Abstract
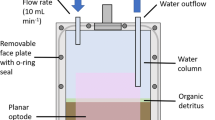
A previous study has demonstrated that in sandy sediment the marine yabby (Trypaea australiensis) stimulated benthic metabolism, nitrogen regeneration and nitrification, but did not stimulate denitrification, as the intense bioturbation of the yabbies eliminated anoxic microzones amenable to denitrification. It was hypothesised that organic matter additions would alleviate this effect as the buried particles would provide anoxic microniches for denitrifiers. To test this hypothesis a 55-day microcosm (75 cm × 36 cm diameter) experiment, comprising four treatments: sandy sediment (S), sediment + yabbies (S + Y), sediment + A. marina litter (S + OM) and sediment + yabbies + A. marina litter (S + Y + OM), was conducted. Trypaea australiensis significantly stimulated benthic metabolism, nitrogen regeneration, nitrification and nitrate reduction in the presence and the absence of litter additions. In contrast, the effects of litter additions alone were more subtle, developed gradually and were only significant for sediment oxygen demand. However, there was a significant interaction between yabbies and litter with rates of total nitrate reduction and denitrification being significantly greater in the S + Y + OM than all other treatments, presumably due to the decaying buried litter providing anoxic micro-niches suitable to nitrate reduction. In addition, both T. australiensis and litter significantly decreased rates of DNRA and its contribution to nitrate reduction.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Public Health Association (APHA), 1998. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 20th ed. American Public Health Association, Washington DC.
Banta, G. T., M. Holmer, M. H. Jensen & E. Kristensen, 1999. Effects of two polychaete worms, Nereis diversicolor and Arenicola marina, on aerobic and anaerobic decomposition in a sandy marine sediment. Aquatic Microbial Ecology 19: 189–204.
Bartoli, M., D. Nizzoli, D. T. Welsh & P. Viaroli, 2000. Short-term influence of recolonisation by the polychaete worm Nereis succinea on oxygen and nitrogen fluxes and denitrification: a microcosm simulation. Hydrobiologia 431: 165–174.
Blackburn, T. H. & N. D. Blackburn, 1993. Rates of microbial processes in sediments. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society London A 344: 49–58.
Burgin, A. J. & S. K. Hamilton, 2007. Have we overemphasized the role of denitrification in aquatic ecosystems? A review of nitrate removal pathways. Frontiers in Ecology 5: 89–96.
Christensen, P. B., S. Rysgaard, N. P. Sloth, T. Dalsgaard & S. Schwaerter, 2000. Sediment mineralization, nutrient fluxes, denitrification and dissimilatory nitrate reduction to ammonium in an estuarine fjord with sea cage trout farms. Aquatic Microbial Ecology 21: 73–84.
Contessa, L. & F. L. Bird, 2004. The impact of bait-pumping on populations of the ghost shrimp Trypaea australiensis (Decapoda: Callianassidae) and the sediment environment. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 304: 75–97.
Dalsgaard, T., L. P. Nielsen, V. Brotas, P. Viaroli, G. I. C. Underwood, D. B. Nedwell, K. Sundback, S. Rysgaard, A. Miles, M. Bartoli, L. Dong, D. C. O. Thornton, L. D. M. Ottosen, G. Castaldelli & N. Risgaard-Petersen, 2000. Protocol Handbook for NICE-Nitrogen Cycling in Estuaries: a Project Under the EU Research Programme. Marine Science and Technology (MAST III). National Environmental Research Institute, Silkeborg, Denmark.
Dalsgaard, T., B. Thamdrup & D. E. Canfield, 2005. Anaerobic ammonium oxidation (Anammox) in the marine environment. Research in Microbiology 156: 457–464.
Davie, J. D. S., 1984. Structural variation, litter production and nutrient status of mangrove vegetation in Moreton bay. In Colemand, R. J., J. Covacevich & P. Davie (eds), Focus on Stradbroke New Information on North Stradbroke Island and Surrounding Areas 1974–1984. Boolarong Publications, Brisbane: 208–223.
Dong, L. F., M. Naqasima Sobey, C. J. Smith, I. Rusmana, W. Philips, A. M. Osborn & D. B. Nedwell, 2011. Dissimilatory nitrate reduction to ammonium, not denitrification or anammox, dominates benthic nitrate reduction in tropical estuaries. Limnology and Oceanography 56: 279–291.
Dunn, R. J. K., D. T. Welsh, S. Y. Lee, C. J. Lemckert, P. R. Teasdale & T. Meziane, 2008. Investigating the distribution and sources of organic matter in surface sediment of Coombabah Lake (Australia) using elemental, isotopic and fatty acid biomarkers. Continental Shelf Research 28: 2535–2549.
Dunn, R. J. K., D. T. Welsh, M. A. Jordan, P. R. Teasdale & C. J. Lemckert, 2009. Influence of natural amphipod (Victoriopisa australiensis) (Chilton, 1923) population densities on benthic metabolism, nutrient fluxes, denitrification and DNRA in sub-tropical estuarine sediment. Hydrobiologia 628: 95–105.
Fenchel, T., G. M. King & T. H. Blackburn, 1998. Bacterial Biogeochemistry: The Ecophysiology of Mineral Cycling. Academic Press, San Diego.
Hansen, K. & E. Kristensen, 1998. The impact of the polychaete Nereis diviscolor and enrichment with macroalgal (Chaetomorpha linum) detritus on benthic metabolism and nutrient dynamics in organic-poor and organic-rich sediment. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 231: 201–223.
Jordan, M. A., D. T. Welsh, R. J. K. Dunn & P. R. Teasdale, 2009. Influence of Trypaea australiensis population density on benthic metabolism and nitrogen dynamics in sandy estuarine sediment: a microcosm simulation. Journal of Sea Research 61: 144–152.
Katrak, G. & F. K. Bird, 2003. Comparative effects of the large bioturbators, Trypaea australiensis and Heloecius cordiformis, on intertidal sediments of Western Port, Victoria, Australia. Marine and Freshwater Research 54: 701–708.
Kristensen, E., 2000. Organic matter diagenesis at the oxic/anoxic interface in coastal marine sediments, with emphasis on the role of burrowing animals. Hydrobiologia 426: 1–24.
Kristensen, E. & O. L. Mikkelsen, 2003. Impact of the burrow-dwelling polychaete Nereis diversicolor on the degradation of fresh and aged macroalgal detritus in coastal marine sediment. Marine Ecology Progress Series 265: 141–153.
Kristensen, E. & R. Pilgaard, 2001. The role of fecal pellet deposition by leaf-eating sesamid crabs on litter decomposition in a mangrove sediment (Phuket, Thailand). In Aller, J. Y., S. A. Wood & R. C. Aller (eds), Organism–Sediment Interactions. Univ. South Carolina Press, Columbia: 369–384.
Laverock, B., C. J. Smith, K. Tait, A. M. Osborn, S. Widdicombe & J. A. Gilbert, 2010. Bioturbating shrimp alter the structure and diversity of bacterial communities in coastal marine sediments. The ISME Journal 4: 1531–1544.
Lee, S. Y., R. J. K. Dunn, R. A. Young, R. M. Connolly, P. E. R. Dale, R. Dehayr, C. J. Lemckert, S. McKinnon, B. Powell, P. R. Teasdale & D. T. Welsh, 2006. Impact of urbanization on coastal wetland structure and function. Austral Ecology 31: 149–163.
Nielsen, L. P., 1992. Denitrification in sediment determined from nitrogen isotope pairing. FEMS Microbiology Ecology 86: 357–362.
Nizzoli, D., D. T. Welsh, E. A. Fano & P. Viaroli, 2006. Impact of clam and mussel farming on benthic metabolism and nitrogen cycling, with emphasis on nitrate reduction pathways. Marine Ecology Progress Series 315: 151–165.
Nizzoli, D., M. Bartoli, M. Cooper, D. T. Welsh, G. J. C. Underwood & P. Viaroli, 2007. Implications for oxygen, nutrient fluxes and denitrification rates during the early stage of sediment colonisation by the polychaete Nereis spp. in four estuaries. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 75: 125–134.
Papaspyrou, S., M. Thessalou-Legaki & E. Kristensen, 2004. Impact of Pestarella tyrrhena on benthic metabolism in sediment microcosms enriched with seagrass and macroalgal detritus. Marine Ecology Progress Series 281: 165–179.
Papaspyrou, S., E. Kristensen & B. Christensen, 2007. Arenicola marina (Polychaeta) and organic matter mineralization in sandy marine sediments: in situ and microcosm comparison. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 72: 213–222.
Papaspyrou, S., M. Thessalou-Legaki & E. Kristensen, 2010. The influence of infaunal (Nereis diversicolor) abundance on degradation of organic matter in sandy sediments. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 393: 148–157.
Pelegrí, S. P. & T. H. Blackburn, 1995. Effect of bioturbation by Nereis sp., Mya arenaria and Cerastoderma on nitrification and denitrification in estuarine sediment. Ophelia 42: 289–299.
Pelegrí, S. P., L. P. Nielsen & T. H. Blackburn, 1994. Denitrification in estuarine sediment stimulated by the irrigation activity of the amphipod Corophium volutator. Marine Ecology Progress Series 105: 285–290.
Risgaard-Petersen, N. & S. Rysgaard, 1995. Nitrate reduction in sediments and waterlogged soil measured by 15N techniques. In Alef, K. & P. S. Nannipieri (eds), Methods in Applied Soil Microbiology. Academic Press, London: 287–310.
Risgaard-Petersen, N., L. P. Nielsen, S. Rysgaard, T. Dalsgaard & R. L. Meyer, 2003. Application of the isotope pairing technique in sediments where anammox and denitrification coexist. Limnology and Oceanography Methods 1: 63–73.
Robertson, D., P. R. Teasdale & D. T. Welsh, 2008. A novel gel-based technique for the two-dimensional determination of iron (II) and sulfide in sediment. Limnology and Oceanography: methods 6: 502–512.
Robertson, D., D. T. Welsh & P. R. Teasdale, 2009. Investigating biogenic heterogeneity in coastal sediments with two-dimensional measurements of iron (II) and sulphide. Environmental Chemistry 6: 60–69.
Spilmont, N., T. Meziane, L. Seuront & D. T. Welsh, 2009. Identification of the food sources of sympatric ghost shrimp (Trypaea australiensis) and soldier crab (Mictyris longicarpus) populations using a lipid biomarker dual stable isotope approach. Austral Ecology 34: 878–888.
Vonk, A., D. Kneer, J. Stapel & H. Asmus, 2008. Shrimp burrow in tropical seagrass meadows: an important sink for litter. Estuarine Coastal Shelf Science 79: 79–85.
Warnken, J., R. J. K. Dunn & P. R. Teasdale, 2004. Investigation of recreational boats as a source of copper at anchorage sites using time-integrated diffusive gradient in thin film and sediment measurements. Marine Pollution Bulletin 49: 833–843.
Webb, A. P. & B. D. Eyre, 2004. Effect of natural populations of burrowing thalassinidean shrimp on sediment irrigation, benthic metabolism, nutrient fluxes and denitrification. Marine Ecology Progress Series 268: 205–220.
Welsh, D. T., 2003. It’s a dirty job but someone has to do it: The role of marine benthic macrofauna in organic matter turnover and nutrient recycling to the water column. Chemistry and Ecology 19: 321–342.
Welsh, D. T. & G. Castadelli, 2004. Bacterial nitrification activity directly associated with isolated benthic marine animals. Marine Biology 144: 1029–1037.
Welsh, D. T., M. Bartoli, D. Nizzoli, G. Castadelli, S. A. Riou & P. Viaroli, 2000. Denitrification, nitrogen fixation, community primary productivity and inorganic-N and oxygen fluxes in an intertidal Zostera noltii meadow. Marine Ecology Progress Series 208: 51–65.
Welsh, D. T., G. Castadelli, M. Bartoli, D. Poli, R. de Wit, M. Careri & P. Viaroli, 2001. Denitrification in an intertidal seagrass meadow, a comparison of 15N-isotope and acetylene block techniques; Dissimilatory nitrate reduction to ammonium as a source of N2O. Marine Biology 139: 1029–1036.
Wenzhöfer, F. & R. N. Glud, 2004. Small-scale spatial and temporal variability in coastal benthic O2 dynamics: effects of fauna activity. Limnology and Oceanography 49: 1471–1481.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Discovery Project Programme of the Australian Research Council (project number: DP0559935). The manuscript was improved by the detailed and helpful comments of two anonymous reviewers.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling editor: Pierluigi Viaroli
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dunn, R.J.K., Welsh, D.T., Jordan, M.A. et al. Interactive influences of the marine yabby (Trypaea australiensis) and mangrove (Avicennia marina) leaf litter on benthic metabolism and nitrogen cycling in sandy estuarine sediment. Hydrobiologia 693, 117–129 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-012-1093-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-012-1093-1