Abstract
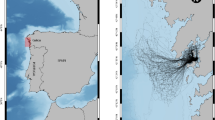
This study presents a 1-year synopsis of the trawl fishery for the European squid Loligo vulgaris in Portuguese waters, integrating length-structured landings with corresponding geo-referenced fishing activities. From vessel monitoring system (VMS) data, landings and biological sampling, a “status-report” was obtained for 2003. Fishing pressure was found to be most intense in inshore areas of the northwest and the south coasts. Population size structure, classified into three categories, was not uniform throughout the fishing areas. Larger squid are found offshore in the northwest (International Council for the Exploration of the Sea—ICES rectangle 10E0) and in the south (rectangles 2E1 and 3E1), whereas all inshore western coast rectangles showed larger proportions of small squid relative to the southern rectangles. The analysis carried out in this study provides an insight into the possible impact of the fishing intensity pattern on the population structure in various zones. The results demonstrate the benefits of combining geo-referenced fisheries information with landings and size data, to produce explicit spatio-temporal information that can contribute to integrated planning and management for the sustainable exploitation of this resource.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afonso-Dias, M. & C. Pinto, 2008. Análise da Distribuição Espacial do Esforço e Rendimentos de Pesca das Frotas Portuguesas de Arrasto Costeiro [Analysis of the spatial distribution of fishing effort and yields from the Portuguese coastal trawl fisheries]. GeoPesca. Final report of Project MARE 22-05-01-00025. 171 pp.
Bettencourt, V., L. Coelho, J. P. Andrade & A. Guerra, 1996. Age and growth of the squid Loligo vulgaris off the south coast of Portugal, using statolith analysis. Journal of Molluscan Studies 62: 359–366.
Boavida-Portugal, J., A. Moreno, L. Gordo & J. Pereira, 2010. Environmentally adjusted reproductive strategies in females of the commercially exploited common squid Loligo vulgaris. Fisheries Research 106: 193–198.
Campos, A., P. Fonseca, T. Fonseca & J. Parente, 2007. Definition of fleet components in the Portuguese bottom trawl fishery. Fisheries Research 83: 185–191.
Chen, C. S., G. J. Pierce, J. Wang, J. P. Robin, J. C. Poulard, J. Pereira, A. F. Zuur, P. R. Boyle, N. Bailey, D. J. Bear, P. Jereb, S. Ragonese, A. Mannini & L. Orsi-Relini, 2006. The apparent disappearance of Loligo forbesi from the south of its range in the 1990s: trends in Loligo spp. abundance in the northeast Atlantic and possible environmental influences. Fisheries Research 78: 44–54.
Coelho, M. L., J. Quintela, V. Bettencourt, G. Olavo & H. Villa, 1994. Population structure, maturation patterns and fecundity of the squid Loligo vulgaris from southern Portugal. Fisheries Research 21: 87–102.
Cunha, M. M., A. Moreno & J. M. F. Pereira, 1995. Spatial and temporal occurrences of Loligo spp. in Portuguese waters. ICES C.M. 1995/K:33.
Cunha, M. E., 2001. Physical control of biological processes in a coastal upwelling system: comparison of the effects of coastal topography, river run-off and physical oceanography in the northern and southern parts of western Portuguese coastal waters. PhD thesis, Faculdade de Ciências da Universidade de Lisboa, Lisboa: 305 pp.
Cunha, M. M. & A. Moreno, 1994. Recent trends in the Portuguese squid fishery. Fisheries Research 21: 231–241.
EC, 1996. Council Regulation (EC) No 2406/96 of 26 November 1996 laying down common marketing standards for certain fishery products (OJ L 334, 23.12.1996).
Fonseca, P., A. Campos & A. Garcia, 2002. Bottom trawl codend selectivity for cephalopods in Portuguese continental waters. Fisheries Research 59: 263–271.
Fonseca, T., A. Campos, M. Afonso-Dias, P. Fonseca & J. Pereira, 2008. Trawling for cephalopods off the Portuguese coast – fleet dynamics and landings composition. Fisheries Research 92: 180–188.
Guerra, A., P. Sanchez & F. Rocha, 1994. The Spanish fishery for Loligo: recent trends. Fisheries Research 21: 217–230.
Hastie, L. C., G. J. Pierce, J. Wang, I. Bruno, A. Moreno, U. Piatkowski, & J. P. Robin, 2009. Cephalopods in the north-east Atlantic: species, biogeography, ecology, exploitation and conservation. In Gibson, N., R. J. A. Atkinson & J. D. M. Gordon (eds), Oceanography and Marine Biology: An Annual Review. Taylor & Francis, Inc., Vol. 47: 119–190.
INE, 2011. Instituto Nacional de Estatística. Estatísticas da Pesca/Fishing Statistics, [online at http://www.ine.pt/xportal/xmain?xpid=INE&xpgid=ine_publicacoes&xlang=en; last accessed in 2012-12-12; in Portuguese].
Lee, J., A. B. South & S. Jennings, 2010. Developing reliable, repeatable, and accessible methods to provide high-resolution estimates of fishing-effort distributions from vessel monitoring system (VMS) data. ICES Journal of Marine Science, 67: 1260–1271.
Marques, A. C. A. M., 2012. Environmental drivers on the life cycle strategies and distribution of cephalopods in the Portuguese coast. PhD thesis, University of Lisbon.
Moreno, A., M. M. da Cunha & J. M. F. Pereira, 1994. Population biology of veined squid (Loligo forbesi) and European squid (Loligo vulgaris) from the Portuguese coast. Fisheries Research 21: 71–86.
Moreno, A., J. Pereira, C. Arvanitidis, J. P. Robin, D. Koutsoubas, C. Perales-Raya, M. M. Cunha, E. Balguerías & V. Denis, 2002. Biological variation of Loligo vulgaris (Cephalopoda: Loliginidae) in the eastern Atlantic and Mediterranean. Bulletin of Marine Science 71: 515–534.
Moreno, A., J. Pereira & M. M. Cunha, 2005. The effect of time of hatching in age and size at maturity of Loligo vulgaris. Aquatic Living Resources 18: 377–384.
Moreno, A., M. Azevedo, J. Pereira & G. J. Pierce, 2007. Growth strategies in the squid Loligo vulgaris from Portuguese waters. Marine Biology Research 3: 49–59.
Moreno, A., A. dos Santos, U. Piatkowski, A. M. P. Santos & H. Cabral, 2009. Distribution of cephalopod paralarvae in relation to the regional oceanography of the western Iberia. Journal of Plankton Research 31: 73–91.
Moreno, A., G. J. Pierce, M. Azevedo, J. Pereira & A. M. P. Santos, 2012. The effect of temperature on growth of early life stages of the common squid Loligo vulgaris. Journal of Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom 92: 1619–1628.
Peliz, A., J. Duberta, A. M. P. Santos, P. B. Oliveira & B. Le Cann, 2005. Winter upper ocean circulation in the Western Iberian Basin – Fronts, Eddies and Poleward Flows: an overview. Deep-Sea Research I 52: 621–646.
Pierce, G. J. & A. Guerra, 1994. Stock assessment methods used for cephalopod fisheries. Fisheries Research 21: 255–285.
Pierce, G. J., V. D. Valavanis, A. Guerra, P. Jereb, L. Orsi-Relini, J. M. Bellido, I. Katara, U. Piatkowski, J. Pereira, E. Balguerias, I. Sobrino, E. Lefkaditou, J. Wang, M. Santurtun, P. R. Boyle, L. C. Hastie, C. D. MacLeod, J. M. Smith, M. Viana, A. F. Gonzalez & A. F. Zuur, 2008. A review of cephalopod-environment interactions in European Seas and other world areas. Hydrobiologia 612: 49–70.
Pilar-Fonseca, T., 2013. Fleet dynamics in multispecies trawlers: a study based on fisheries-dependent data. PhD thesis, University of the Algarve.
Relvas, P., E. D. Barton, J. Dubert, P. B. Oliveira, A. Peliz, J. C. B. da Silva & A. M. P. Santos, 2007. Physical oceanography of the western Iberia ecosystem: latest views and challenges. Progress in Oceanography 74: 149–173.
Rocha, F. & A. Guerra, 1999. Age and growth of two sympatric squid Loligo vulgaris and Loligo forbesi, in Galician waters (north-west Spain). Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom 79: 697–707.
Rocha, F., A. Guerra & A. F. González, 2001. A review of reproductive strategies in cephalopods. Biological Reviews 76: 291–304.
Sanchez, P. & P. Martin, 1993. Population dynamics of the exploited cephalopod species of the Catalan Sea (NW Mediterranean). Scientia Marina 57: 153–159.
Smith, J. M., G. J. Pierce, A. F. Zuur, H. Martins, M. C. Martins, F. Porteiro & F. Rocha, 2011. Patterns of investment in reproductive and somatic tissues in the loliginid squid Loligo forbesii and Loligo vulgaris in Iberian and Azorean waters. Hydrobiologia 670: 201–221.
Steer, M. A., G. Pecl & N. A. Moltschaniwskyj, 2003. Are bigger calamary Sepioteuthis australis hatchlings more likely to survive? A study based on statolith dimensions. Marine Ecology Progress Series 261: 175–182.
Tsangridis, A., E. Lefkaditou & A. Adamidou, 1998. Analysis of catch and effort data of Loligo vulgaris in the W. Thracian Sea (NE Mediterranean, Greece) using a depletion model. Rapport Commission International pour l’exploration scientifique de la Mer Mediterranee 35: 494–495.
Vidal, E. A. G., F. P. DiMarco, J. H. Wormuth & P. G. Lee, 2002. Influence of temperature and food availability on survival, growth and yolk utilization in hatchling squid. Bulletin of Marine Science 71(2): 915–931.
Vila, Y., L. Silva, M. A. Torres & I. Sobrino, 2010. Fishery, distribution pattern and biological aspects of the common European squid Loligo vulgaris in the Gulf of Cadiz. Fisheries Research 106: 222–228.
Villanueva, R., 2000. Effect of temperature on statolith growth of the European squid Loligo vulgaris during early life. Marine Biology 136: 449–460.
Villanueva, R., A. Arkhipkin, P. Jereb, E. Lefkaditou, M. R. Lipinski, C. Perales-Raya, C. Riba & F. Rocha, 2003. Embryonic life of the loliginid squid Loligo vulgaris: comparison between statoliths of Atlantic and Mediterranean populations. Marine Ecology Progress Series 253: 197–208.
Worms, J., 1983. Loligo vulgaris. In Boyle, P. R. (ed). Cephalopod Life Cycles, Vol. I, Species Accounts. Academic Press, London: 143–157.
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by FCT PhD SFRH/BD/43409/2008, MARE 22-05-01-00025 (GeoPesca) and PTDC/BIA-BEC/103266/2008 (MTE) projects. GEoCrust 2.0 was developed initially by the project GeoCrust and subsequently by GeoPesca. This research was partially financed by the “Data Collection for Fisheries Sector Programme” (DCF-EC/DG Maritime Affairs & Fisheries/Joint Research Center). The first author would like to thank three colleagues, namely Melissa Shinn, for the revision of this manuscript. This study was presented to the CIAC 2012 symposium as a poster (“P83 CIAC 2012”) in October 2012.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Guest editors: Erica A. G. Vidal, Mike Vecchione & Sigurd von Boletzky / Cephalopod Life History, Ecology and Evolution
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pilar-Fonseca, T., Pereira, J., Campos, A. et al. VMS-based fishing effort and population demographics for the European squid (Loligo vulgaris) off the Portuguese coast. Hydrobiologia 725, 137–144 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-013-1736-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-013-1736-x