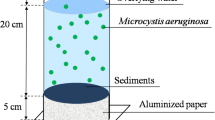
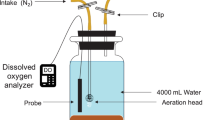
Abstract
Phosphorus (P) is a limiting nutrient in some freshwater ecosystems. Phosphate solubilizing bacteria (PSB) are candidates for enhancing P availability in rhizoplane, but their P release potential in freshwater environments needs further evaluations. This study conducted in floodplain wetlands correlated PSB abundance, decline in sediment pH, and natural mobilization of sediment Ca–P. PSB were abundantly present in floodplain wetland waters, sediments, and in river and ponds, showing low to moderate Ca–P solubilization activity; PSB from Churni River and Bhomra wetland sediments had comparatively higher activity than those from other environments. In laboratory sediment microcosms, PSB were effective in enhancing available P concentration in interstitial water indicating their P release potential. However, P-fractionation of incubated sediments showed only a short-term decline in Ca–P by PSB, suggesting that Ca–P might not be their sole or preferred metabolic target. Despite low to moderate activity in culture medium, high population density and efficacy in P release in sediment suggest significant role of PSB in P cycling in freshwater environments.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ann, Y., K. R. Reddy & J. J. Delfino, 2000. Influence of redox potential on phosphorus availability in chemically amended wetland organic soils. Ecological Engineering 14: 169–180.
Bagyaraj, D. J., P. U. Krishnaraj & S. P. S. Khanuja, 2000. Mineral phosphate solubilization: agronomic implications, mechanism and molecular genetics. Proceedings of the Indian National Science Academy B66(2&3): 69–82.
Battle, J. M. & T. B. Mihuc, 2000. Decomposition dynamics of aquatic macrophytes in the lower Atchafalaya, a large floodplain river. Hydrobiologia 418: 123–136.
Boström, B., J. M. Andersen, S. Fleischer & M. Jansson, 1988. Exchange of phosphorus across the sediment-water interface. Hydrobiologia 170: 229–244.
Chen, Y. P., P. D. Rekha, A. B. Arun, F. T. Shen, W.-A. Lai & C. C. Young, 2006. Phosphate solubilizing bacteria from subtropical soil and their tricalcium phosphate solubilizing abilities. Applied Soil Ecology 34: 33–41.
Das, S., P. S. Lyla & S. A. Khan, 2007. Biogeochemical processes in the continental slope of Bay of Bengal: I. Bacterial solubilization of inorganic phosphate. Revista de Biologia Tropical 55: 1–9.
De Souza, B. D., S. Nair & D. Chandramohan, 2000. Phosphate solubilizing bacteria around Indian peninsula. Indian Journal of Marine Science 29: 48–51.
Fankem, H., D. Nwaga, A. Deubel, L. Dieng, W. Merbach & F. X. Etoa, 2006. Occurrence and functioning of phosphate solubilizing microorganisms from oil palm tree (Elaeis guineensis) rhizosphere in Cameroon. African Journal of Biotechnology 5: 2450–2460.
Gächter, R. & J. S. Meyer, 1993. The role of microorganisms in mobilization and fixation of phosphorus in sediments. Hydrobiologia 253: 103–121.
Geurts, J. J. M., A. J. P. Smolders, A. M. Banach, J. P. M. van de Graf, J. G. M. Roelofs & L. P. M. Lamers, 2010. The interaction between decomposition, net N and P mineralisation and their mobilization to surface water in fens. Water Research 44: 3487–3495.
Goldstein, A. H., 1994. Involvement of the quinoprotein glucose dehydrogenase in the solubilization of exogenous phosphates by gram-negative bacteria. In Torriani-Gorini, A., E. Yagil & S. Silver (eds), Phosphate in Microorganisms: Cellular and Molecular Biology. ASM Press, Washington DC: 197–203.
Gyaneshwar, P., G. Naresh Kumar & L. J. Parekh, 1998. Effect of buffering on the phosphate-solubilizing ability of microorganisms. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology 14: 669–673.
Hu, X.-J., Z.-J. Li, Y.-C. Cao, J. Zhang, Y.-X. Gong & Y.-F. Yang, 2010. Isolation and identification of a phosphate solubilizing bacterium Pantoea stewartii subsp. Stewartii g6, and effects of temperature, salinity, and pH on its growth under indoor culture conditions. Aquaculture International 18: 1079–1091.
Illmer, P., A. Barbato & F. Schinner, 1995. Solubilization of hardly-soluble AlPO4 with p-solubilizing microorganisms. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 27: 265–270.
Jackson, M. L., 1973. Soil Chemical Analysis. Prentice-Hall of India Private Limited, New Delhi.
Jana, B. B., 2007. Distribution pattern and role of phosphate solubilizing bacteria in the enhancement of fertilizer value of rock phosphate in aquatic ponds: state-of-the-art. Development in Plant and Soil Sciences 102: 229–238.
Kalinowska, K., A. Guśpiel, B. Kiersztyn & R. J. Chróst, 2013. Factors controlling bacteria and protists in selected Mazurian eutrophic lakes (North-Eastern Poland) during spring. Aquatic Biosystems 9: 9.
Kucey, R. M. N., H. H. Janzen & M. E. Legett, 1989. Microbially mediated increases in plant-available phosphorus. Advances in Agronomy 42: 198–228.
Lin, T.-F., H.-I. Huang, F.-T. Shen & C.-C. Young, 2006. The protons of gluconic acid are the major factor responsible for the dissolution of tricalcium phosphate by Burkholderia cepacia CC-A174. Bioresource Technology 97: 957–1060.
Maitra N., W. B. Whitman, S. Ayyampalayam, S. Samanta, K. Sarkar, C. Bandopadhyay, M. Aftabuddin, A. P. Sharma & S. K. Manna, 2014. Draft genome sequence of the aquatic phosphorus-solubilizing and -mineralizing bacterium Bacillus sp. strain CPSM8. Genome Announcements 2(1): e01265–13.
Mehta, S. & C. S. Nautiyal, 2001. An efficient method for qualitative screening of phosphate-solubilzing bacteria. Current Microbiology 43: 51–56.
Millero, F., F. Huang, X. Zhu, X. Liu & J. Zhang, 2001. Adsorption and desorption of phosphate on calcite and aragonite in seawater. Aquatic Geochemistry 7: 33–56.
Mudryk, Z. J., 2004. Decomposition of organic and solubilization of inorganic phosphorus compounds by bacteria isolated from a marine sandy beach. Marine Biology 145: 1227–1234.
Murphy, J. & J. Riley, 1962. A modified single solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural waters. Analytica Chimica Acta 27: 31–36.
Nautiyal, C. S., 1999. An efficient microbiological growth medium for screening phosphate solubilizing bacteria. FEMS Microbiology Letters 170: 265–270.
Pérez, E., M. Sulbarán, M. M. Ball & A. Yarzábal, 2007. Isolation and characterization of mineral phosphate-solubilizing bacteria naturally colonizing a limonitic crust in the south-eastern Venezuelan region. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 39: 2905–2914.
Qian, Y., J. Shi, Y. Chen, L. Lou, X. Cui, R. Cao, P. Li & J. Tang, 2010. Characterization of phosphate solubilizing bacteria in sediments from a shallow eutrophic lake and a wetland: isolation, molecular identification and phosphorus release ability determination. Molecules 15: 8518–8533.
Ray, A. K., K. Ghosh & E. Ringo, 2012. Enzyme-producing bacteria isolated from fish gut: a review. Aquaculture Nutrition 18: 465–492.
Reddy, K. R. & W. F. DeBusk, 1991. Decomposition of water hyacinth detritus in eutrophic lake water. Hydrobiologia 211: 101–109.
Renjith, K. R., N. Chandramohanakumar & M. M. Joseph, 2011. Fractionation and bioavialbility of phosphorus in a tropical estuary, Southwest India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment 174: 299–312.
Rzepecki, M., 2010. The dynamics of phosphorus in lacustrine sediments: contents and fractions in relation to lake trophic state and chemical composition of bottom sediments. Polish Journal of Ecology 58: 409–427.
Sahu, S. N. & B. B. Jana, 2000. Enhancement of the fertilizer value of rock phosphate engineered through phosphate-solubilizing bacteria. Ecological Engineering 15: 27–39.
Sahu, M. K., K. Sivakumar, T. Thangaradjou & L. Kannan, 2007. Phosphate solubilizing actinomycetes in the estuarine environment: an inventory. Journal of Environmental Biology 28: 795–798.
Sardessai, S., 1994. Organic carbon and humic acids in sediments of the Arabian Sea and factors governing their distribution: peer-reviewed full-text journals. Oceanologica Acta 17(3): 263–270.
Seshadri, S., S. Ignacimuthu & C. Lakshminarsimhan, 2002. Variations in heterotrophic and phosphate solubilizing bacteria from Chennai, southeast coast of India. Indian Journal of Marine Sciences 31: 69–72.
Sharma, S. B., R. Z. Sayyed, M. H. Trivedi & T. A. Gobi, 2013. Phosphate solubilizing microbes: sustainable approach for managing phosphorus deficiency in agricultural soils. SpringerPlus 2: 587.
Søndergaard, M., J. P. Jensen & E. Jeppesen, 1999. Internal phosphorus loading in shallow Danish lakes. Hydrobiologia 408(409): 145–152.
Song, C. L., X. Y. Cao, Y. Y. Liu & Y. Y. Zhou, 2009. Seasonal variations in chlorophyll a concentrations in relation to potentials of sediment phosphate release by different mechanisms in a large Chinese shallow eutrophic lake (Lake Taihu). Geomicrobiology Journal 26: 508–515.
Sri Ramkumar, V. & E. Kannapiran, 2011. Isolation of total heterotrophic bacteria and phosphate solubilizing bacteria and in vitro study of phosphatase activity and production of phytohormones by PSB. Archives of Applied Science Research 3: 581–586.
Sugunan, V. V., 2000. Ecology and fisheries management of reservoirs in India. Hydrobiologia 430: 121–147.
Tong, Y., G. Lin, X. Ke, F. Liu, G. Zhu, G. Gao & J. Shen, 2005. Comparison of microbial community between two shallow freshwater lakes in middle Yangtze basin, East China. Chemosphere 60: 85–92.
Trivedi, P. & T. Sa, 2008. Pseudomonas corrugate (NRRL B-30409) mutants increased phosphate solubilization, organic acid, and plant growth at lower temperatures. Current Microbiology 56: 140–144.
Venkateswaran, K. & R. Natarajan, 1983. Seasonal distribution of inorganic phosphate solubilizing bacteria and phosphate producing bacteria in Porto-Novo waters. Indian Journal of Marine Sciences 12: 213–217.
Weber, K. A., L. A. Achenbach & J. D. Coates, 2006. Microorganisms pumping iron: anaerobic microbial iron oxidation and reduction. Nature Reviews Microbiology 4: 752–764.
Wu, G. F. & X. P. Zhou, 2005. Characterization of phosphorus-releasing bacteria in a small eutrophic shallow lake, Eastern China. Water Research 39: 1035–1040.
Xiaojiang, G., X. Shiyuan & Z. Nianli, 2001. Distribution and forms of phosphorus in tidal flat sediments of the Yangtze estuary and coast. Science in China Series B: Chemistry 44: 190–196.
Yu, X., X. Liu, T. H. Zhu & G. H. Liu, 2011. Isolation and characterization of phosphate-solubilizing bacteria from walnut and their effect on growth and phosphorus mobilization. Biology and Fertility of Soil 47: 437–446.
Zhou, C., C. Song, D. Huang, Y. Liu, X. Cao & Y. Zhou, 2011. Isolation and characterization of organic phosphorus-mineralizing bacteria in sediment of a Chinese large shallow eutrophic lake (Lake Taihu). Geomicrobiology Journal 28: 660–666.
Acknowledgements
The work was conducted under ICAR-funded AMAAS network project on “Microbial phosphorus transformations in inland open waters.”
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling editor: Stefano Amalfitano
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maitra, N., Manna, S.K., Samanta, S. et al. Ecological significance and phosphorus release potential of phosphate solubilizing bacteria in freshwater ecosystems. Hydrobiologia 745, 69–83 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-014-2094-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-014-2094-z