Abstract
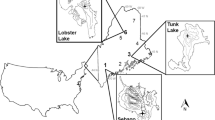
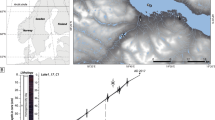
Alpine lakes may be particularly useful as sentinels of climate change because they are highly sensitive to environmental conditions. To explore the potential biotic consequences of climate change in these systems, we conducted paleo- and neoecological observational studies, as well as a short-term experiment to examine Daphnia responses to changing environmental conditions in Rocky Mountain alpine lakes. Our analysis of a sediment core from Emerald Lake representing two periods from the Holocene revealed a significant positive relationship between the abundance of Daphnia remains and fossil Aulacoseira lirata, a diatom associated with deeper mixing depths. In addition, we detected a significant increase in mean Daphnia density in the long-term record (1991–2005) from Pipit Lake, a trend that correlated well with increases in mean surface temperature. In our survey of Daphnia in 10 lakes in the Canadian Rocky Mountains, Daphnia abundance was positively correlated with both dissolved organic carbon concentration and temperature. Finally, our short-term incubation experiment demonstrated significant effects of physical conditions (i.e., temperature and/or UV radiation) and water chemistry on the juvenile growth rate of Daphnia. Overall, our findings highlight the sensitivity of Daphnia to changes in mixing depth, water temperature, and dissolved organic matter, three limnological variables that are highly sensitive to changes not only in air temperature, but also to precipitation and location of the treeline in alpine catchments. Thus, we conclude that Daphnia abundance could serve as a powerful sentinel response to climate change in alpine lakes of the Rocky Mountains.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acharya, K., M. Kyle & J. Elser, 2004. Biological stoichiometry of Daphnia growth: an ecophysiological test of the growth rate hypothesis. Limnology and Oceanography 49: 656–665.
Anderson, R. S., 1974. Crustacean plankton communities of 340 lakes and ponds in and near the national parks of the Canadian Rocky Mountains. Journal of the Fisheries Research Board of Canada 31: 855–869.
Anderson, T. R. & D. O. Hessen, 2005. Threshold elemental ratios for carbon versus phosphorus limitation in Daphnia. Freshwater Biology 50: 2063–2075.
Appleby, P. G. & F. Oldfield, 1978. The calculation of 210Pb dates assuming a constant rate of supply of unsupported 210Pb to the sediment. Catena 5: 1–8.
Balseiro, E., B. Modenutti, C. Queimaliños & M. Reissig, 2007. Daphnia distribution in Andean Patagonian lakes: effect of low food quality and fish predation. Aquatic Ecology 41: 599–609.
Balseiro, E., M. S. Souza, B. Modenutti & M. Reissig, 2008. Living in transparent lakes: low food P:C ratio decreases antioxidant response to ultraviolet radiation in Daphnia. Limnology and Oceanography 53: 2383–2390.
Battarbee, R. W., 1986. Diatom analysis. In Berglund, B. (ed.), Handbook of Holocene Palaeoecology and Palaeohydrology. Wiley, New York: 527–570.
Beniston, M., H. F. Diaz & R. S. Bradley, 1997. Climatic change at high elevation sites: an overview. Climatic Change 36: 233–251.
Bradley, R. S., F. T. Keimig & H. F. Diaz, 2004. Projected temperature changes along the American Cordillera and the planned GCOS network. Geophysical Research Letters 31: L16210–L16213.
Cantin, A., B. E. Beisner, J. M. Gunn, Y. T. Prairie & J. G. Winter, 2011. Effects of thermocline deepening on lake plankton communities. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 68: 260–276.
Chételat, J. & M. Amyot, 2009. Elevated methylmercury in high arctic Daphnia and the role of productivity in controlling their distribution. Global Change Biology 15: 706–718.
Cole, J. J., S. R. Carpenter, J. Kitchell, M. L. Pace, C. T. Solomon & B. Weidel, 2011. Strong evidence for terrestrial support of zooplankton in small lakes based on stable isotopes of carbon, nitrogen, and hydrogen. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. doi:10.1073/pnas.1012807108.
Cooke, S. L., C. E. Williamson & J. E. Saros, 2006. How do temperature, dissolved organic matter, and nutrients influence the response of Leptodiaptomus ashlandi to UV radiation in a subalpine lake? Freshwater Biology 51: 1827–1837.
de Lange, H. J., D. P. Morris & C. E. Williamson, 2003. Solar ultraviolet photodegradation of DOC may stimulate freshwater food webs. Journal of Plankton Research 25: 111–117.
DeMott, W. R. & A. J. Tessier, 2002. Stoichiometric constraints vs. algal defenses: testing mechanisms of zooplankton food limitation. Ecology 83: 3426–3433.
Dodson, S. I., 1984. Predation of Heterocope septentrionalis on 2 species of Daphnia—morphological defenses and their cost. Ecology 65: 1249–1257.
Donald, D. B., R. S. Anderson & D. W. Mayhood, 1994. Coexistence of fish and large Hesperodiaptomus species (Crustacea, Calanoida) in sub-alpine and alpine lakes. Canadian Journal of Zoology 72: 259–261.
Elser, J. J., W. J. O’Brien, D. R. Dobberfuhl & T. E. Dowling, 2000. The evolution of ecosystem processes: growth rate and elemental stoichiometry of a key herbivore in temperate and arctic habitats. Journal of Evolutionary Biology 13: 845–853.
Fee, E. J., R. E. Hecky, S. E. M. Kasian & D. R. Cruikshank, 1996. Effects of lake size, water clarity, and climatic variability on mixing depths in Canadian Shield lakes. Limnology and Oceanography 41: 912–920.
Frey, D. G., 1986. Cladocera analysis. In Berglund, B. (ed.), Handbook of Holocene Palaeoecology and Palaeohydrology. Wiley, New York: 667–692.
George, D. G., 2000. The impact of regional-scale changes in the weather on the long-term dynamics of Eudiaptomus and Daphnia in Esthwaite Water, Cumbria. Freshwater Biology 45: 111–121.
George, D. G. & A. H. Taylor, 1995. UK plankton and the Gulf Stream. Nature 378: 139.
Gillooly, J. F. & S. I. Dodson, 2000. Latitudinal patterns in the size distribution and seasonal dynamics of new world, freshwater cladocerans. Limnology and Oceanography 45: 22–30.
Graham, M. D. & R. D. Vinebrooke, 2009. Extreme weather events alter planktonic communities in boreal lakes. Limnology and Oceanography 54: 2481–2492.
Hairston, N. G. Jr., 1976. Photoprotection by carotenoid pigments in copepod Diaptomus nevadensis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 73: 971–974.
Harsch, M. A., P. E. Hulme, M. S. Mcglone & R. P. Duncan, 2009. Are treelines advancing? A global meta-analysis of treeline response to climate warming. Ecology Letters 12: 1040–1049.
Hassett, R. P., B. Cardinale, L. B. Stabler & J. J. Elser, 1997. Ecological stoichiometry of N and P in pelagic ecosystems: comparison of lakes and oceans with emphasis on the zooplankton–phytoplankton interaction. Limnology and Oceanography 42: 648–662.
Hobbs, W. O., R. J. Telford, H. J. B. Birks, J. E. Saros, R. R. O. Hazewinkel, B. B. Perren, E. Saulnier-Talbot & A. P. Wolfe, 2010. Quantifying recent ecological changes in remote lakes of North America and Greenland using sediment diatom assemblages. PLoS One 5(4): e10026.
Holzapfel, A. M. & R. D. Vinebrooke, 2005. Environmental warming increases invasion potential of alpine lake communities by imported species. Global Change Biology 11: 2009–2015.
Houser, J. N., 2006. Water color affects the stratification, surface temperature, heat content, and mean epilimnetic irradiance of small lakes. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 63: 2447–2455.
Infante, A. & H. Litt, 1985. Differences between two species of Daphnia in the use of 10 species of algae in Lake Washington. Limnology and Oceanography 30: 1053–1059.
Jankowski, T., D. M. Livingstone, H. Buhrer, R. Forster & P. Niederhauser, 2006. Consequences of the 2003 European heat wave for lake temperature profiles, thermal stability, and hypolimnetic oxygen depletion: implications for a warmer world. Limnology and Oceanography 51: 815–819.
Jewson, D. H., 1992. Size reduction, reproductive strategy and the life cycle of a centric diatom. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London B 336: 191–213.
Jones, R. I., 1992. The influence of humic substances on lacustrine planktonic food chains. Hydrobiologia 229: 73–91.
Kagami, M., N. R. Helmsing & E. van Donk, 2011. Parasitic chytrids could promote copepod survival by mediating material transfer for inedible diatoms. Hydrobiologia 659: 49–54.
Karst-Riccoch, T. L., M. F. J. Pisaric & J. P. Smol, 2005. Diatom responses to 20th century climate-related environmental changes in high-elevation mountain lakes of the northern Canadian Cordillera. Journal of Paleolimnology 33: 265–282.
Kessler, K., R. S. Lockwood, C. E. Williamson & J. E. Saros, 2008. Vertical distribution of zooplankton in subalpine and alpine lakes: ultraviolet radiation, fish predation, and the transparency-gradient hypothesis. Limnology and Oceanography 53: 2374–2382.
Kissman, C., C. E. Williamson, K. Rose, J. E. Saros, in review. Climate change-induced effects on food web structure in an alpine lake: terrestrial DOM subsidies alter consumer: producer biomass ratios. Global Change Biology.
Lampert, W. & I. Trubetskova, 1996. Juvenile growth rate as a measure of fitness in Daphnia. Functional Ecology 10: 631–635.
Leavitt, P. R., P. R. Sanford, S. R. Carpenter, J. F. Kitchell & D. Benkowski, 1993. Annual fossil records of food-web manipulation. In Carpenter, S. R. & J. F. Kitchell (eds), The Trophic Cascade in Lakes. Cambridge University Press, New York: 278–309.
Leavitt, P. R., S. C. Fritz, N. J. Anderson, P. A. Baker, T. Blenckner, L. Bunting, J. Catalan, D. J. Conley, W. O. Hobbs, E. Jeppesen, A. Korhola, S. McGowan, K. Rühland, J. A. Rusak, G. L. Simpson, N. Solovieva & J. Werne, 2009. Paleolimnological evidence of the effects on lakes of energy and mass transfer from climate and humans. Limnology and Oceanography 54: 2330–2348.
Luckman, B. & T. Kavanagh, 2000. Impact of climate fluctuations on mountain environments in the Canadian Rockies. Ambio 29: 371–380.
Luckman, B. H. & R. J. S. Wilson, 2005. Summer temperatures in the Canadian Rockies during the last millennium: a revised record. Climate Dynamics 24: 131–144.
Luecke, C. & W. J. O’Brien, 1983. Photoprotective pigments in a pond morph of Daphnia middendorffiana. Arctic 36: 365–368.
Magnuson, J. J., D. M. Robertson, B. J. Benson, R. H. Whynne, D. M. Livingstone, A. Arai, R. A. Assel, R. G. Barry, V. Card, E. Kuusisto, N. G. Granin, T. D. Prowse, K. M. Stewart & V. S. Vuglinski, 2000. Historical trends in lake and river ice cover in the northern hemisphere. Science 289: 1743–1746.
Marinone, M. C., S. M. Marque, D. A. Suarez, M. D. C. Dieguez, P. Perez, P. D. L. Rios, D. Soto & H. E. Zagarese, 2006. UV radiation as a potential driving force for zooplankton community structure in Patagonian lakes. Photochemistry and Photobiology 82: 962–971.
McNaught, A. S., D. E. Schindler, B. R. Parker, A. J. Paul, R. S. Anderson, D. B. Donald & M. Agbeti, 1999. Restoration of the food web of an alpine lake following fish stocking. Limnology and Oceanography 44: 127–136.
Murphy, C. A., P. L. Thompson & R. D. Vinebrooke, 2010. Assessing the sensitivity of alpine lakes and ponds to nitrogen deposition in the Canadian Rocky Mountains. Hydrobiologia 648: 83–90.
Olsen, Y., K. M. Varum & A. Jensen, 1986. Dependence of the rate of release of phosphorus by zooplankton on the C:P ratio in the food supply, as calculated by a recycling model. Limnology and Oceanography 31: 34–44.
Parker, B. R. & D. W. Schindler, 2006. Cascading trophic interactions in an oligotrophic species-poor alpine lake. Ecosystems 9: 157–166.
Parker, B. R., F. M. Wilhelm & D. W. Schindler, 1996. Recovery of Hesperodiaptomus arcticus populations from diapausing eggs following elimination by stocked salmonids. Canadian Journal of Zoology 74: 1292–1297.
Parker, B. R., R. D. Vinebrooke & D. W. Schindler, 2008. Recent climate extremes alter alpine lake ecosystems. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 105: 12927–12931.
Pechar, T. T., 1987. Use of acetone:methanol mixture for extraction and spectrophotometric determination of chlorophyll a in phytoplankton. Archiv für Hydrobiologie Supplement 78: 99–117.
Persson, I. & I. D. Jones, 2008. The effect of water colour on lake hydrodynamics: a modelling study. Freshwater Biology 53: 2345–2355.
Ringelberg, J., A. L. Keyser & B. J. G. Flik, 1984. The mortality effects of ultraviolet radiation in a translucent and in a red morph of Acathodiaptomus denticornis (Crustacea, Copepoda) and its possible ecological relevance. Hydrobiologia 112: 217–222.
Rose, K. C., C. E. Williamson, J. E. Saros, R. Sommaruga & J. M. Fischer, 2009. Differences in UV transparency and thermal structure between alpine and subalpine lakes: implications for organisms. Photochemical and Photobiological Sciences 8: 1244–1256.
Rühland, K., A. Priesnitz & J. P. Smol, 2003. Paleolimnological evidence from diatoms for recent environmental changes in 50 Lakes across Canadian Arctic Treeline. Arctic, Antarctic, and Alpine Research 35: 110–123.
Sala, O. E., F. S. Chapin, J. J. Armesto, E. Berlow, J. Bloomfield, R. Dirzo, E. Huber-Sanwald, L. F. Huenneke, R. B. Jackson, A. Kinzig, R. Leemans, D. M. Lodge, H. A. Mooney, M. Oesterheld, N. L. Poff, M. T. Sykes, B. H. Walker, M. Walker & D. H. Wall, 2000. Global biodiversity scenarios for the year 2100. Science 287: 1770–1774.
Sarnelle, O. & R. Knapp, 2004. Zooplankton recovery after fish removal: limitations of the egg bank. Limnology and Oceanography 49: 1382–1392.
Saros, J. E., S. J. Interlandi, A. P. Wolfe & D. R. Engstrom, 2003. Recent changes in the diatom community structure of lakes in the Beartooth Mountain Range (USA). Arctic, Antarctic, and Alpine Research 35: 18–23.
Saros, J. E., T. J. Michel, S. J. Interlandi & A. P. Wolfe, 2005. Resource requirements of Asterionella formosa and Fragilaria crotonensis in oligotrophic alpine lakes: implications for recent phytoplankton community reorganizations. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 62: 1681–1689.
Saros, J. E., K. C. Rose, D. W. Clow, V. C. Stephens, A. B. Nurse, H. A. Arnett, J. R. Stone, C. E. Williamson & A. P. Wolfe, 2010. Melting alpine glaciers enrich high-elevation lakes with reactive nitrogen. Environmental Science and Technology 44: 4891–4896.
Shuman, B., A. Henderson, S. M. Colman, J. R. Stone, S. C. Fritz, L. R. Stevens, M. J. Power & C. Whitlock, 2009. Holocene lake-level trends in the Rocky Mountains U.S.A. Quaternary Science Reviews 28: 1861–1879.
Snucins, E. & J. Gunn, 2000. Interannual variation in the thermal structure of clear and colored lakes. Limnology and Oceanography 45: 1639–1646.
Sommaruga, R., R. Psenner, E. Schafferer, K. A. Koinig & S. Sommaruga-Wograth, 1999. Dissolved organic carbon concentration and phytoplankton biomass in high-mountain lakes of the Austrian Alps: potential effects of climatic warming on UV underwater attenuation. Arctic, Antarctic, and Alpine Research 31: 247–253.
Sterner, R. W., J. J. Elser, E. J. Fee, S. J. Guildford & T. H. Chrzanowski, 1997. The light:nutrient ratio in lakes: the balance of energy and materials affects ecosystem structure and process. American Naturalist 150: 663–684.
Stuiver, M., P. J. Reimer & R. W. Reimer, 2005. CALIB 5.0 [program and documentation]. http://calib.qub.ac.uk/calib/.
Tartarotti, R., S. Cabrera, R. Psenner & R. Sommaruga, 1999. Survivorship of Cyclops abyssorum tatricus (Cyclopoida, Copepoda) and Boeckella gracilipes (Calanoida, Copepoda) under ambient levels of solar UV radiation in two high mountain lakes. Journal of Plankton Research 21: 549–560.
Tollrain, R. & C. Heibl, 2004. Phenotypic plasticity in pigmentation in Daphnia induced by UV radiation and fish kairomones. Functional ecology 18: 497–502.
Urabe, J. & Y. Watanabe, 1992. Possibility of N or P limitation for planktonic cladocerans: an experimental test. Limnology and Oceanography 37: 244–251.
Urabe, J., J. Clasen & R. W. Sterner, 1997. Phosphorus limitation of Daphnia growth: is it real? Limnology and Oceanography 42: 1436–1443.
Van Geest, G. J., P. Spierenburg, E. Van Donk & D. Hessen, 2007. Daphnia growth rates in arctic ponds: limitation by nutrients or carbon? Polar Biology 30: 235–242.
Viau, A. E., K. Gajewski, M. C. Sawada & P. Fines, 2006. Millennial-scale temperature variations in North America during the Holocene. Journal of Geophysical Research 111: D09102.
Wang, L., L. Houyan, J. Liu, Z. Gu, J. Mingram, G. Chu, J. Li, P. Rioual, J. F. W. Negendank, J. Han & T. Liu, 2008. Diatom-based inference of variations in the strength of Asian winter monsoon winds between 17,500 and 6000 calendar years B.P. Journal of Geophysical Research 113: D21101.
Williamson, C. E. & J. E. Saros, 2008. What do lakes and reservoirs tell us about climate change? EOS Transactions of the American Geophysical Union 89: 546.
Williamson, C. E., D. P. Morris, M. L. Pace & O. G. Olson, 1999. Dissolved organic carbon and nutrients as regulators of lake ecosystems: resurrection of a more integrated paradigm. Limnology and Oceanography 44: 795–803.
Williamson, C. E., O. G. Olson, S. E. Lott, N. D. Walker, D. R. Engstrom & B. R. Hargreaves, 2001. Ultraviolet radiation and zooplankton community structure following deglaciation in Glacier Bay, Alaska. Ecology 82: 1748–1760.
Williamson, C. E., J. E. Saros & D. W. Schindler, 2009a. Sentinels of change. Science 323: 887–888.
Williamson, C. E., J. E. Saros, W. F. Vincent & J. P. Smol, 2009b. Lakes and reservoirs as sentinels, integrators, and regulators of climate change. Limnology and Oceanography 54: 2273–2282.
Yurista, P. M., 1999. Temperature-dependent energy budget of an arctic cladoceran, Daphnia middendorffiana. Freshwater Biology 42: 21–34.
Yurista, P. M. & W. J. O’Brien, 2001. Growth, survivorship and reproduction of Daphnia middendorffiana in several Arctic lakes and ponds. Journal of Plankton Research 23: 733–744.
Acknowledgments
Erin Overholt and Patricia Sanford provided invaluable technical support and guidance in paleocladoceran work. David Schindler and Brian Parker collected and shared the historic data from Pipit Lake. We thank the Parks Canada Agency for their permission to conduct our research in the national mountain parks of Canada (YNP-2008-1585, KOONP-2009-3154). This study was supported by Franklin and Marshall College, the Andrew W. Mellon Foundation through its grant in support of faculty development within the Central Pennsylvania Consortium, a Kayal Memorial Scholarship to JCE, Miami University Department of Zoology’s Field Workshop Program, and grants from the National Science Foundation (DEB-0734277 and DGE IGERT-0903560) and Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Guest editors: H. Eggermont & K. Martens / Cladocera as indicators of environmental change
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fischer, J.M., Olson, M.H., Williamson, C.E. et al. Implications of climate change for Daphnia in alpine lakes: predictions from long-term dynamics, spatial distribution, and a short-term experiment. Hydrobiologia 676, 263–277 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-011-0888-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-011-0888-9