. Fish but not macroinvertebrates promote trophic cascading effects in high density submersed plant experimental lake food webs in two contrasting climate regions. Water 9: 514.
Jeppesen, E., T. L. Lauridsen, T. Kairesalo & M. Perrow, 1998. Impact of submerged macrophytes on fish–zooplankton interactions in lakes. In Jeppesen, E., M. Søndergaard, M. Søndergaard & K. Christoffersen (eds), The Structuring Role of Submerged Macrophytes in Lakes Ecological Studies, 131. Springer, New York: 91–114.
Jeppesen, E., J. P. Jensen, M. Søndergaard & T. Lauridsen, 1999. Trophic dynamics in turbid and clearwater lakes with special emphasis on the role of zooplankton for water clarity. Hidrobiología 408(409): 217–231.
Jeppesen, E., J. P. Jensen, M. Søndergaard, T. Lauridsen & F. Landkildehus, 2000. Trophic structure, species richness and biodiversity in Danish lakes: changes along a phosphorus gradient. Freshwater Biology 45: 201–218.
Jeppesen, E., M. Søndergaard, N. Mazzeo, M. Meerhoff, C. C. Branco, V. Huszar & F. Scasso, 2005. Lake restoration and biomanipulation in temperate lakes: relevance for subtropical and tropical lakes. In Reedy, M. V. (ed.), Tropical Eutrophic Lakes: Their Restoration and Management. Science Publishers, Enfield: 331–359.
Lauridsen, T. L. & I. Buenk, 1996. Diel changes in the horizontal distribution of zooplankton in the littoral zones of two shallow eutrophic lakes. Archiv für Hydrobiologie 137: 161–176.
Lauridsen, T., L. J. Pedersen, E. Jeppesen & M. Sønergaard, 1996. The importance of macrophyte bed size for cladoceran composition and horizontal migration in a shallow lake. Journal of Plankton Research 18: 2283–2294.
Lauridsen, T. L., E. Jeppesen, M. Søndergaard & D. M. Lodge, 1998. Horizontal migration of zooplankton: predator-mediated use of macrophyte habitat. In Jeppesen, E., M. Søndergaard, M. Søndergaard & K. Christoffersen (eds), The Structuring Role of Submerged Macrophytes in Lakes. Ecological Studies, 131. Springer, New York: 233–239.
Lopretto, E. C. & G. Tell, 1995. Ecosistemas de Aguas Continentales. Ediciones Sur, La plata.
Meerhoff, M., C. Fosalba, C. Bruzzone, N. Mazzeo, W. Noordoven & E. Jeppesen, 2006. An experimental study of habitat choice by Daphnia: plants signal danger more than refuge in subtropical lakes. Freshwater Biology 51: 1320–1330.
Meerhoff, M., C. Iglesias, F. Teixeira de Mello, J. M. Clemente, E. Jensen, T. L. Lauridsen & E. Jeppesen, 2007a. Effects of habitat complexity on community structure and predator avoidance behaviour of littoral zooplankton in temperate versus subtropical shallow lakes. Freshwater Biology 52: 1009–1021.
Meerhoff, M., J. M. Clemente, F. Teixeira de Mello, C. Iglesias, A. R. Pedersen & E. Jeppesen, 2007b. Can warm climate-related structure of littoral predator assemblies weaken the clear water state in shallow lakes? Global Change Biology 13: 1888–1897.
Moss, B., 1998. Ecology of Fresh Waters Man and Medium, Past to Future, 3rd ed. Blackwell Science Limited, London.
Nurminen, L. K. & J. A. Horppila, 2002. A diurnal study on the distribution of filter feeding zooplankton: Effect of emergent macrophytes, pH and lake trophy. Aquatic Sciences-Research Across Boundaries 64: 198–206.
O’Brien, J. W., 1979. The predator – prey interaction of planktivorous fish and zooplankton. American scientist 67: 572–581.
Onsem, S., S. Backer & L. Triest, 2010. Microhabitat–zooplankton relationship in extensive macrophyte vegetations of eutrophic clear-water ponds. Hydrobiologia 656: 67–81.
Paggi, J. C., 1995. Crustacea Cladocera. In Lopretto, E. C. & G. Tell (eds), Ecosistemas de Aguas Continentales. Ediciones Sur, La Plata.
Palacios, G. G., 2016. Controlando a los controladores. Interacciones tróficas y refugio de los herbívoros en lagunas eutrofizadas: acción de los peces zooplanctívoros sobre el zooplancton. Tesis de grado, Facultad de Agronomía, Universidad de Buenos Aires.
Popper, A. N., M. Salomon & H. W. Kenneth, 2001. Acoustic detection and communication by decapod crustaceans. Journal of Comparative Physiology 178: 83–89.
Quirós, R., 1988. Relationships between air temperature, depth, nutrients and chlorophyll in 103 Argentinian lakes. Vereinigung fur Theoretische und Angewandte Limnologie Verhandlungen 23: 647–658.
Relyea, R. A., 2003. How prey respond to combined predators: a review and an empirical test. Ecology 84: 1827–1839.
Rennella, A. M. & R. Quirós, 2002. Relations between planktivorous fish and zooplankton in two very shallow lakes of the pampa plain. Verhandlungen des Internationalen Verein Limnologie 28: 887–891.
Ringuelet, R. A., R. Iriart & A. H. Escalante, 1980. Alimentación del pejerrey (Basilichthys bonariensis bonariensis, Atherinidae) en laguna de Chascomús (Buenos Aires, Argentina). Relaciones ecológicas de complementación y eficiencia trófica del plancton. Limnobios 1: 447–460.
Romero, M. E., 2012. Análisis de la predación selectiva de Odontesthes bonariensis sobre el zooplancton en la laguna pampeana de Gómez. Tesis de grado, Facultad de Agronomía, Universidad de Buenos Aires.
Rosso, J. J., 2006. Peces pampeanos: guía y ecología. LOLA, Buenos Aires.
Rosso, J. J., A. Rennella Sosnovsky, A. M. Rennella & R. Quirós, 2010. Relationships between fish species abundances and water transparency in hypertrophic turbid waters of temperate shallow lakes. International Review of Hydrobiology 95: 142–155.
Scheffer, M., 1998. Ecology of Shallow Lakes. Chapman & Hall, London.
Scheffer, M. & E. H. van Nes, 2007. Shallow lakes theory revisited: various alternative regimes driven by climate, nutrients, depth and lake size. Hydrobiologia 584: 455–466.
Scheffer, M., S. H. Hosper, M. L. Meijer, B. Moss & E. Jeppesen, 1993. Alternative equilibria in shallow lakes. Trends in Ecology 8: 275–279.
Schriver, P., J. Bøgestrand, E. Jeppesen & M. Søndergaard, 1995. Impact of submerged macrophytes on fish–zooplankton–phytoplankton interactions: large-scale experiments in a shallow eutrophic lake. Freshwater Biology 33: 255–270.
Seminara, M., D. Vagaggini & F. G. Margaritor, 2008. Differential responses of zooplankton assemblages to environmental variation in temporary and permanent ponds. Aquatic Ecology 42: 129–140.
Sosnovsky, A. & R. Quirós, 2009. Effects of fish manipulation on the plankton community in small hypertrophic lakes from the Pampa Plain (Argentina). Limnologica-Ecology and Management of Inland Waters 39: 219–229.
Tavşanoğlu, Ü. N., S. Brucet, E. E. Levi, T. Bucak, G. Bezirci, A. Özen, L. S. Johansson, E. Jeppesen & M. Beklioğlu, 2015. Size--based diel migration of zooplankton in Mediterranean shallow lakes assessed from in situ experiments with artificial plants. Hydrobiologia 753: 47–59.
Teixeira de Mello, F., M. Meerhoff, Z. Pekcan-Hekim & E. Jeppesen, 2009. Substantial differences in littoral fish community structure and dynamics in subtropical and temperate shallow lakes. Freshwater Biology 54: 1202–1215.
Timms, R. M. & B. Moss, 1984. Prevention of growth of potentially dense phytoplankton populations by zooplankton grazing, in presence of zooplanktivorous fish, in a shallow wetland ecosystem. Limnology and Oceanography 29: 472–486.
Van den Berg, M. S., H. Coops, M. L. Meijer, M. Scheffer & J. Simons, 1998. Clear water associated with a dense Chara vegetation in the shallow and turbid Lake Veluwemeer, The Netherlands. In Jeppesen, E., M. Søndergaard, M. Søndergaard & K. Christoffersen (eds), The Structuring Role of Submerged Macrophytes in Lakes. Ecological Studies, 131. Springer, New York: 339–351.
Vinyard, G. L. & W. J. O’Brien, 1976. Effects of light and turbidity on the reactive distance of bluegill (Lepomis macrochirus). Journal of the Fisheries Board of Canada 33: 2845–2849.
Wicklum, D., 1999. Variation in horizontal zooplankton abundance in mountain lakes: shore avoidance or fish predation? Journal of Plankton Research 21: 1957–1975.
Acknowledgements
We thank A. Rennella, A. López, P. Binder, and F. Olarte for their assistance in preparing the manuscript; the staff and volunteers of Acuicultura who helped during the experiment; and the editor and two anonymous referees for their valuable suggestions. We also thank Chascomús Hydrobiological Station for the fish supply. This study was supported by the Universidad de Buenos Aires, Programación científica 2013–2016, UBACyT, 20020130200198BA: Caracterización del ecosistema de las lagunas pampeanas bajo distintas condiciones de uso del suelo en su cuenca de drenaje.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Guest editors: S. Nandini, S.S.S. Sarma, Erik Jeppesen & Linda May / Shallow Lakes Research: Advances and Perspectives
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mamani, A., Koncurat, M.L. & Boveri, M. Combined effects of fish and macroinvertebrate predation on zooplankton in a littoral mesocosm experiment. Hydrobiologia 829, 19–29 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-018-3712-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-018-3712-y