Abstract
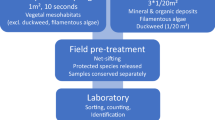
Lake shores are characterised by a high natural variability, which is increasingly threatened by a multitude of anthropogenic disturbances including morphological alterations to the littoral zone. The European Water Framework Directive (EU WFD) calls for the assessment of lake ecological status by monitoring biological quality elements including benthic macroinvertebrates. To identify cost- and time-efficient sampling strategies for routine lake monitoring, we sampled littoral invertebrates in 32 lakes located in different geographical regions in Europe. We compared the efficiency of two sampling methodologies, defined as habitat-specific and pooled composite sampling protocols. Benthic samples were collected from unmodified and morphologically altered shorelines. Variability within macroinvertebrate communities did not differ significantly between sampling protocols across alteration types, lake types and geographical regions. Community composition showed no significant differences between field composite samples and artificially generated composite samples, and correlation coefficients between macroinvertebrate metrics calculated with both methods and a predefined morphological stressor index were similar. We conclude that proportional composite sampling represents a time- and cost-efficient method for routine lake monitoring as requested under the EU WFD, and may be applied across various European geographical regions.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, M. J., R. N. Gorley & K. R. Clarke, 2008. PERMANOVA+ for PRIMER: guide to software and statistical methods. Plymouth, UK, PRIMER-E.
AQEM Consortium, 2002. Manual for the application of the AQEM system. A comprehensive method to assess European streams using benthic macroinvertebrates, developed for the purpose of the Water Framework Directive. Version 1.0.—February 2002. (http://www.aqem.de).
Böhmer, J., K. Arbaciauskas, R. Benstead, W. Gabriels, G. Porst, B. Reeze & H. Timm, 2014. Water Framework Directive Intercalibration Technical Report: Central Baltic Lake Benthic Invertebrate Ecological Assessment Methods. Publications Office of the European Union, Luxembourg.
Brauns, M., X.-F. Garcia, N. Walz & M. T. Pusch, 2007a. Effects of human shoreline development on littoral macroinvertebrates in lowland lakes. Journal of Applied Ecology 44: 1138–1144.
Brauns, M., X.-F. Garcia, M. T. Pusch & N. Walz, 2007b. Eulittoral macroinvertebrate communities of lowland lakes: discrimination among trophic states. Freshwater Biology 52: 1022–1032.
Brodersen, K. P. & C. Lindegaard, 1999. Classification, assessment and trophic reconstruction of Danish lakes using chironomids. Freshwater Biology 42: 143–157.
Carpenter, S. R., B. J. Benson, R. Biggs, J. W. Chipman, J. A. Foley, S. A. Golding, R. B. Hammer, P. C. Hanson, P. T. J. Johnson, A. M. Kamarainen, T. K. Kratz, R. C. Lathrop, K. D. McMahon, B. Provencher, J. A. Rusak, C. T. Solomon, E. H. Stanley, M. G. Turner, M. J. Vander Zanden, C.-H. Wu & H. Yuan, 2007. Understanding regional change: a comparison of two lake districts. BioScience 57: 323–335.
Clarke, K. R. & R. M. Warwick, 2001. Change in marine communities: an approach to statistical analysis and interpretation, 2nd ed. Plymouth, PRIMER-E.
EC, 2000. Council Directive 2000/60/EC establishing a framework for Community action in the field of water policy. Official Journal no L 321/1, 22122000.
Ferraro, S. P., F. A. Cole, W. A. Deben & R. C. Swartz, 1989. Power-cost efficiency of 8 macrobenthic sampling schemes in Puget Sound, Washington, USA. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 46: 2157–2165.
Gabel, F., X. F. Garcia, I. Schnauder & M. T. Pusch, 2012. Effects of ship-induced waves on littoral benthic invertebrates. Freshwater Biology 57: 2425–2435.
Gabriels, W., K. Lock, N. De Pauw & P. L. M. Goethals, 2010. Multimetric Macroinvertebrate Index Flanders (MMIF) for biological assessment of rivers and lakes in Flanders (Belgium). Limnologica – Ecology and Management of Inland Waters 40: 199–207.
Gotelli, N. J. & A. M. Ellison, 2004. A primer of ecological statistics. Sinauer Associates Inc, Sunderland, MA.
Haase, P., S. Lohse, S. Pauls, K. Schindehütte, A. Sundermann, P. Rolauffs & D. Hering, 2004. Assessing streams in Germany with benthic invertebrates: development of a practical standardised protocol for macroinvertebrate sampling and sorting. Limnologica – Ecology and Management of Inland Waters 34: 349–365.
Harrison, S. S. C. & A. A. G. Hildrew, 1998. Patterns in the epilithic community of a lake littoral. Freshwater Biology 39: 477–492.
Hering, D., C. Feld, O. Moog & T. Ofenböck, 2006. Cook book for the development of a Multimetric Index for biological condition of aquatic ecosystems: experiences from the European AQEM and STAR projects and related initiatives. Hydrobiologia 566: 311–324.
Jennings, M. J., M. A. Bozek, G. R. Hatzenbeler, E. E. Emmons & M. D. Staggs, 1999. Cumulative Effects of Incremental Shoreline Habitat Modification on Fish Assemblages in North Temperate Lakes. North American Journal of Fisheries Management 19: 18–27.
Jurca, T., L. Donohue, D. Laketić, S. Radulović & K. Irvine, 2012. Importance of the shoreline diversity features for littoral macroinvertebrate assemblages. Fundamental and Applied Limnology 180: 175–184.
Langdon, P. G., Z. Ruiz, K. P. Brodersen & I. D. L. Foster, 2006. Assessing lake eutrophication using chironomids: understanding the nature of community response in different lake types. Freshwater Biology 51: 562–577.
Lorenz, A., D. Hering, C. Feld & P. Rolauffs, 2004. A new method for assessing the impact of hydromorphological degradation on the macroinvertebrate fauna of five German stream types. Hydrobiologia 516: 107–127.
Mastrantuono, L., F. Pilotto, M. Rossopinti, M. Bazzanti & A. G. Solimini, 2015. Response of littoral macroinvertebrates to morphological disturbances in Mediterranean lakes: the case of Lake Piediluco (central Italy). Fundamental and Applied Limnology 186: 297–310.
McGoff, E., J. Aroviita, F. Pilotto, O. Miler, A. G. Solimini, G. Porst, T. Jurca, L. Donohue & L. Sandin, 2013. Assessing the relationship between the Lake Habitat Survey and littoral macroinvertebrate communities in European lakes. Ecological Indicators 25: 205–214.
Miler, O., Brauns, M., Böhmer, J., & M. Pusch, 2012. Feinabstimmung des Bewertungsverfahrens von Seen mittels Makrozoobenthos. Projektreport Länderfinanzierungsprogramm ‘Wasser, Boden und Abfall‘(Projektnr. O 5.10/2011).
Miler, O., G. Porst, E. McGoff, F. Pilotto, L. Donohue, T. Jurca, A. Solimini, L. Sandin, K. Irvine, J. Aroviita, R. Clarke & M. T. Pusch, 2013. Morphological alterations of lake shores in Europe: a multimetric ecological assessment approach using benthic macroinvertebrates. Ecological Indicators 34: 398–410.
Miler, O., G. Porst, E. McGoff, F. Pilotto, L. Donohue, T. Jurca, A. Solimini, L. Sandin, K. Irvine, J. Aroviita, R. Clarke & M. T. Pusch, 2015. An index of human alteration of lake shore morphology. Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems 25: 353–364.
Mischke, U., S. Thackeray, M. Dunbar, C. McDonald, L. Carvalho, C. de Hoyos, M. Jarvinen, C. Laplace-Treyture, G. Morabito, B. Skjelbred, A. L. Solheim, B. Brierley & B. Dudley, 2012. Guidance document on sampling, analysis and counting standards for phytoplankton in lakes Project report WISER Deliverable D31-4.
Moss, B., D. Stephen, C. Alvarez, E. Becares, W. V. D. Bund, S. E. Collings, E. V. Donk, E. D. Eyto, T. Feldmann, C. Fernández-Aláez, M. Fernández-Aláez, R. J. M. Franken, F. García-Criado, E. M. Gross, M. Gyllström, L.-A. Hansson, K. Irvine, A. Järvalt, J.-P. Jensen, E. Jeppesen, T. Kairesalo, R. Kornijów, T. Krause, H. Künnap, A. Laas, E. Lill, B. Lorens, H. Luup, M. R. Miracle, P. Nõges, T. Nõges, M. Nykänen, I. Ott, W. Peczula, E. T. H. M. Peeters, G. Phillips, S. Romo, V. Russell, J. Salujõe, M. Scheffer, K. Siewertsen, H. Smal, C. Tesch, H. Timm, L. Tuvikene, I. Tonno, T. Virro, E. Vicente & D. Wilson, 2003. The determination of ecological status in shallow lakes – a tested system (ECOFRAME) for implementation of the European Water Framework Directive. Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems 13: 507–549.
O’Connor, N. A., 1991. The effects of habitat complexity on the macroinvertebrates colonising wood substrates in a lowland stream. Oecologia 85: 504–512.
Phillips., G., G. Morabito, L. Carvalho, A. L. Solheim, B. Skjelbred, J. Moe, T. Andersen, U. Mischke, C. de Hoyos & G. Borics, 2011. Report on lake phytoplankton composition metrics, including a common metric approach for use in intercalibration by all GIGs. Project report WISER Deliverable D31-1.
Pilotto, F., M. Bazzanti, V. D. Vito, D. Frosali, F. Livretti, L. Mastrantuono, M. T. Pusch, F. Sena & A. G. Solimini, 2015. Relative impacts of morphological alteration to shorelines and eutrophication on littoral macroinvertebrates in Mediterranean lakes. Freshwater Science 34: 410–422.
Pinel-Alloul, B., G. Méthot, L. Lapierre & A. Willsie, 1996. Macroinvertebrate community as a biological indicator of ecological and toxicological factors in Lake Saint-François (Québec). Environmental Pollution 91: 65–87.
Porst, G., S. Bader, E. Münch & M. Pusch, 2012. Sampling approaches for the assessment of shoreline development based on littoral macroinvertebrates: the case of Lake Werbellin, Germany. Fundamental and Applied Limnology 180: 123–131.
Porst, G., F. Gabel, S. Lorenz & O. Miler, 2015. Implications of hydromorphological alterations to the littoral zone for freshwater ecosystem functioning. Fundamental and Applied Limnology 186: 279–282.
R Core Team, 2013. R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. ISBN 3-900051-07-0, URL http://www.R-project.org/.
Rasmussen, J. B., 1988. Littoral zoobenthic biomass in lakes, and its relationship to physical, chemical, and trophic factors. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 45: 1436–1447.
Reice, S. R. & M. Wohlenberg, 1993. Monitoring freshwater benthic macroinvertebrates and benthic processes: measures for assessment of ecosystem health. In Rosenberg, D. M. & V. H. Resh (eds), Freshwater Biomonitoring and Benthic Macroinvertebrates. Chapman & Hall, New York.
Rowan, J. S., J. Carwardine, R. W. Duck, O. M. Bragg, A. R. Black, M. E. J. Cutler, I. Soutar & P. J. Boon, 2006. Development of a technique for Lake Habitat Survey (LHS) with applications for the European Union Water Framework Directive. Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems 16: 637–657.
Rowan, J. S., R. W. Duck, J. Carwardine, O. M. Bragg, A. R. Black, M. E. J. Cutler & I. Soutar, 2008. Lake Habitat Survey in the United Kingdom – Field Survey Guidance Manual. SNIFFER, Edinburgh.
Saether, O. A., 1979. Chironomid communities as water quality indicators. Ecography 2: 65–74.
Schartau, A., S. J. Moe, L. Sandin, B. McFarland & G. Raddum, 2008. Macroinvertebrate indicators of lake acidification: analysis of monitoring data from UK, Norway and Sweden. Aquatic Ecology 42: 293–305.
Scheuerell, M. D. & D. E. Schindler, 2004. Changes in the spatial distribution of fishes in lakes along a residential development gradient. Ecosystems 7: 98–106.
Schmieder, K., 2004. European lake shores in danger – concepts for a sustainable development. Limnologica – Ecology and Management of Inland Waters 34: 3–14.
Schneider, K. & K. Winemiller, 2008. Structural complexity of woody debris patches influences fish and macroinvertebrate species richness in a temperate floodplain-river system. Hydrobiologia 610: 235–244.
Schreiber, J. & M. Brauns, 2010. How much is enough? Adequate sample size for littoral macroinvertebrates in lowland lakes. Hydrobiologia 649: 365–373.
Solimini, A. G. & L. Sandin, 2012. The importance of spatial variation of benthic invertebrates for the ecological assessment of European lakes. Fundamental and Applied Limnology 180: 85–89.
Solimini, A. G., G. Free, I. Donohue, K. Irvine, M. T. Pusch, B. Rossaro, L. Sandin & A. C. Cardoso, 2006. Using Benthic Macroinvertebrates to Assess Ecological Status of Lakes: Current Knowledge and Way Forward to Support WFD Implementation. Office for Official Publications of the European Communities, Luxembourg.
Søndergaard, M., S. E. Larsen, T. B. Jørgensen & E. Jeppesen, 2011. Using chlorophyll a and cyanobacteria in the ecological classification of lakes. Ecological Indicators 11: 1403–1412.
STAR Consortium, 2003. The AQEM sampling method to be applied in STAR. Unpublished report, available at http://www.eu-star.at/pdf/AqemMacroinvertebrateSamplingProtocol.pdf.
Strayer, D. & S. Findlay, 2010. Ecology of freshwater shore zones. Aquatic Sciences – Research Across Boundaries 72: 127–163.
Taniguchi, H., S. Nakano & M. Tokeshi, 2003. Influences of habitat complexity on the diversity and abundance of epiphytic invertebrates on plants. Freshwater Biology 48: 718–728.
Timm, H. & T. Möls, 2012. Littoral macroinvertebrates in Estonian lowland lakes: the effects of habitat, season, eutrophication and land use on some metrics of biological quality. Fundamental and Applied Limnology 180: 145–156.
Tolonen, K. T. & H. Hämäläinen, 2010. Comparison of sampling methods and habitat types for detecting impacts on lake littoral macroinvertebrate assemblages along a gradient of human disturbance. Fundamental and Applied Limnology 176: 43–59.
Urbanič, G., 2014. A Littoral Fauna Index for assessing the impact of lakeshore alterations in Alpine lakes. Ecohydrology 7: 703–716.
Urbanič, G., V. Petkovska & M. Pavlin, 2012. The relationship between littoral benthic invertebrates and lakeshore modification pressure in two alpine lakes. Fundamental and Applied Limnology 180: 157–173.
Vadeboncoeur, Y., M. J. Vander Zanden & D. M. Lodge, 2002. Putting the lake back together: reintegrating benthic pathways into lake food web models. BioScience 52: 44–54.
Weatherhead, M. A. & M. R. James, 2001. Distribution of macroinvertebrates in relation to physical and biological variables in the littoral zone of nine New Zealand lakes. Hydrobiologia 462: 115–129.
Wetzel, R. G., 2001. Limnology. Lake and River Ecosystems, 3rd ed. Academic Press, London.
White, J. & K. Irvine, 2003. The use of littoral mesohabitats and their macroinvertebrate assemblages in the ecological assessment of lakes. Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems 13: 331–351.
Acknowledgments
This paper is a result of the project WISER (Water bodies in Europe: Integrative Systems to assess Ecological status and Recovery) funded by the European Union under the 7th Framework Programme, Theme 6 (Environment including Climate Change) (contract No. 226273), http://www.wiser.eu. We thank Daniel Graeber for help with the statistical analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling editor: Sonja Stendera
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Porst, G., Miler, O., Donohue, L. et al. Efficient sampling methodologies for lake littoral invertebrates in compliance with the European Water Framework Directive. Hydrobiologia 767, 207–220 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-015-2500-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-015-2500-1