Abstract
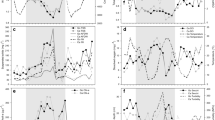
The role of the microbial communities in the classical planktonic food web and its response to eutrophication in shallow lakes is still contradictory. Mediterranean shallow lakes with different eutrophication levels were sampled to study the influence of eutrophication on the microbial food web (MFW) and their contribution to the planktonic food web. Percentage of ciliate biomass in the metazooplankton (MZP) showed a U-shaped trend with eutrophication, with maximum at both ends of the chlorophyll-a (Chla) gradient. The MZP to phytoplankton ratio demonstrated a unimodal pattern with minimum values at the two ends of the Chla gradient and maximum values in the Chla range 5-10 μg l−1. In contrast, the MFW to phytoplankton ratio reached its minimum in the central part of the Chla gradient and maximum values at the extremes of the gradient. These patterns support the hypothesis that the relative importance of bacteria and ciliates is lowest in mesotrophic shallow lakes, and highest in oligotrophic and hypereutrophic systems. These results stress the importance of protozoan in the trophic web, and indicate it is essential to include this group, especially ciliates, when quantifying zooplankton in warm shallow lakes.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adrian, R. & B. Schneider-Olt, 1999. Top-down effects of crustacean zooplankton on pelagic microorganisms in a mesotrophic lake. Journal of Plankton Research 21: 2175–2190.
AEMET & IM, 2011. Iberian Climate Atlas. Agencia Estatal de Meteorología and Instituto de Meteorologia, Madrid.
APHA, 1995. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 19th ed. American Public Health Association, Washington, DC.
Arvola, L., 1981. Spectrophotometric determination of chlorophyll-a and phaeopigments in ethanol extractions. Annales Botanici Fennici 18: 221–227.
Auer, B., U. Elzer & H. Arndt, 2004. Comparison of pelagic food webs in lakes along a trophic gradient and with seasonal aspects: influence of resource and predation. Journal of Plankton Research 26: 697–709.
Beaver, J. R. & T. L. Crisman, 1982. The trophic response of ciliated protozoans in freshwater lakes. Limnology and Oceanography 27: 246–253.
Beaver, J. R. & T. L. Crisman, 1989. The role of ciliated protozoa in pelagic freshwater ecosystems. Microbial Ecology 17: 111–136.
Bécares, E., A. Conty, C. Rodríguez-Villafañe & S. Blanco, 2004. Funcionamiento de los lagos someros mediterráneos. Ecosistemas 13: 1–14.
Beklioglu, M., S. Romo, I. Kagalou, X. Quintana & E. Bécares, 2007. State of the art in the functioning of shallow Mediterranean lakes: workshop conclusions. Hydrobiologia 584: 317–326.
Berninger, U.-G., B. J. Finlay & P. Kuuppo-Leinikki, 1991. Protozoan control of bacterial abundances in freshwater. Limnology and Oceanography 36: 139–147.
Blanco, S., S. Romo, M. J. Villena & S. Martínez, 2003. Fish communities and food web interactions in some shallow Mediterranean lakes. Hydrobiologia 506: 473–480.
Blanco, S., S. Romo & M. J. Villena, 2004. Experimental study on the diet of mosquitofish (Gambusia holbrooki) under different ecological conditions in a shallow lake. International Review of Hydrobiology 89: 250–262.
Bottrell, H. H., A. Duncan, Z. M. Gliwicz, E. Grygierek, A. Herzig, A. Hillbricht-IIkowska, H. Kurasawa, P. Larsson & T. Weglenska, 1976. A review of some problems in zooplankton production studies. Norwegian Journal of Zoology 24: 419–456.
Chaney, A. L. & E. P. Morbach, 1982. Modified reagents for the determination of urea and ammonia. Clinical Chemistry 8: 130–132.
Chróst, R. J. & W. Siuda, 2006. Microbial production, utilization and enzymatic degradation of organic matter in the upper trophogenic layer in the pelagial zone of lakes along a eutrophication gradient. Limnology and Oceanography 51: 749–762.
Conty, A., F. García-Criado & E. Bécares, 2007. Changes in bacterial and ciliate densities with trophic status in Mediterranean shallow lakes. Hydrobiologia 584: 327–335.
Cotner, J. B. & B. A. Biddanda, 2002. Small players, large role: microbial influence on biogeochemical processes in pelagic aquatic ecosystems. Ecosystems 2: 105–121.
Dumont, H. J., I. Van de Velde & S. Dumont, 1975. The dry weight estimate of biomass of a selection of Cladocera, Copepoda, and Rotifera from the plankton, periphyton, and benthos of continental waters. Oecologia 19: 75–97.
Fernández-Aláez, M., C. Fernández-Aláez, E. Bécares, M. Valentín, J. Gomá & P. Castillo, 2004. A 2-year experimental study on nutrient and predator influences on food web constituents in a shallow lake of north-west Spain. Freshwater Biology 49: 1574–1592.
Gasol, J. M., R. Guerrero & C. Pedrós-Alió, 1991. Seasonal variations in size structure and prokaryotic dominance in sulphurous Lake Cisó. Limnology and Oceanography 36: 860–872.
Goubanova, K. & L. Li, 2007. Extremes in temperature and precipitation around the Mediterranean basin in an ensemble of future climate scenario simulations. Global and Planetary Change 57: 27–42.
Guerrero, R. & C. Pedrós-Alió, 1992. The microbial component in Spanish aquatic ecosystems. Limnetica 8: 175–184.
Jeffrey, S. W. & G. C. Humphrey, 1975. New spectrophotometric equations for the determination of chlorophylls-a, b, c1 and c2 in higher plants, algae and natural phytoplankton. Biochemie und Physiologie der Pflanzen 167: 191–194.
Jeppesen, E., 1998. The ecology of shallow lakes: trophic interactions in the pelagial. Ph.D. Thesis, National Environmental Research Institute, Silkeborg, Denmark. NERI Technical Report 247.
Jeppesen, E., M. Erlandsen & M. Søndergaard, 1997. Can simple empirical equations describe the seasonal dynamics of bacterioplankton in lakes? An eight-year study in shallow hypertrophic and biologically highly dynamic lake Søbygård, Denmark. Microbial Ecology 34: 11–26.
Jeppesen, E., M. Søndergaard, N. Mazzeo, M. Meerhoff, C. Branco, V. Huszar & F. Scasso, 2005. Lake restoration and biomanipulation in temperate lakes: relevance for subtropical and tropical lakes. In Reddy, M. V. (ed.), Tropical Eutrophic Lakes: Their Restoration and Management. Oxford & IBH Publishing Co, New Delhi: 331–359.
Jerome, C. A., D. J. S. Montagnes & F. J. R. Taylor, 1993. The effect of the quantitative protargol stain and lugol’s and bouin’s fixatives on cell size: a more accurate estimate of ciliate species biomass. Journal of Eukaryotic Microbiology 40: 254–259.
Jürgens, K. & E. Jeppesen, 1998. Cascading effects on microbial food web structure in a dense macrophyte bed. In Jeppesen, E., Ma. Søndergaard, Mo. Søndergaard & K. Christoffersen (eds), The Structuring Role of Submerged Macrophytes in Lakes. Springer, Berlin. Ecological Studies 131: 262–273.
Latja, R. & K. Salonen, 1978. Carbon analysis for the determination of individual biomasses of planktonic animals. Verhandlungen der Internationalen Vereinigung für Theoretische und Angewandte Limnologie 20: 2556–2560.
Lau, S. S. S. & S. N. Lane, 2002. Biological and chemical factors influencing shallow lake eutrophication: a long-term study. Science of the Total Environment 288: 167–181.
Lazzaro, X., M. Bouvy, R. A. Ribeiro-Filho, V. S. Oliveira, L. T. Sales, A. R. M. Vasconcelos & M. R. Mata, 2003. Do fish regulate phytoplankton in shallow eutrophic Northeast Brazilian reservoirs? Freshwater Biology 48: 649–668.
Loferer-Kröβbacher, M., J. Klima & R. Psenner, 1998. Determination of bacterial cell dry mass by transmission electron microscopy and densitometric image analysis. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 64: 688–694.
Matena, J., K. Šimek & C. H. Fernando, 1995. Ingestion of suspended bacteria by fish: a modified approach. Journal of Fish Biology 47: 334–336.
Mathes, J. & H. Arndt, 1994. Biomass and composition of protozoan plankton in relation to lake trophy in north German lakes. Marine Microbial Food Webs 8: 357–375.
Meerhoff, M., C. Iglesias, F. Teixeira de Mello, J. M. Clemente, E. Jensen, T. Lauridsen & E. Jeppesen, 2007. Effects of habitat complexity on community structure and predator avoidance behaviour of littoral zooplankton in temperate versus subtropical shallow lakes. Freshwater Biology 52: 1009–1021.
Menden-Deuer, S. & E. J. Lessard, 2000. Carbon to volume relationships for dinoflagellates, diatoms and other protist plankton. Limnology and Oceanography 45: 569–579.
Moss, B., D. Stephen, D. Balayla, E. Bécares, S. E. Collings, C. Fernández-Aláez, M. Fernández-Aláez, C. Ferriol, P. García, J. Gomá, M. Gyllström, L.-A. Hansson, J. Hietala, T. Kairesalo, M. R. Miracle, S. Romo, J. Rueda, V. Rusell, A. Ståhl-Delbanco, M. Svennson, K. Vakkilainen, M. Valentín, W. J. Van de Bund, E. Van Donk, E. Vicente & M. J. Villena, 2004. Continental-scale patterns of nutrient and fish effects of shallow wetland lakes: synthesis of a pan-European mesocosm experiment. Freshwater Biology 49: 1633–1650.
Murphy, J. & J. P. Riley, 1962. A modified single solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural waters. Analytica Chimica Acta 27: 31–36.
Pace, M. L., 1986. An empirical analysis of zooplankton community structure across lake trophic gradients. Limnology and Oceanography 31: 45–55.
Pace, M. L., J. J. Cole & S. R. Carpenter, 1998. Trophic cascades and compensation: differential responses of microzoan plankton in whole-lake experiments. Ecology 79: 138–152.
Pace, M. L., J. J. Cole, S. R. Carpenter, J. F. Kitchell, J. R. Hodgson, M. C. Van de Bogert, D. L. Bade, E. S. Kritzberg & D. Bastviken, 2004. Whole-lake carbon-13 additions reveal terrestrial support of aquatic food webs. Nature 427: 240–243.
Pfister, G., B. Auer & H. Arndt, 2002. Pelagic ciliates (Protozoa, Ciliophora) of different brackish and freshwater lakes: a community analysis at the species level. Limnologica 32: 147–168.
Pomeroy, L. R. & W. J. Wiebe, 1988. Energetics of microbial food webs. Hydrobiologia 159: 7–18.
Porter, K. G. & Y. S. Feig, 1980. The use of DAPI for identifying and counting aquatic microflora. Limnology and Oceanography 25: 943–948.
Porter, K. G., H. Paerl, R. Hodson, M. L. Pace, J. Priscu, B. Riemann, D. Scavia & J. Stockner, 1988. Microbial interactions in lake food webs. In Carpenter, S. R. (ed.), Complex Interactions in Lake Communities. Springer, Berlin: 209–227.
Posch, T., J. Pernthaler, A. Alfreider & R. Psenner, 1997. Cell-specific respiratory activity of aquatic bacteria studied with the tetrazolium reduction method, cyto-clear slides, and image analysis. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 63: 867–873.
Rahmatullah, S. M. & M. C. M. Beveridge, 1993. Ingestion of bacteria in suspension by Indian major carps (Catla catla, Labeo rohita) and Chinese carps (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix, Aristichtys nobilis). Hydrobiologia 264: 79–84.
Riemann, B. & K. Christoffersen, 1993. Microbial trophodynamics in temperate lakes. Marine Microbial Food Webs 7: 69–100.
Rolff, C. & R. Elmgren, 2000. Use of riverine organic matter in plankton food webs of the Baltic Sea. Marine Ecology Progress Series 197: 81–101.
Romo, S., M. R. Miracle, M. J. Villena, J. Rueda, C. Ferriol & E. Vicente, 2004. Mesocosm experiments on nutrient and fish effects on shallow lake food webs in a Mediterranean climate. Freshwater Biology 49: 1593–1607.
Sánchez, E., C. Gallardo, M. A. Gaertner, A. Arribas & M. Castro, 2004. Future climate extreme events in the Mediterranean simulated by a regional climate model: a first approach. Global and Planetary Change 44: 180–183.
Sandberg, J., A. Andersson, S. Johansson & J. Wikner, 2004. Pelagic food web structure and carbon budget in three brackish water environments: potential importance of terrigenous carbon. Marine Ecology Progress Series 268: 13–29.
Sanders, R. W. & S. A. Wickham, 1993. Planktonic protozoa and metazoa: predation, food quality and population control. Marine Microbial Food Webs 7: 197–223.
Sanders, R. W., K. G. Porter, S. J. Bennett & A. E. DeBiase, 1989. Seasonal patterns of bacterivory by flagellates, ciliates, rotifers, and cladocerans in a freshwater planktonic community. Limnology and Oceanography 34: 673–687.
Scheffer, M., 1998. Ecology of Shallow Lakes. Champman & Hall, New York.
Sherr, E. B., D. A. Caron & B. F. Sherr, 1993. Staining of heterotrophic protists for visualization via epifluorescence microscopy. In Kemp, P. F., B. F. Sherr, E. B. Sherr & J. J. Cole (eds), Handbook of Methods in Aquatic Microbial Ecology. Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton: 213–227.
Šimek, K., K. Jürgens, J. Nedoma, M. Comerma & J. Armengol, 2000. Ecological role and bacterial grazing of Halteria spp.: small freshwater oligotrichs as dominant pelagic ciliate bacterivores. Aquatic Microbial Ecology 22: 43–56.
Skibbe, O., 1994. An improved quantitative protargol stain for ciliates and other planktonic protists. Archiv für Hydrobiologie 130: 339–347.
Stabell, T., 1996. Ciliate bacterivory in epilimnetic waters. Aquatic Microbial Ecology 10: 265–272.
StatSoft, Inc, 2004. STATISTICA (Data Analysis Software System), Version 6. Tulsa, StatSoft.
Stoecker, D. K. & J. M. Capuzzo, 1990. Predation on protozoa: its importance to zooplankton. Journal of Plankton Research 12: 891–908.
Thouvenot, A., M. Richardot, D. Debroas & J. Devaux, 1999. Bacterivory of metazooplankton, ciliates and flagellates in a newly flooded reservoir. Journal of Plankton Research 21: 1659–1679.
Utermöhl, H., 1958. Zur Vervollkommung der quantitativen phytoplankton-methodik. Mitteilungen der internationalen Vereingung für theoretische und angewandte Limnologie 9: 1–38.
Weisse, T., 1991. The microbial food web and its sensitivity to eutrophication and contaminant enrichment: a cross-system overview. Internationale Revue der Gesamten Hydrobiologie 76: 327–337.
Weisse, T. & J. Stockner, 1994. Eutrophication: the role of microbial food webs. In Proceedings of the Fifth International Conference on Conservation and Management of Lakes: 191–194.
Wetzel, R. G., 2001. Limnology: Lake and River Ecosystems, 3rd ed. Academic Press, San Diego.
Zingel, P., E. Huitu, S. Mäkelä & L. Arvola, 2002. The abundance and diversity of planktonic ciliates in 12 boreal lakes of varying trophic state. Archiv für Hydrobiologie 155: 315–332.
Acknowledgments
We would like to express our thanks to Cristina Trigal, Saúl Blanco, Celia de la Vega, Joan Gomá, and all the other members of the limnology group at the University of Leon. We also thank Phaedra Budy for critical reading of the manuscript and valuable comments. This research was funded by the University of León, the Spanish Ministry of Science and Technology (REN2003-03718/HID), and the Castilla y León Government.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling editor: Mariana Meerhoff
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Conty, A., Bécares, E. Unimodal patterns of microbial communities with eutrophication in Mediterranean shallow lakes. Hydrobiologia 700, 257–265 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-012-1235-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-012-1235-5