Abstract
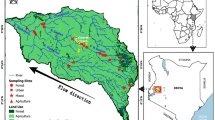
The effects of land use on the elemental stoichiometry of aquatic organisms have rarely been studied in semi-arid watersheds. In eight semi-arid sub-watersheds differing in land use, we determined which predictor variable(s) best explains the elemental variability in two basal food resources and benthic macroinvertebrates (BMI). The elemental composition of periphyton and seston was best explained by percentage of urban and agricultural areas, forested land and associated differences in SRP, DOC, and stream water N:P ratios. In contrast, consumer elemental stoichiometry was related to taxonomic identity and feeding mode. Elemental imbalances were higher for collector-gatherer than for scraper and collector-filterer. However, high spatial and temporal variability in the elemental composition of basal food resources obscured clear spatial patterns of imbalances between nutrient-poor upstream and nutrient-rich downstream sites. Results from this study suggest that land use can affect BMI due to alteration in stoichiometry of their food resources. However, taxonomy and allometry must be taken into account to better understand spatial and temporal changes in the elemental composition of BMI. Our results indicate the importance of considering multiple effects to accurately assess land use effects on producer and consumer stoichiometry, particularly the in highly variable Great Basin watersheds.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allan, J. D., 2004. Landscapes and riverscapes: the influence of land use on stream ecosystems. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics 35: 257–284.
American Public Health Association, 1992. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 18th ed. American Public Health Association, Washington, DC.
Atkinson, C. L., S. W. Golladay, S. P. Opsahl & A. P. Covich, 2009. Stream discharge and floodplain connections affect seston quality and stable isotopic signatures in a coastal plain stream. Journal of the North American Benthological Society 28: 360–370.
Baldwin, C. K., F. H. Wagner & U. Lall, 2003. Water Resources. In Wagner, F. H. (ed.), Rocky Mountain/Great Basin Regional Climate-Change Assessment. Report of the U.S. Global Change Research Program. Utah State University, Logan, UT: 240 pp.
Bothwell, M. L., 1985. Phosphorus limitation of lotic periphyton growth rates – an intersite comparison using continuous-flow troughs (Thompson River system, British Columbia). Limnology and Oceanography 30: 527–542.
Bowes, M. J., W. A. House & R. A. Hodgkinson, 2003. Phosphorus dynamics along a river continuum. Science of the Total Environment 313: 199–212.
Bowman, M. F., P. A. Chambers & D. W. Schindler, 2005. Changes in stoichiometric constraints in epilithon and benthic macroinvertebrates in response to slight nutrient enrichment of mountain rivers. Freshwater Biology 50: 1836–1852.
Chambers, J. C., J. R. Miller & D. Germanoski, 2011. Geomorphology, hydrology, and ecology of Great Basin meadow complexes – implications for management and restoration. U. S. Department of Agriculture Forest Service. General Technical Report, Fort Collins, CO: 152 pp.
Cross, W. F., J. P. Benstead, A. D. Rosemond & J. B. Wallace, 2003. Consumer–resource stoichiometry in detritus-based streams. Ecology Letters 6: 721–732.
Cross, W. F., J. B. Wallace & A. D. Rosemond, 2007. Nutrient enrichment reduces constraints on material flows in a detritus-based food web. Ecology 88: 2563–2575.
DeMott, W. R. & B. J. Pape, 2005. Stoichiometry in an ecological context: testing links between Daphnia P-content, growth rate and habitat preference. Oecologia 142: 20–27.
Elser, J. J. & R. P. Hassett, 1994. A stoichiometric analysis of the zooplankton–phytoplankton interaction in marine and freshwater ecosystems. Nature 370: 211–213.
Evans-White, M. A., R. S. Stelzer & G. A. Lamberti, 2005. Taxonomic and regional patterns in benthic macroinvertebrate elemental composition in streams. Freshwater Biology 50: 1786–1799.
Fagan, W. F., E. Siemann, C. Mitter, R. F. Denno, A. F. Huberty, H. A. Woods & J. J. Elser, 2002. Nitrogenin insects: implications for trophic complexity and species diversification. American Naturalist 160: 784–802.
Fink, P. & E. von Ehlert, 2006. Physiological responses to stoichiometric constraints: nutrient limitation and compensatory feeding in a freshwater snail. Oikos 115: 484–494.
Fisher, S. G. & G. E. Likens, 1973. Energy flow in Bear Brook, New Hampshire: an integrative approach to stream ecosystems metabolism. Ecological Monographs 43: 421–439.
Frost, P. C., R. S. Stelzer, G. A. Lamberti & J. J. Elser, 2002. Ecological stoichiometry of trophic interactions in benthos: understanding the role of C:N:P ratios in lentic and lotic habitats. Journal of North American Benthological Society 21: 515–528.
Frost, P. C., S. E. Tank, M. A. Turner & J. J. Elser, 2003. Elemental composition of littoral invertebrates from oligotrophic and eutrophic Canadian lakes. Journal of North American Benthological Society 22: 51–62.
Frost, P. C., L. E. Kinsman, C. A. Johnston & J. H. Larson, 2009. Watershed discharge modulates relationship between landscape components and nutrient ratios in stream seston. Ecology 90: 1631–1640.
Gaines, W. L., C. E. Cushing & S. D. Smith, 1989. Trophic relations and functional group composition of benthic insects in three cold desert streams. The Southwestern Naturalist 34: 478–482.
Green, M. B. & J. C. Finlay, 2010. Patterns of hydrologic control over stream water total nitrogen to total phosphorus ratios. Biogeochemistry 99: 15–30.
Grimm, N., 1988. Role of macroinvertebrates in nitrogen dynamics of a desert stream. Ecology 69: 1884–1893.
Grimm, N. B. & S. G. Fisher, 1986. Nitrogen limitation in a Sonoran Desert stream. Journal of North American Benthological Society 5: 2–15.
Grimm, N. B., J. R. Arrowsmith, C. Eisinger, J. Heffernan, A. MacLeod, D. B. Lewis, L. Prashad, T. Rychener, W. J. Roach & R. W. Sheibley, 2004. Effects of Urbanization on Nutrient Biogeochemistry of Aridland Streams. Ecosystems and Land Use Change. Geophysical Monograph Series, 153. American Geophysical Union, Washington, D.C.
Harding, J. S., R. G. Young, J. W. Hayes, K. A. Shearer & J. D. Stark, 1999. Changes in agricultural intensity and river health along a river continuum. Freshwater Biology 42: 345–357.
Hoorman, J., T. Hone, T. Sudman, Jr., T. Dirksen, J. Iles & K. R. Islam, 2008. Agricultural Impacts on Lake and Stream Water Quality in Grand Lake St. Marys, Western Ohio. Water Air Soil Pollution. doi:10.1007/s11270-008-9692-1.
Jarvie, H. P., P. J. A. Withers, R. Hodgkinson, A. Bates, M. Neal, H. D. Wickham, S. A. Harman & L. Armstrong, 2008. Influence of rural land use on streamwater nutrients and their ecological significance. Journal of Hydrology 350: 166–186.
Kahlert, M., 1998. C:N: P ratios of freshwater benthic algae. Archiv fuer Hydrobiologie, Advances in Limnology 51: 105–114.
Klausmeier, C. A., E. Litchman, T. Daufresne & S. A. Levin, 2004. Optimal nitrogen-to-phosphorus stoichiometry of phytoplankton. Letters to Nature 429: 171–174.
Laudon, H., M. Berggren, A. Agren, I. Buffam, K. Bishop, T. Grabs, M. Jansson. & S. Koehler, 2011. Patterns and Dynamics of Dissolved Organic Carbon (DOC) in Boreal Streams: The Role of Processes, Connectivity, and Scaling. Ecosystems. doi:10.1007/s10021-011-9452-8.
Lauridsen, R. B., F. K. Edwards, M. J. Bowes, G. Woodward, A. G. Hildrew, A. T. Ibbotson & J. I. Jones, 2012. Consumer–resource elemental imbalances in a nutrient-rich stream. Freshwater Science 31: 408–422.
Liess, A. & H. Hillebrand, 2005. Stoichiometric variation in C:N, C:P, and N:P ratios of littoral benthic invertebrates. Journal of North American Benthological Society 24: 256–269.
Merritt, R. W. & K. W. Cummins, 1996. An Introduction to the Aquatic Insects of North America. Kendall/Hunt, Dubuque, IA.
Minshall, G. W., 1978. Autotrophy in stream ecosystems. BioScience 28: 767–770.
O’Brien, P. J. & J. D. Wehr, 2010. Periphyton biomass and ecological stoichiometry in streams within an urban to rural land-use gradient. Hydrobiologia 657: 89–115.
Paul, M. J. & J. L. Meyer, 2001. Streams in the urban landscape. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics 32: 333–365.
Petersen, C. G. & N. B. Grimm, 1992. Temporal variation in enrichment effects during periphyton succession in a nitrogen-limited desert stream ecosystem. North American Benthological Society 11: 20–36.
Redfield, A. C., 1958. The biological control of chemical factors in the environment. American Naturalist 46: 205–222.
Rier, S. T. & R. J. Stevenson, 2006. Response of periphytic algae to gradients in nitrogen and phosphorus in streamside mesocosms. Hydrobiologia 561: 131–147.
Sada, D., C. Rosamond, D. Henneberry & J. Dillon, 2009. Relationships between aquatic environments and benthic macroinvertebrates communities, Nevada and California with consideration of the influence of discharge on community structure. In Collopy, M. W. & J. M. Thomas (eds), Restoration of a Desert Lake in an Agriculturally Dominated Watershed: The Walker Lake Basin, Final Report: pp. 1–24.
Schade, J. D. & S. G. Fisher, 1997. Leaf litter in a Sonoran Desert stream ecosystem. Journal of North American Benthological Society 16: 612–626.
Sharpe S. E., 2009. Past elevations and ecosystems of Walker Lake provide a context for future management decisions. In Collopy, M. W. & J. M. Thomas (eds), Restoration of a Desert Lake in an Agriculturally Dominated Watershed: The Walker Lake Basin, Final Report: pp. 1–24.
Small, G. E. & C. M. Pringle, 2010. Deviation from strict homeostasis across multiple levels in an invertebrate consumer assemblage exposed to high chronic phosphorus enrichment in a Neotropical stream. Oecologia 162: 581–590.
Smith, G., 2000. Sierra East: Edge of the Great Basin. University of California Press, Berkeley, CA.
Soulsby, C., R. Malcolm, C. Gibbins & C. Dilks, 2001. Seasonality, water quality trends and biological responses in four streams in the Cairngorm Mountains, Scotland. Hydrology and Earth Science 5: 433–450.
Stelzer, R. A. & G. A. Lamberti, 2001. Effects of N:P ratio and total nutrient concentration on stream periphyton community structure, biomass, and elemental composition. Limnology and Oceanography 46: 356–367.
Sterner, R. W. & J. J. Elser, 2002. Ecological Stoichiometry. The Biology of Elements from Molecules to the Biosphere. Princeton University Press, Princeton, NJ.
Townsend, C. R., S. Doledec, R. Norris, K. Peacock & C. Arbuckle, 2003. The influence of scale and geography on relationships between stream community composition and landscape variables: description and prediction. Freshwater Biology 48: 768–785.
Tsoi, W. Y., W. L. Hadwen & C. S. Fellows, 2011. Spatial and temporal variation in the ecological stoichiometry of aquatic organisms in an urban catchment. Journal of North American Benthological Society 30: 533–545.
Vannote, R. L., W. G. Minshall, K. W. Cummins, J. R. Sedell & C. E. Cushing, 1980. The river continuum concept. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Science 37: 130–137.
Velasco, J. A., M. R. Millan, M. L. Vidal-Abarca, C. Suarez, Guerrero & M. Ortega, 2003. Macrophytic, epipelic and epilithic primary production in a semiarid Mediterranean stream. Freshwater Biology 48: 1408–1420.
Walsh, C. J., A. H. Roy, J. W. Feminella, P. D. Cottingham, P. M. Groffmans & R. P. Morgen II, 2005. The urban stream syndrome: current knowledge and the search for a cure. Journal of North American Benthological Society 24: 706–723.
Wetzel, R. G., 2001. Limnology, 3rd ed. Academic Press, San Diego, California, USA.
Whiles, M. R. & W. K. Doods, 2002. Relationships between stream size, suspended particles, and filter-feeding macroinvertebrates in a Great Plains drainage network. Journal of Environmental Quality 31: 1589–1600.
Wiens, J. A., 2002. Riverine landscapes: taking landscape ecology into the water. Freshwater Biology 47: 501–515.
Wold, A. P. & A. E. Hershey, 1999. Spatial and temporal variability of nutrient limitation in 6 North Shore tributaries to Lake Superior. Journal of the North American Benthological Society 18: 2–14.
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by a Grant under Public Laws 109-103, Section 208 (a) through the U.S. Bureau of Reclamation (Cooperative Agreement 06FC204044). Thanks to Chris Rosamond from the Desert Research Institute, Reno, Nevada for his assistance in the field. The authors are grateful to Cathy Kochert who performed the carbon and nitrogen content analyses at the Goldwater Environmental Laboratory, Arizona State University. We thank Mary Miller from Water Quality Laboratory at the Desert Research Institute, Reno, Nevada for performing the water chemistry analyses. Finally, we sincerely thank the anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments on this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling editor: Sonja Stendera
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mehler, K., Acharya, K., Sada, D. et al. Elemental stoichiometry of basal resources and benthic macroinvertebrates along a land use gradient in a Great Basin watershed. Hydrobiologia 716, 115–129 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-013-1549-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-013-1549-y