Abstract
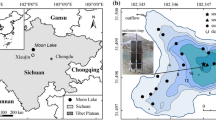
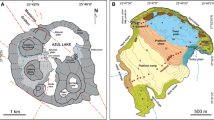
Within-lake spatio-temporal variability of remains of cladocerans and diatoms were examined, using trap and surficial sediment sampling approaches in Lugu Lake, one of the deep mountain lakes in the subtropical region of southwest China, to understand the response to recent environmental change. Seasonality played a strong role in the distribution patterns of both cladocerans and diatoms, but their responses to seasonal change varied. The rich resources of food supported a cladoceran population peak during summer, while increased mixing and higher nutrient triggered diatom blooms in spring. The summer also witnessed increased grazing effects of primary consumers on diatoms when the water column was nutrient-enriched. In particular, Ceriodaphnia intensified grazing on small diatoms (Cyclotella ocellata), consequently affecting community patterns during summer, while increased wind activity during spring induced turbulence, remixing, transportation and depositional processes of remains of littoral Alona guttata and benthic diatoms. The distribution pattern of cladocerans in surface sediments was similar to that of diatoms. Seasonal community patterns and trophic interactions between cladocerans and diatoms in trap and surface sediments of differential depth gradients provide evidence that high-resolution sampling of multi-proxy biological remains in deep mountain lakes of southwest China can help reduce biases in paleoenvironmental reconstructions.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrantes, N., S. C. Antunes, M. J. Pereira & F. Gonçalves, 2006. Seasonal succession of cladocerans and phytoplankton and their interactions in a shallow eutrophic lake (Lake Vela, Portugal). Acta Oecologica 29(1): 54–64.
Anderson, N. J., 2000. Diatoms, temperature and climatic change. European Journal of Phycology 35(4): 307–314.
Anneville, O., J. C. Molinero, S. Souissi & D. Gerdeaux, 2010. Seasonal and interannual variability of cladoceran communities in two peri-alpine lakes: uncoupled response to the 2003 heat wave. Journal of Plankton Research 32(6): 913–925.
Antunes, S. C., N. Abrantes & F. Gonçalves, 2009. Seasonal variation of the abiotic parameters and the cladoceran assemblage of Lake Vela: comparison with previous studies. Annales de Limnologie – International Journal of Limnology 39(3): 255–264.
Battarbee, R. W., 1986. Diatom analysis. Wiley Interscience, Chichester.
Battarbee, R. W., 2000. Palaeolimnological approaches to climate change, with special regard to the biological record. Quaternary Science Reviews 19(1): 107–124.
Battarbee, R. W. & M. Kneen, 1982. The use of electronically counted microspheres in absolute diatom analysis. Limnology and Oceanography 27(1): 184–188.
Battarbee, R. W., N. J. Anderson, E. Jeppesen & P. R. Leavitt, 2005. Combining palaeolimnological and limnological approaches in assessing lake ecosystem response to nutrient reduction. Freshwater Biology 50(10): 1772–1780.
Bennion, H., S. Wunsam & R. Schmidt, 1995. The validation of diatom-phosphorus transfer functions: an example from Mondsee, Austria. Freshwater Biology 34: 271–283.
Berger, S. A., S. Diehl, H. Stibor, G. Trommer & M. Ruhenstroth, 2010. Water temperature and stratification depth independently shift cardinal events during plankton spring succession. Global Change Biology 16(7): 1954–1965.
Birks, H. J. B., 2010. Numerical methods for the analysis of diatom assemblage data. In Smol, J. P. & E. F. Stoermer (eds), The Diatoms: Applications for the Environmental and Earth Science. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge: 23–54.
Bos, D. G. & B. F. Cumming, 2003. Sedimentary Cladoceran remains and their relationship to nutrients and other limnological variables in 53 lakes from British Columbia, Canada. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 60(10): 1177–1189.
Bos, D. G., B. F. Cumming & J. P. Smol, 1999. Cladocera and Anostraca from the Interior Plateau of British Columbia, Canada, as paleolimnological indicators of salinity and lake level. Hydrobiologia 392(2): 129–141.
Bottrell, H. H., 1975. The relationship between temperature and duration of egg development in some epiphytic Cladocera and Copepoda from the River Thames, Reading, with a discussion of temperature functions. Oecologia 18(1): 63–84.
Bradbury, J. P., Y. V. Bezrukova, G. P. Chernyaeva, S. M. Colman, G. Khursevich, J. W. King & Y. V. Likoshway, 1994. A synthesis of post-glacial diatom records from Lake Baikal. Journal of Paleolimnology 10: 213–252.
Brett, M. T. & D. C. Müller-Navarra, 1997. The role of highly unsaturated fatty acids in aquatic foodweb processes. Freshwater Biology 38(3): 483–499.
Burks, R. L., E. Jeppesen & D. M. Lodge, 2001. Littoral zone structures as Daphnia refugia against fish predators. Limnology and Oceanography 46(2): 230–237.
Carpenter, S. R. & K. L. Kitchell, 1993. The trophic Cascade in Lakes. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Catalan, J. M., M. Ventura, A. Brancelj, I. Granados, H. Thies, U. Nickus, A. Korhola, A. F. Lotter, A. Barbieri, E. Stuchlík, L. Lien, P. Bitušík, T. Buchaca, L. Camarero, G. H. Goudsmit, J. Kopácek, G. Lemcke, D. M. Livingston, B. Müller, M. Rautio, M. Šiško, S. Sorvari, F. S. Šporka & O. M. Toro, 2002. Seasonal ecosystem variability in remote mountain lakes-implications for detecting climatic signals in sediment records. Journal of Paleolimnology 28: 25–46.
Chu, G., J. Liu, G. Schettler, J. Li, Q. Sun, Z. Gu, H. Lu, Q. Liu & T. Liu, 2005. Sediment fluxes and varve formation in Sihailongwan, a maar lake from northeastern China. Journal of Paleolimnology 34(3): 311–324.
Davidson, T. A., C. D. Sayer, M. R. Perrow, M. Bramm & E. Jeppesen, 2007. Are the controls of species composition similar for contemporary and sub-fossil cladoceran assemblages? A study of 39 shallow lakes of contrasting trophic status. Journal of Paleolimnology 38(1): 117–134.
De Senerpont Domis, L. N., J. J. Elser, A. S. Gsell, V. L. Huszar, B. W. Ibelings, E. Jeppesen, S. Kosten, W. M. Mooij, F. Roland & U. Sommer, 2013. Plankton dynamics under different climatic conditions in space and time. Freshwater Biology 58(3): 463–482.
DeMott, W. R., 1982. Feeding selectivities and relative ingestion rates. Limnology and Oceanography 27(3): 518–527.
Deng, D., P. Xie, Q. Zhou, H. Yang, L. Guo & H. Geng, 2008. Field and experimental studies on the combined impacts of cyanobacterial blooms and small algae on crustacean zooplankton in a large, eutrophic, subtropical. Chinese lake. Limnology 9(1): 1–11.
DeSellas, A. M., A. M. Paterson, J. N. Sweetman & J. P. Smol, 2008. Cladocera assemblages from the surface sediments of south-central Ontario (Canada) lakes and their relationships to measured environmental variables. Hydrobiologia 600(1): 105–119.
Dickman, E. M., J. M. Newell, M. J. Gonzalez & M. J. Vanni, 2008. Light, nutrients, and food-chain length constrain planktonic energy transfer efficiency across multiple trophic levels. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 105(47): 18408–18412.
Duigan, C. A. & H. H. Birks, 2000. The late-glacial and early-Holocene palaeoecology of cladoceran microfossil assemblages at Kråkenes, western Norway, with a quantitative reconstruction of cladoceran. Journal of Paleolimnology 23: 67–76.
Fourtanier, E. & J. P. Kociolek, 1999. Catalogue of the diatom genera. Diatom Research 14(1): 1–190.
Frey, D. G., 1958. The late-glacial cladoceran fauna of a small lake. Archiv fur Hydrobiologie 54: 209–275.
Frey, D. G., 1959. The taxonomic and phylogenetic significance of the head pores of the Chydoridae (Cladocera). Internationale Revue der gesamten Hydrobiologie und Hydrographie 44(1–4): 27–50.
Frey, D. G., 1973. Comparative morphology and biology of three species of Eurycercus (Chydoridae, Cladocera) with a description of Eurycercus macrocanthus sp. nov. Internationale Revue der gesamten Hydrobiologie und Hydrographie 58(2): 221–267.
Frey, D. G., 1986. Cladocera analysis. Handbook of Holocene palaeoecology and palaeohydrology: 667–692.
Frey, D. G., 1988. Littoral and offshore communities of diatoms, cladocerans and dipterous larvae, and their interpretation in paleolimnology. Journal of Paleolimnology 1: 179–191.
Gillooly, J. F. & S. I. Dodson, 2000. Latitudinal patterns in the size distribution and seasonal dynamics of new world, freshwater cladocerans. Limnology and Oceanography 45(1): 22–30.
Gliwicz, Z. M., 2003. Between Hazards of starvation and risk of predation: the ecology of offshore animals. International Ecology Institute, Oldendorf/Luhe.
Greenwood, T. L., J. D. Green, B. J. Hicks & M. A. Chapman, 1999. Seasonal abundance of small cladocerans in Lake Mangakaware, Waikato, New Zealand. New Zealand Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research 33(3): 399–415.
Gyllström, M., L.-A. Hansson, E. Jeppesen, F. Garcia-Criado, E. Gross, K. Irvine, T. Kairesalo, R. Kornijów, M. R. Miracle, M. Nykänen, T. Noges, S. Romo, D. Stephen, Ev Donk & B. Moss, 2005. The role of climate in shaping zooplankton communities of shallow lakes. Limnology and Oceanography 50: 2008–2021.
Hambright, K. D., T. Zohary, J. Easton, B. Azoulay & T. Fishbein, 2001. Effects of zooplankton grazing and nutrients on the bloom-forming, N2-fixing cyanobacterium Aphanizomenon in Lake Kinneret. Journal of Plankton Research 23(2): 165–174.
Hausmann, S. & R. Pienitz, 2009. Seasonal water chemistry and diatom changes in six boreal lakes of the Laurentian Mountains (Québec, Canada): impacts of climate and timber harvesting. Hydrobiologia 635(1): 1–14.
Hofmann, W., 1978. Bosmina (Eubosmina) populations of Grosser Plöner See and Schöhsee lakes during late-glacial and postglacial times. Polskie Archiwum Hydrobiolgll 25: 167–176.
Hofmann, W., 1996. Empirical relationships between cladoceran fauna and trophic state in thirteen northern German lakes: analysis of surficial sediments. Hydrobiologia 318: 195–201.
Hofmann, W., 1998. Cladocerans and chironomids as indicators of lake level changes in north temperate lakes. Journal of Paleolimnology 19(1): 55–62.
Hu, Z. J., N. J. Anderson, X. D. Yang & S. McGowan, 2014. Catchment-mediated atmospheric nitrogen deposition drives ecological change in two alpine lakes in SE Tibet. Global Change Biology 20(5): 1614–1628.
Huisman, J. & B. Sommeijer, 2002. Population dynamics of sinking phytoplankton in light-limited environments- simulation techniques and critical parameters. Journal of Sea Research 48: 83–96.
Huisman, J., P. van Oostveen & F. J. Weissing, 1999. Critical Depth and Critical Turbulence- Two Different Mechanisms for the Development of phytoplankton bloom. Limnology and Oceanography 44(7): 1781–1787.
Hülsmann, S., 2001. Reproductive potential of Daphnia galeata in relation to food conditions: implications of a changing size-structure of the population. Hydrobiologia 442(1–3): 241–252.
Interlandi, S. J., S. S. Kilham & E. C. Theriot, 1999. Responses of phytoplankton to varied resource availability in large lakes of the Greater Yellowstone Ecosystem. Limnology and Oceanography 44(3): 668–682.
Jeppesen, E., J. Peder Jensen, M. Sondergaard, T. Lauridsen & F. Landkildehus, 2000. Trophic structure, species richness and biodiversity in Danish lakes: changes along a phosphorus gradient. Freshwater Biology 45(2): 201–218.
Jeppesen, E., P. Leavitt, L. D. Meester & J. P. Jensen, 2001. Functional ecology and palaeolimnology-using cladoceran remains to reconstruct anthropogenic impact. Trends in Ecology and Evolution 16(4): 191–198.
Jeppesen, E., P. Nõges, T. A. Davidson, J. Haberman, T. Nõges, K. Blank, T. L. Lauridsen, M. Søndergaard, C. Sayer, R. Laugaste, L. S. Johansson, R. Bjerring & S. L. Amsinck, 2011. Zooplankton as indicators in lakes: a scientific-based plea for including zooplankton in the ecological quality assessment of lakes according to the European Water Framework Directive (WFD). Hydrobiologia 676(1): 279–297.
Ji, J. & Y. Q. Fan, 1983. Preliminary analysis on the hydrologic characteristics of Lake Lugu. In: The Comprehensive Scientific Expedition to the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau, Chinese Academy of Sciences Qinghai-Xizang Plateau Research, Hengduan Mountains Expedition. Yunnan People’s Publishing House, Kunming, 214–225 (in Chinese).
Kato, M., Y. Tanimura, K. Matsuoka & H. Fukusawa, 2003. Planktonic diatoms from sediment traps in Omura Bay, western Japan with implications for ecological and taphonomic studies of coastal marine environments. Quaternary International 105(1): 25–31.
Kattel, G. R., R. W. Battarbee, A. Mackay & H. J. B. Birks, 2007. Are cladoceran fossils in lake sediment samples a biased reflection of the communities from which they are derived? Journal of Paleolimnology 38(2): 157–181.
Kattel, G. R., R. W. Battarbee, A. W. Mackay & H. J. B. Birks, 2008. Recent ecological change in a remote Scottish mountain loch: an evaluation of a Cladocera-based temperature transfer-function. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 259(1): 51–76.
Kirilova, E. P., P. Bluszcz, O. Heiri, H. Cremer, C. Ohlendorf, A. F. Lotter & B. Zolitschka, 2008. Seasonal and interannual dynamics of diatom assemblages in Sacrower See (NE Germany): a sediment trap study. Hydrobiologia 614(1): 159–170.
Kong, L., 2015. Study on the response of cladoceran in alpine lakes to environment change during the past 200 years in Western Sichuan Plateau. Nanjing Institute of Geography and Limnology, Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Kong, L., X. Yang, G. Kattel, N. J. Anderson & Z. Hu, 2016. The response of Cladocerans to recent environmental forcing in an Alpine Lake on the SE Tibetan Plateau. Hydrobiologia 784(1): 171–185.
Korhola, A., 1999. Distribution patterns of Cladocera in subarctic Fennoscandian lakes and their potential in environmental reconstruction. Ecography: 357–373.
Korhola, A. & M. Rautio, 2001. Cladocera and other branchiopod crustaceans. In Smol, J. P., H. J. B. Birks & W. M. Last (eds), Tracking Environmental Change Using Lake Sediments, Vol. 4. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht: 5–41.
Korhola, A., H. Olander & T. Blom, 2000. Cladoceran and chironomid assemblages as qualitative indicators of water depth in subarctic Fennoscandian lakes. Journal of Paleolimnology 24: 43–54.
Köster, D. & R. Pienitz, 2006. Seasonal diatom variability and paleolimnological inferences – a case study. Journal of Paleolimnology 35(2): 395–416.
Krammer, K. & H. Lange-Bertalot, 1986. Bacillariophyceae. 1: Teil: Naviculaceae. Gustav Fischer Verlag, Stuttgart.
Krammer, K. & H. Lange-Bertalot, 1988. Bacillariophyceae. 2: Teil: Bacillariaceae, Epithmiaceae, Surirellaceae. In Ettl, H., G. Gärtner, J. Gerloff, H. Heynig & D. Mollenhauer (eds), Süßwasserflora von Mitteleuropa, 2/2. Gustav Fischer Verlag, Stuttgart, Jena: 1–596.
Krammer, K. & H. Lange-Bertalot, 1991a. Bacillariophyceae. 3: Teil: Centrales, Fragilariaceae, Eunotiaceae. Unter Mitarbeit von H. Håkannson und M. Nörpel. In Ettl, H., Gärtner, G., Gerloff, J., Heynig, H., Mollenhauer, D. (eds), Süßwasserflora von Mitteleuropa, 2/3. Gustav Fischer Verlag, Stuttgart.
Krammer, K. & H. Lange-Bertalot, 1991b. Bacillariophyceae. 4: Teil: Achnanthaceae, Kritische Erganzungen zu Navicula (Lineolatae) und Gomphonema Gesamtliteraturverzeichnis. In Ettl, H., G. Gärtner, J. Gerloff, H. Heynig & D. Mollenhauer (eds), Süßwasserflora von Mitteleuropa, 2/4. Gustav Fischer Verlag, Stuttgart, Jena: 1–437.
Lotter, A. E., H. J. B. Birks, W. Hofmann & A. Marchetto, 1997. Modern diatom, cladocera, chironomid, and chrysophyte cyst assemblages as quantitative indicators for the reconstruction of past environmental conditions in the Alps. I. Climate. Journal of Paleolimnology 18: 395–420.
Lund, J., 1950. Studies on Asterionella formosa hass: iI. Nutrient depletion and the spring maximum. The. Journal of Ecology 38(1): 15–35.
Luoto, T. P., L. Nevalainen & K. Sarmaja-Korjonen, 2013. Zooplankton (Cladocera) in assessments of biologic integrity and reference conditions: application of sedimentary assemblages from shallow boreal lakes. Hydrobiologia 707(1): 173–185.
Maberly, S. C., M. A. Hurley, C. Butterwick, J. E. Corry, S. I. Heaney, A. E. Irish, G. H. M. Jaworski, J. W. G. Lund, C. S. Reynolds & J. V. Roscoe, 1994. The rise and fall of Asterionella formosa in the South Basin of Windermere-analysis of a 45-year series of data. Freshwater Biology 31: 19–34.
Marinone, M. C., S. M. Marque, D. A. Suárez, M. d. C. Dieguez, P. Pérez, P. Ríos, D. Soto & H. E. Zagarese, 2006. UV radiation as a potential driving force for zooplankton community structure in Patagonian lakes. Photochemistry and Photobiology 82(4): 962–971.
Mueller, W. P., 1964. The distribution of cladoceran remains in surficial sediments from three northern Indiana lakes. Invest Indiana Lakes Streams 6(1): 3.
Müller, H., 1985. The niches of Bosmina coregoni and Bosmina longirostris in the ecosystem of Lake Constance. Verhandlungen der Internationalen Vereinigung fur Theoretische und Angewandte Limnologie 22: 3137–3143.
Murdoch, W., R. Nisbet, E. McCauley, A. DeRoos & W. Gurney, 1998. Plankton abundance and dynamics across nutrient levels: tests of hypotheses. Ecology 79(4): 1339–1356.
Nandini, S. & S. S. S. Sarma, 2003. Population growth of some genera of cladocerans (Cladocera) in relation to algal food (Chlorella vulgaris) levels. Hydrobiologia 491: 211–219.
Parker, B. R., R. D. Vinebrooke & D. W. Schindler, 2008. Recent climate extremes alter alpine lake ecosystems. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 105(35): 12927–12931.
Patalas, K., 1990. Diversity of the zooplankton communities in Canadian lakes as a function of climate. Internationale Vereinigung fuer Theoretische und Angewandte Limnologie Verhandlungen 24(1): 360–368.
Patrick, R. & C. W. Reimer, 1966. The diatoms of the United States 1 Fragilariaceae, Eunotiaceae, Achnanthaceae, Naviculaceae. Academy of Natural Sciences Monograph 13, Philadelphia, USA.
Rautio, M., 1998. Community structure of crustacean zooplankton in subarctic ponds — effects of altitude and physical heterogeneity. Ecography 21: 327–335.
Rautio, M., S. Sorvari & A. Korhola, 2000. Diatom and crustacean zooplankton communities, their seasonal variability and representation in the sediments of subarctic Lake Saanajärvi. Journal of Limnology 59: 81–96.
Reynolds, C. S., 1984. The Ecology of Freshwater Plankton. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Reynolds, C. S., 1990. Temporal scales of variability in pelagic environments and the response of phytoplankton. Freshwater Biology 23: 25–53.
Reynolds, C. S., H. R. Morison & C. Butterwick, 1982. The sedimentary flux of phytoplankton in the south basin of Windermere. Limnology and Oceanography 27(6): 1162–1175.
Reynolds, C. S., A. E. Irish & J. A. Elliott, 2001. The ecological basis for simulating phytoplankton responses to environmental change (PROTECH). Ecological Modelling 140: 271–291.
Round, F. E., R. M. Cra Wford & D. G. Mann, 1990. Diatoms: Biology and Morphology of the Genera. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Rühland, K. M., A. M. Paterson, K. Hargan, A. Jenkin, B. J. Clark & J. P. Smol, 2010. Reorganization of algal communities in the Lake of the Woods (Ontario, Canada) in response to turn-of-the-century damming and recent warming. Limnology and Oceanography 55(6): 2433–2451.
Rühland, K. M., A. M. Paterson & J. P. Smol, 2015. Lake diatom responses to warming: reviewing the evidence. Journal of Paleolimnology 54(1): 1–35.
Sakuma, M., T. Hanazato, A. Saji & R. Nakazato, 2004. Migration from plant to plant: an important factor controlling densities of the epiphytic cladoceran Alona (Chydoridae, Anomopoda) on lake vegetation. Limnology 5(1): 17–23.
Sarnelle, O., 1992. Nutrient enrichment and grazer effects on phytoplankton in lakes. Ecology 73(2): 551–560.
Sarnelle, O., 2003. Nonlinear effects of an aquatic consumer: causes and consequences. The American Naturalist 161(3): 478–496.
Saros, J. E., T. J. Michel, S. J. Interlandi & A. P. Wolfe, 2005. Resource requirements of Asterionella formosa and Fragilaria crotonensis in oligotrophic alpine lakes: implications for recent phytoplankton community reorganizations. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 62(7): 1681–1689.
Saros, J. E., K. E. Strock, J. McCue, E. Hogan & N. J. Anderson, 2013. Response of Cyclotella species to nutrients and incubation depth in Arctic lakes and incubation depth in Arctic lakes. Journal of Plankton Research 36(2): 450–460.
Schalau, K., K. Rinke, D. Straile & F. Peeters, 2008. Temperature is the key factor explaining interannual variability of Daphnia development in spring: a modelling study. Oecologia 157(3): 531–543.
Sommer, U., 1985. Seasonal Succession of Phytoplankton in Lake Constance. BioScience 35(6): 351–357.
Sommer, U., 1988. Growth and survival strategies of planktonic diatoms. Growth and reproductive strategies of freshwater phytoplankton Cambridge University Press, Cambridge: 227–260.
Sommer, U., 1989. The role of competition for resources in phytoplankton succession Plankton ecology. Springer, 57–106.
Sommer, U., Z. M. Gliwicz, W. Lampert & A. Duncan, 1986. The PEG-model of seasonal succession of planktonic events in fresh waters. Archiv fur Hydrobiologie 106(4): 433–471.
Stone, J. R. & S. C. Fritz, 2004. Three-dimensional modeling of lacustrine diatom habitat areas: improving paleolimnological interpretation of planktonic:benthic ratios. Limnology and Oceanography 49(5): 1540–1548.
Stone, J. R., K. S. Westover & A. S. Cohen, 2011. Late Pleistocene paleohydrography and diatom paleoecology of the central basin of Lake Malawi, Africa. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 303(1-4): 51v70.
Sverdrup, H., 1953. On conditions for the vernal blooming of phytoplankton. Journal du Conseil 18(3): 287–295.
Swadling, K. M., R. Pienitz & T. Nogrady, 2000. Zooplankton community composition of lakes in the Yukon and Northwest Territories (Canada): relationship to physical and chemical limnology. Hydrobiologia 431(2–3): 211–224.
Sweetman, J. N., K. M. Rühland & J. P. Smol, 2010. Environmental and spatial factors influencing the distribution of cladocerans in lakes across the central Canadian Arctic treeline region. Journal of Limnology 69(1): 76–87.
Ter Braak, C. J. F., 1995. Ordination. In Jongman, R. H. G., C. J. F. ter Braak & O. F. R. van Tongeren (eds), Data Analysis in Community and Landscape Ecology. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge: 91–169.
ter Braak, C. J. F. & P. Šmilauer, 2002. CANOCO Reference Manual and CanoDraw for Windows User’s Guide: Software for Canonical Community Ordination (Version 4.5). Microcomputer Power, Ithaca.
Tremel, B., S. L. Frey, N. D. Yan, K. M. Somers & T. W. Pawson, 2000. Habitat specificity of littoral Chydoridae (Crustacea, Branchiopoda, Anomopoda) in Plastic Lake, Ontario. Canada. Hydrobiologia 432(1–3): 195–205.
Vijverberg, J., 1980. Effect of temperature in laboratory studies on development and growth of Cladocera and Copepoda from Tjeukemeer. The Netherlands. Freshwater Biology 10(4): 317–340.
Wang, S. M. & H. S. Dou, 1998. Journal of Chinese lakes. Science Press, Beijing: 378–379 (in Chinese).
Wang, L., J. Li, H. Lu, Z. Gu, P. Rioual, Q. Hao, A. W. Mackay, W. Jiang, B. Cai, B. Xu, J. Han & G. Chu, 2012a. The East Asian winter monsoon over the last 15,000 years: its links to high-latitudes and tropical climate systems and complex correlation to the summer monsoon. Quaternary Science Reviews 32: 131–142.
Wang, Q., X. D. Yang, P. B. Hamilton & E. L. Zhang, 2012b. Linking spatial distributions of sediment diatom assemblages with hydrological depth profiles in a plateau deep–water lake system of subtropical China. Fottea 12(1): 59–73.
Wang, Q., X. Yang, N. J. Anderson, E. Zhang & Y. Li, 2014. Diatom response to climate forcing of a deep, alpine lake (Lugu Hu, Yunnan, SW China) during the Last Glacial Maximum and its implications for understanding regional monsoon variability. Quaternary Science Reviews 86: 1–12.
Wang, Q., X. D. Yang, J. N. Anderson & J. F. Ji, 2015. Diatom seasonality and sedimentation in a subtropical alpine lake (Lugu Hu, Yunnan-Sichuan, Southwest China). Arctic, Antarctic, and Alpine Research 47(3): 55–66.
Wang, Q., X. Yang, N. J. Anderson & X. Dong, 2016. Direct versus indirect climate controls on Holocene diatom assemblages in a sub-tropical deep, alpine lake (Lugu Hu, Yunnan, SW China). Quaternary Research 86(1): 1–12.
Whiteside, M. C. & R. V. Harmsworth, 1967. Species diversity in Chydorid (Cladocera) communities. Ecology 48(4): 664–667.
Whiteside, M. C., J. B. Williams & C. P. White, 1978. Seasonal abundance and pattern of Chydorid, Cladocera in mud and vegetative habitats. Ecology 59(6): 1177–1188.
Whitlock, C., W. E. Dean, S. C. Fritz, L. R. Stevens, J. R. Stone, M. J. Power, J. R. Rosenbaum, K. L. Pierce & B. B. Bracht-Flyr, 2012. Holocene seasonal variability inferred from multiple proxy records from Crevice Lake, Yellowstone National Park, USA. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 331–332: 90–103.
Wilkinson, L., 1988. SYSTAT: The system for statistics. Illinois, SYSTAT Inc, Evanston.
Williamson, C. E., O. G. Olson, S. E. Lott, N. D. Walker, D. R. Engstrom & B. R. Hargreaves, 2001. Ultraviolet radiation and zooplankton community structure following deglaciation in Glacial Bay, Alaska. Ecology 82: 1748–1760.
Wiltshire, K. H. & B. F. Manly, 2004. The warming trend at Helgoland Roads, North Sea: phytoplankton response. Helgoland Marine Research 58(4): 269–273.
Winder, M. & D. A. Hunter, 2008. Temporal organization of phytoplankton communities linked to physical forcing. Oecologia 156(1): 179–192.
Winder, M. & D. E. Schindler, 2004a. Climate change uncouples trophic interactions in an aquatic ecosystem. Ecology 85(8): 2100–2106.
Winder, M. & D. E. Schindler, 2004b. Climatic effects on the phenology of lake processes. Global Change Biology 10(11): 1844–1856.
Wolin, J. A. & J. R. Stone, 2010. Diatoms as indicators of water-level change in fresh-water lakes. In Smol, J. P. & E. F. Stoermer (eds), The Diatoms: Applications for the Environmental and Earth Sciences, 2nd ed. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge: 174–185.
Yang, L., 1984. The preliminary study on the original classification and distribution law of lakes on the Yunnan Plateau. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology 1: 34–39.
Zhang, S. S., 2001. Environmental monitoring technologies. Higher Education Press, Beijing: 204–208 (in Chinese).
Zhang, Y., Z. Wu, M. Liu, J. He, K. Shi, M. Wang & Z. Yu, 2014. Thermal structure and response to long-term climatic changes in Lake Qiandaohu, a deep subtropical reservoir in China. Limnology and Oceanography 59(4): 1193–1202.
Zonxing, L., Y. He, W. H. Wang, W. H. Theakstone, W. An, X. Wang, A. Lu, W. Zhang & W. Cao, 2012. Changes of daily climate extremes in southwestern China during 1961–2008. Global and Planetary Change 80–81: 255–272.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2016YFA0600502), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41502170, 41701232), the State Key Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China (41530753) and the Scientific Research Foundation of Nanjing Institute of Geography and Limnology, Chinese Academy of Sciences (NIGLAS2015QD05). Giri R. Kattel would also like to acknowledge the CAS-PIFI Visiting Professorial Fellowship Program (CAS #2016VEA050) at NIGLAS and NSFC Grants (41530753 and 41272379).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling editor: Gideon Gal
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Q., Yang, X. & Kattel, G.R. Within-lake spatio-temporal dynamics of cladoceran and diatom communities in a deep subtropical mountain lake (Lugu Lake) in southwest China. Hydrobiologia 820, 91–113 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-018-3645-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-018-3645-5