Abstract
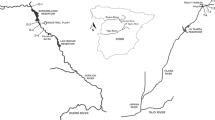
Benthic macrophyte communities of different substratum types (soft, hard) were studied in eleven differently impacted sites belonging in two different water typologies (transitional waters: Lesina Lagoon, Varna Lake; coastal waters: Varna Bay) and two ecoregions (Mediterranean Sea, Black Sea). Species lists were compiled for each study site, 20 taxa were found at Lesina and Varna Lake and Bay, and the abundance of each taxon was determined at each site. The relationship between nine metrics related to community structure [species richness, % of total coverage, dry biomass (g/m−2), and cluster and multi-dimensional scaling plot of Bray–Curtis similarity] and function [Ecological Status Group I % coverage, ESG II % coverage, Ecological Evaluation Index (EEI-c) and Ecological Index (EIEEI)] and key abiotic factors and an anthropogenic stress index (EnII) were studied. A strong relationship (Spearman rank correlation coefficient ρ ≤ −0.89; R 2 ≥ 0.89) between anthropogenic stress and functional indices, EEI-c and EIEEI, was found. The structural index ‘species richness’ correlated negatively with EnII and positively with salinity, demonstrating a freshwater and confinement influence on species diversity. EEI-c and EIEEI indices classified the studied sites and locations in different Ecological Status Classes in accordance with the anthropogenic stress gradient.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agostini, S., A. Capiomont, B. Marchand & G. Pergent, 2003a. Distribution and estimation of basal area coverage of subtital seagrass meadows in a Mediterranean coastal lagoon. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 56: 1021–1028.
Agostini, S., B. Marchand & G. Pergent, 2003b. Temporal and spatial changes of seagrass meadows in a Mediterranean coastal lagoon. Oceanologica Acta 25: 297–302.
Agostini, S., G. Pergent & B. Marchand, 2003c. Growth and primary production of Cymodocea nodosa in a coastal lagoon. Aquatic Botany 76: 185–193.
Andersen, J. H., L. Schlüter & G. Ærtebjerg, 2006. Coastal eutrophication: recent developments in definitions and implications for monitoring strategies. Journal of Plankton Research 28: 621–628.
Aubry, A. & M. Elliott, 2006. The use of environmental integrative indicators to assess seabed disturbance in estuaries and coasts: application to the Humber Estuary, UK. Marine Pollution Bulletin 53: 175–185.
Bakker, E. S., E. Van Donka, S. A. J. Declercka, N. R. Helmsinga, B. Hiddinga & B. A. Noletd, 2010. Effect of macrophyte community composition and nutrient enrichment on plant biomass and algal blooms. Basic and Applied Ecology 11: 432–439.
Ballesteros, E., X. Torras, S. Pinedo, M. García, L. Mangialajo & M. de Torres, 2007. A new methodology based on littoral community cartography dominated by macroalgae for the implementation of the European Water Framework Directive. Marine Pollution Bulletin 55: 172–180.
Basset, A., L. Sabetta, A. Fonnesu, D. Mouillot, D. Do Chi, P. Viaroli, G. Giordani, S. Reizopoulou, M. Abbiati & G. C. Carrada, 2006. Typology in Mediterranean transitional waters: new challenges and perspectives. Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems 16: 441–455.
Birk, S., J. Strackbein & D. Hering, 2010. WISER methods database. Version: May 2010. Available at http://www.wiser.eu/programme-and-results/data-and-guidelines/method-database/.
Borja, A., E. Barbone, A. Basset, G. Borgersen, M. Brkljacic, J. M. Garmendia, J. C. Marques, K. Mazik, I. Muxika, J. M. Neto, K. Norling, J. G. Rodríguez, I. Rosati, B. Rygg, H. Teixeira & A. Trayanova, 2011. Response of single benthic metrics and multi-metric methods to anthropogenic pressure gradients, in five distinct European coastal and transitional ecosystems. Marine Pollution Bulletin 62: 499–513.
Breber P., R. Povilanskas & A. Armaitiene, 2008. Recent evolution of fishery and land reclamation in Curonian and Lesina lagoons. Hydrobiologia 611: 105–114.
Calado, G. & P. Duarte, 2000. Modelling growth of Ruppia cirrhosa. Aquatic Botany 68: 29–44.
Carletti, A. & A.S. Heiskanen, 2009. Water Framework Directive intercalibration technical report – Part 3: coastal and transitional waters. EUR 23838 EN/3.
Carr, M. R., 1997. Primer user manual. Plymouth Marine Laboratory, Plymouth: 44 pp.
Casagranda, C. & C. F. Boudouresque, 2007. Biomass of Ruppia cirrhosa and Potamogeton pectinatus in a Mediterranean brackish lagoon, Lake Ichkeul, Tunisia. Archiv für Hydrobiologie 168: 243–255.
Cecere, E., A. Petrocelli, G. Izzo & A. Sfriso, 2009. Flora and vegetation of the Italian transitional water systems. Corila, Lagunet, Venezia.
Cloern, J. E., 2001. Our evolving conceptual model of the coastal eutrophication problem. Marine Ecology Progress Series 210: 223–253.
Coutino, R. & U. Seeliger, 1984. The horizontal distribution of the benthic algal flora in the Patos Lagoon estuary, Brazil, in relation to salinity, substratum and wave exposure. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 80: 247–257.
Curiel, D., A. Rismondo, G. Bellemo & M. Marzocchi, 2004. Macroalgal biomass and species variations in the lagoon of Venice (Northern Adriatic Sea, Italy): 1981–1998. Scientia Marina 68: 57–67.
Curiel, D., A. Falace, V. Bandelj & A. Rismondo, 2012. Applicability and intercalibration of macrophyte quality indices to characterise the ecological status of Mediterranean transitional waters: the case of the Venice lagoon. Marine Ecology 33: 437–459.
De Jonge, V. N., M. Elliott & E. Orive, 2002. Causes, historical development, effects and future challenges of a common environmental problem: eutrophication. Hydrobiologia 475(476): 1–19.
De Vries, I., C. J. M. Philippart, E. G. De Groot & M. W. M. Van der Tol, 1996. Coastal eutrophication and marine benthic vegetation: a model analysis. In Schramm, W. & P. H. Nienhuis (eds), Marine benthic vegetation: recent changes and the effects of eutrophication. Springer, Berlin: 79–113.
Dencheva, K., 2010. State of macrophytobenthic communities and ecological status of the Varna Bay, Varna lakes and Burgas Bay. Phytologia Balcanica 16: 43–50.
Dennison, W. C., R. J. Orth, K. A. Moore, J. C. Stevenson, V. Carter, S. Kollar, P. W. Berstrom & R. A. Batiuk, 1993. Assessing water quality with submerged aquatic vegetation. BioScience 43: 86–94.
Domin, A., H. Schubert, J. C. Krause & U. Schiewer, 2004. Modelling of pristine depth limits for macrophyte growth in the southern Baltic Sea. Hydrobiologia 514: 29–39.
Duarte, C. M., 1995. Submerged aquatic vegetation in relation to different nutrient regimes. Ophelia 41: 87–112.
Duke, C. S., A. Cezeaux & M. M. Allen, 1989. Changes in polypeptide composition of Synechocystis sp. strain 6308 phycobilisomes induced by nitrogen starvation. Journal of Bacteriology 4: 1960–1966.
Duraco, M. J., 1995. Indicators of seagrass ecological conditions: an assessment based on spatial and temporal changes associated with the mass mortality of the tropical seagrass Thalassia testudinum. In Dyer, K. R. & R. J. Orth (eds), Changes in fluxes in estuaries: implications for science to management. Olsen and Olsen, Fredensborg: 261–266.
Elliot, M. & V. Quintino, 2007. The estuarine quality paradox, environmental homeostatis and the difficulty of detecting anthropogenic stress in naturally stressed areas. Marine Pollution Bulletin 54: 640–645.
European Commission (EC), 2000. Directive 2000/60/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 23 October 2000 establishing a framework for Community actions in the field of water policy. Official Journal of the European Communities L327, 1–73. 22.12.2000.
European Parliament Council (EPC), 2008. Directive 2008/56/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 17 June 2008 Establishing a framework for community action in the field of marine environmental policy (Marine Strategy Framework Directive).http://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=OJ:L:2008:164:0019:0040:EN:PDF.
Falace, A., D. Curiel & A. Sfriso, 2009. Study of the macrophyte assemblages and application of phytobenthic indices to assess the Ecological Status of the Marano–Grado Lagoon (Italy). Marine Ecology 30: 480–494.
Gambi C., C. Totti & E. Manini, 2008. Impact of organic loads and environmental gradients on microphytobenthos and meiofaunal distribution in a coastal lagoon. Chemistry and Ecology 19: 207–223.
García-Sánchez, M., N. Korbee, I. M. Pérez-Ruzafa, C. Marcos, B. Domínguez, F. L. Figueroa & Á. Pérez-Ruzafa, 2012. Physiological response and photoacclimation capacity of Caulerpa prolifera (Forsskål) J.V. Lamouroux and Cymodocea nodosa (Ucria) Ascherson meadows in the Mar Menor lagoon (SE Spain). Marine Environmental Research 79: 37–47.
Gibson, G.R., M .L. Bowman, J. Gerritsen & B. D. Snyder, 2000. Estuarine and coastal marine waters: bioassessment and biocriteria technical guidance. EPA 822-B-00-024. US Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Water, Washington, DC. Available online at http://www.epa.gov/ost/biocriteria/States/estuaries/Estuaries-final.pdf.
Grece, T. M. & T. Binzer, 2004. Which factors regulate seagrass growth and distribution? In Borum, J., C.M. Duarte, D. Krause-Jensen & T. M. Greve (ed.), European seagrasses: an introduction to monitoring and management. Monitoring and Managing of European Seagrasses Project (M&MS): 19–23.
Guiry, M.D. & G.M. Guiry, 2013. AlgaeBase. World-wide electronic publication, National University of Ireland, Galway. http://www.algaebase.org.
Hein, M., M. F. Pedersen & K. Sand-Jensen, 1995. Size-dependent nitrogen uptake in micro- and macroalgae. Marine Ecology Progress Series 118: 247–253.
Hemminga, M. A. & C. M. Duarte, 2000. Seagrass Ecology. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Holling, C.S., 1973. Resilience and stability of ecological systems. Annual Review of Ecology & Systematics 4: 1–23. http://publications.jrc.ec.europa.eu/repository/bitstream/111111111/10473/1/3010_08-volumecoast.pdf.
Irving, A. D. & S. D. Connell, 2006. Predicting understorey structure from the presence and composition of canopies: an assembly rule for marine algae. Oecologia 148: 491–502.
Iveša, L., D. M. Lyons & M. Devescovi, 2009. Assessment of the ecological status of north-eastern Adriatic coastal waters (Istria, Croatia) using macroalgal assemblages for the European Union Water Framework Directive. Aquatic Conservation: Marine & Freshwater Ecosystems 19: 14–23.
Kautsky, H., 1995. Quantitative distribution of sublittoral plant and animal communities along the Baltic Sea gradient. In Eleftheriou, A., A. D. Ansell & C. J. Smint (eds), Biology and Ecology of Shallow Coastal Waters. Proceedings of the 28th European Marine Biology Symposium, Olsen and Olsen, Fredensborg: 23–30.
Körner, S. & A. Nicklisch, 2002. Allelopathic growth inhibition of selected phytoplankton species by submerged macrophytes. Journal of Phycology 38: 862–871.
Krause-Jensen, D., T. M. Greve & K. Nielsen, 2004. Eelgrass as bioindicator under the European Water Framework Directive. Water Resources Management 19: 63–75.
Kunii, H. & K. Minamoto, 2000. Temporal and spatial variation in the macrophyte distribution in coastal lagoon Lake Nakaumi and its neighbouring waters. Journal of Marine Systems 26: 223–231.
Lüning, K., 1990. Seaweeds: Their Environment, Biogeography and Ecophysiology. Wiley, New York.
Lobban, C. S. & P. J. Harrison, 1994. Seaweed Ecology and Physiology. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge: 163–209.
Lugoli, F., M. Garmendia, S. Lehtinen, P. Kauppila, S. Moncheva, M. Revilla, L. Roselli, N. Slabakova, V. Valencia, K. M. Dromph & A. Basset, 2012. Application of a new multi-metric phytoplankton index to the assessment of ecological status in marine and transitional waters. Ecological Indicators 23: 338–355.
Malea, P., T. Kevrekidis & A. Mogias, 2004. Annual versus perennial growth cycle in Ruppia maritima L.: temporal variation in population characteristics in Mediterranean lagoons (Monolimni and Drana Lagoons, Northern Aegean Sea). Botanica Marina 47: 357–366.
Mannino, A. M. & G. Sarà, 2006. The effect of Ruppia cirrhosa features on macroalgae and suspended matter in a Mediterranean shallow system. Marine Ecology 27: 350–360.
Marbà, N., D. Krause-Jensen, T. Alcoverro, S. Birk, A. Pedersen, J. A. Neto, S. Orfanidis, J. M. Garmendia, I. Muxika, A. Borja, K. Dencheva & C. M. Duarte, 2013. Diversity of European seagrass indicators: patterns within and across regions. Hydrobiologia 704: 265–278.
May, R. M., 1977. Thresholds and breakpoints in ecosystems with a multiplicity of stable states. Nature 267: 471–477.
McGlathery, K. J., K. Sundbäck & I. C. Anderson, 2007. Eutrophication in shallow coastal bays and lagoons: the role of plants in the coastal filter. Marine Ecology Progress Series 348: 1–18.
Menéndez, M., 2002. Net production of Ruppia cirrhosa in Ebro Delta. Aquatic Botany 73: 107–113.
Middelboe, A. L., K. Sand-Jensen & D. Krause-Jensen, 1998. Patterns of macroalgal species diversity in Danish estuaries. Journal of Phycology 34: 457–466.
Mouillot, D., S. Spatharis, S. Reizopoulou, T. Laugier, L. Sabetta, A. Basset & T. Do Chi, 2006. Alternatives to taxonomic-based approaches to assess changes in transitional water communities. Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems 16: 469–482.
Nedwell, D. B., A. S. Sage & G. J. C. Underwood, 2002. Rapid assessment of macro algal cover on intertidal sediments in a nutrified estuary. The Science of Total Environment 285: 97–105.
Nielsen, S. L. & K. Sand-Jensen, 1990. Allometric scaling of maximal photosynthetic growth rate to surface/volume ratio. Limnology & Oceanography 35: 177–181.
Odum, E. P., 1985. Trends expected in stressed ecosystems. Bioscience 35: 419–422.
Orfanidis, S., M. Pinna, L. Sabetta, N. Stamatis & K. Nakou, 2008. Variation of structural and functional metrics in macrophyte communities within two habitats of eastern Mediterranean coastal lagoons: natural versus human effects. Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems 18: S45–S61.
Orfanidis, S., P. Panayotidis & K. Ugland, 2011. Ecological Evaluation Index continuous formula (EEI-c) application: a step forward for functional groups, the formula and reference condition values. Mediterranean Marine Science 12: 199–231.
Orth, R. J., T. J. B. Carruthers, W. C. Dennison, C. M. Duarte, J. W. Fourqurean, K. Heck, A. R. Hughes, G. A. Kendrick, W. J. Kenworthy, S. Olyarnik, F. T. Short, M. Waycott & S. L. Williams, 2006. A global crisis for seagrass ecosystems. BioScience 56: 987–996.
Panayotidis, P., B. Montesanto & S. Orfanidis, 2004. Use of low-budget monitoring of macroalgae to implement the European Water Framework Directive. Journal of Applied Phycology 16: 49–59.
Patrício, J., J. M. Neto, H. Teixeira & J. C. Marques, 2007. Opportunistic macroalgae metrics for transitional waters. Testing tools to assess ecological quality status in Portugal. Marine Pollution Bulletin 54: 1887–1896.
Pauly, D., 1995. Anecdotes and the shifting baseline syndrome of fisheries. Tree 10: 430.
Pedersen, M. F. & J. Borum, 1997. Nutrient control of estuarine algae: growth strategy and the balance between nitrogen requirements and uptake. Marine Ecology Progress Series 161: 155–163.
Peychev, V. & M. Stancheva, 2009. Changes of sediment balance at the Bulgarian Black Sea coastal zone influenced by anthropogenic impacts. Comptes rendus de l’Académie bulgare des Sciences 62(2): 277–285.
Phillips, G. L., D. Eminson & B. Moss, 1978. A mechanism to account for macrophyte decline in progressively eutrophicated freshwaters. Aquatic Botany 4: 103–126.
Pinedo, S., M. García, M. P. Satta, M. de Torres & E. Ballesteros, 2007. Rocky-shore communities as indicators of water quality: a case study in the Northwestern Mediterranean. Marine Pollution Bulletin 55: 126–135.
Renzi, M., A. Specchiulli, D. Baroni, T. Scirocco, L. Cilenti, S. Focardi, P. Breber & S. Focardi, 2012. Trace elements in sediments and bioaccumulation in European eels (Anguilla anguilla) from a Mediterranean lagoon (SE Italy). International Journal of Environmental Analytical Chemistry 92: 676–697.
Rismondo, A., D. Curiel, M. Marzocchi & M. Scattolin, 1997. Seasonal patterns of Cymodocea nodosa biomass and production in the lagoon of Venice. Aquatic Botany 58: 55–64.
Roselli, L., A. Fabbrocini, C. Manzo & R. D’Adamo, 2009. Hydrological heterogeneity, nutrient dynamics and water quality of a non-tidal lentic ecosystem (Lesina Lagoon, Italy). Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 84: 539–552.
Roselli L., M. Cañedo-Argüelles, P. Costa Goela, S. Cristina, M. Rieradevall, R. D’Adamo & A. Newton, 2013. Do physiography and hydrology determine the physico-chemical properties and trophic status of coastal lagoons? A comparative approach. Estuarine, Coastal & Shelf Science 117: 29–36.
Rosenberg, G. & J. Ramus, 1984. Uptake of inorganic nitrogen and seaweed surface area: volume ratios. Aquatic Botany 19: 65–72.
Rozhdestvensky, A., 1986. Hydrochemistry of the Bulgarian sector of the Black Sea. Publishing House Bulgarian Academy of Science, Sofia. (in Bulgarian).
Rozhdestvensky, A., 1992. The impact of anthropogenic factors on the hydrology and on the hydrochemistry of the Varna Lake. Proceedings of Institute of Oceanology, Bulgarian Academy of Science 1: 48–57.
Sand-Jensen, K., T. Binzer & A. L. Middelboe, 2007. Scaling of photosynthetic production of aquatic macrophytes – a review. Oikos 116: 280–294.
Scanlan, C. M., J. Foden, E. Wells & M. A. Best, 2007. The monitoring of opportunistic macroalgal blooms for the water framework directive. Marine Pollution Bulletin 55: 162–171.
Scheffer, M., S. Carpenter, J. A. Foley, C. Folke & B. Walker, 2001. Catastrophic shifts in ecosystems. Nature 413: 591–596.
Schernewski, G. & M. Wielgat, 2004. A Baltic Sea typology according to the EC-Water Framework Directive: integration of national typologies and the water body concept. In Schernewski, G. & M. Weilgat (eds), Baltic Sea Typology. Coastline Reports, Vol. 4. EUCC – The Coastal Union, Leiden: 1–26.
Schramm, W., 1999. Factors influencing seaweed responses to eutrophication: some results from EU-project EUMAC. Journal of Applied Phycology 11: 69–78.
Schramm, W. & P. H. Nienhuis, 1996. Marine Benthic Vegetation. Recent Changes and the Effects of Eutrophication. Springer, New York.
Schubert, H., P. Feuerpfeil, R. Marquardt, I. Telesh & S. Skarlato, 2011. Macroalgal diversity along the Baltic Sea salinity gradient challenges Remane’s species-minimum concept. Marine Pollution Bulletin 62: 1948–1956.
Sfriso, A. & P. F. Ghetti, 1998. Seasonal variation in biomass, morphometric parameters and production of seagrasses in the lagoon of Venice. Aquatic Botany 61: 1–17.
Sfriso, A., A. Marcomini & B. Pavoni, 1987. Relationships between macroalgal biomass and nutrient concentration in a hypertrophic area of the Venice Lagoon Italy. Marine Environmental Research 22: 297–312.
Sfriso, A., B. La Rocca & E. Godini, 2002. Inventario dei taxa macroalali in tre aree della laguna di Venezia a differente livello di trofia. Società Veneziana Scienze Naturali 27: 85–99.
Shtereva, G., O. Hristova, B. Dzurova & A. Krastev, 2012. Hydrochemistry of Varna Bay (2000–2008). Journal of Environmental Protection and Ecology (JEPE) 13: 1695–1702.
Spatharis, S., S. Orfanidis, P. Panayotidis & G. Tsirtsis, 2011. Assembly processes in upper sublittoral macroalage: the effect of wave exposure. Estuarine, Coastal & Shelf Science 91: 298–305.
Specchiulli, A., R. D’Adamo, M. Renzi, F. Vignes, A. Fabbrocini, T. Scirocco, L. Cilenti, M. Florio, P. Breber & A. Basset, 2009. Fluctuations of physicochemical characteristics in sediments and overlying water during an anoxic event: a case study from Lesina lagoon (SE Italy). Transitional Waters Bulletin 3: 15–32.
Specchiulli, A., M. Renzi, T. Scirocco, L. Cilenti, M. Florio, P. Breber, S. Focardi & S. Bastianoni, 2010. Comparative study based on sediment characteristics and macrobenthic communities in two Italian lagoons. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment 160: 237–256.
Specchiulli A., M. Renzi, G. Perra, L. Cilenti, T. Scirocco, M. Florio, S. Focardi, P. Breber & S. Focardi, 2011. Distribution and sources of polycyclic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in surface sediments of some Italian lagoons exploited for aquaculture and fishing activities. International Journal of Environmental Analytical Chemistry 91: 367–386.
Stojanov, A., 1991. Negative changes in hydrochemical regime in Beloslav Lake – Varna Bay area. In Union of Scientists, Rational Use and Protection of Natural Resources of Varna Region, Varna: 38–46 (in Bulgarian).
Telesh, I. V. & V. V. Khlebovich, 2010. Principal processes within the estuarine salinity gradient: a review. Marine Pollution Bulletin 61: 149–155.
Terrados, J. & J. D. Ros, 1992. Growth and primary production of Cymodocea nodosa (Ucria) Ascherson in a Mediterranean coastal lagoon: the Mar Menor (SE Spain). Aquatic Botany 43: 63–78.
Thiebaut, G., F. Guérold & S. Muller, 2002. Are trophic and diversity indices on macrophyte communities pertinent tools to monitor water quality? Water Research 36: 3602–3610.
United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA), 2003. Guidance for 2004 Assessment, Listing and Reporting Requirements Pursuant to Sections 303(d) and 305(b) of the Clean Water Act. United States Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Water, Office of Wetlands, Oceans, and Watersheds.
Vadrucci, M. R., A. Fiocca, F. Vignes, A. Fabbrocini, L. Rosselli, R. D’Adamo, N. Ungaro & A. Basset, 2009. Dynamics of phytoplankton under dystrophic pressures in Lesina lagoon. Transitional Waters Bulletin 3: 89–103.
Verhoeven, J. T. A., 1979. The ecology of Ruppia-dominated communities in western Europe. I. Distribution of Ruppia representatives in relation to their autecology. Aquatic Botany 6: 197–268.
Verhoeven, J. T. A., 1980. The ecology of Ruppia-dominated communities in western Europe. III. Aspects of production, consumption and decomposition. Aquatic Botany 8: 209–253.
Viaroli, P., M. Bartoli, G. Giordani, M. Naldi, S. Orfanidis & J. M. Zaldivar, 2008. Community shifts, alternative stable states, biogeochemical controls and feedbacks and in eutrophic coastal lagoons: a brief review. Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems 18: S105–S117.
Vignes, F., E. Barbone, P. Breber, R. D’Adamo, L. Roselli, N. Ungaro, S. Focardi, M. Renzi & A. Basset, 2009. Spatial and temporal description of the dystrophic crisis in Lesina lagoon during summer 2008. Transitional Waters Bulletin 3: 114–119.
Wallentinus, I., 1991. The Baltic Sea gradient. In Mathieson, A. C. & P. H. Nienhuis (eds), Ecosystems of the World. Elsevier, Amsterdam: 83–108.
Waycott, M., C. M. Duarte, T. J. B. Cattuthers, R. J. Orth, W. C. Dennison, S. Olayarnik, A. Calladine, J. W. Fourqurean, K. Heck, A. R. Hughes, G. A. Kenrick, W. J. Kenworthy, F. T. Short & S. Williams, 2009. Accelerating loss of seagrasses across the globe threatens coastal ecosystems. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 106: 12377–12381.
Wilkinson, M., P. Wood, E. Wells & C. Scanlan, 2007. Using attached macroalgae to assess ecological status of British estuaries for the European water framework directive. Marine Pollution Bulletin 55: 136–150.
Acknowledgments
This paper is a result of the project WISER (Water bodies in Europe: Integrative Systems to assess Ecological status and Recovery) funded by the European Union under the 7th Framework Programme, Theme 6 (Environment including Climate Change) (Contract No. 226273), http://www.wiser.eu. The Greek team is also very grateful to the TOTAL Foundation (Paris; Project ‘Brown algal biodiversity and ecology in the Eastern Mediterranean Sea’) for additional support. We are very grateful to Dr. Claire Gachon for her contribution in the tentative identification of Oedogonium sp.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling editor: Pierluigi Viaroli
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Orfanidis, S., Dencheva, K., Nakou, K. et al. Benthic macrophyte metrics as bioindicators of water quality: towards overcoming typological boundaries and methodological tradition in Mediterranean and Black Seas. Hydrobiologia 740, 61–78 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-014-1938-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-014-1938-x