Abstract
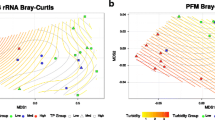
Humans have increased the availability of nutrients including nitrogen and phosphorus worldwide; therefore, understanding how microbes process nutrients is critical for environmental conservation. We examined nutrient limitation of biofilms colonizing inorganic (fritted glass) and organic (cellulose sponge) substrata in spring, summer, and autumn in three streams in Michigan, USA. Biofilms were enriched with nitrate (NO3 −), phosphate (PO4 3−), ammonium (NH4 +), NO3 − + PO4 3−, NH4 + + PO4 3−, or none (control). We quantified biofilm structure and function as chlorophyll a (i.e., primary producer biomass) and community respiration on all substrata. In one stream, we characterized bacterial and fungal communities on cellulose in autumn using clone library sequencing and denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis to determine if community structure was linked to nutrient limitation status. Despite oligotrophic conditions, primary producer biomass was infrequently nutrient limited. In contrast, respiration on organic substrata was frequently limited by N + P combinations. We found no difference between biofilm response to NH4 + versus NO3 − enrichment, although the response to both N-species was positively related to water column PO4 3− concentrations and temperature. Molecular analysis for fungal community composition suggested no relationship to nutrient limitation, but the dominant members of the bacterial community on cellulose were different on NO3 −, PO 34 , and NO3 − + PO4 3− treatments relative to control, NH4 +, and NH4 + + PO4 3− treatments, which matched patterns for biofilm respiration rates from each treatment. Our results show discrete patterns of nutrient limitation dependent upon substratum type and season, and imply changes in bacterial community structure and function may be linked following nutrient enrichment in streams.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander, R. B., R. A. Smith & G. E. Schwarz, 2000. Effect of stream channel size on the delivery of nitrogen to the Gulf of Mexico. Nature 403: 758–761.
Altschul, S. F., W. Gish, W. Miller, E. W. Myers & D. J. Lipman, 1990. Basic local alignment search tool. Journal of Molecular Biology 215: 403–410.
Bärlocher, F., L. G. Nikolcheva, K. P. Wilson & D. D. Williams, 2006. Fungi in the hyporheic zone of a springbrook. Microbial Ecology 52: 708–715.
Battin, T. J., A. Wille, B. Sattler & R. Psenner, 2001. Phylogenetic and functional heterogeneity of sediment biofilms along environmental gradients in a glacial stream. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 67: 799–807.
Brummer, I. H. M., A. Felske & I. Wagner-Dobler, 2003. Diversity and seasonal variability of beta-proteobacteria in biofilms of polluted rivers: analysis by temperature gradient gel electrophoresis and cloning. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 69: 4463–4473.
Cottrell, M. T. & D. L. Kirchman, 2000. Natural assemblages of marine proteobacteria and members of the Cytophaga-Flavobacter cluster consuming low- and high-molecular-weight dissolved organic matter. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 66: 1692–1697.
Cross, W. F., J. B. Wallace, A. D. Rosemond & S. L. Eggert, 2006. Whole-system nutrient enrichment increases secondary production in a detritus-based ecosystem. Ecology 87: 1556–1565.
Das, M., T. V. Royer & L. G. Leff, 2007. Diversity of fungi, bacteria, and actinomycetes on leaves decomposing in a stream. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 73: 756–767.
de Figueiredo, D. R., M. J. Pereira, A. Moura, L. Silva, S. Barrios, F. Fonseca, I. Henriques & A. Correia, 2007. Bacterial community composition over a dry winter in meso- and eutrophic Portuguese water bodies. FEMS Microbiology Ecology 59: 638–650.
Dodds, W. K., 2006. Eutrophication and trophic state in rivers and streams. Limnology and Oceanography 51: 671–680.
Dortch, Q., 1990. The interaction between ammonium and nitrate uptake in phytoplankton. Marine Ecology-Progress Series 61: 183–201.
Entrekin, S. A., E. J. Rosi-Marshall, J. L. Tank, T. J. Hoellein & G. A. Lamberti, 2007. Macroinvertebrate secondary production in 3 forested streams of the upper Midwest, USA. Journal of the North American Benthological Society 26: 472–490.
Francoeur, S. N., B. J. F. Biggs, R. A. Smith & R. L. Lowe, 1999. Nutrient limitation of algal biomass accrual in streams: seasonal patterns and a comparison of methods. Journal of the North American Benthological Society 18: 242–260.
Glockner, F. O., E. Zaichikov, N. Belkova, L. Denissova, J. Pernthaler, A. Pernthaler & R. Amann, 2000. Comparative 16S rRNA analysis of lake bacterioplankton reveals globally distributed phylogenetic clusters including an abundant group of actinobacteria. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 66: 5053.
Green, S. J., F. C. Michel, Y. Hadar & D. Minz, 2007. Contrasting patterns of seed and root colonization by bacteria from the genus Chryseobacterium and from the family Oxalobacteraceae. ISME Journal 1: 291–299.
Hall, R. O. & J. L. Meyer, 1998. The trophic significance of bacteria in a detritus-based stream food web. Ecology 79: 1995–2012.
Hill, B. H., A. T. Herlihy & P. R. Kaufmann, 2002. Benthic microbial respiration in Appalachian Mountain, Piedmont, and Coastal Plains streams of the eastern USA. Freshwater Biology 47: 185–194.
Hoellein, T. J., J. L. Tank, E. J. Rosi-Marshall, S. A. Entrekin & G. A. Lamberti, 2007. Controls on spatial and temporal variation of nutrient uptake in three Michigan headwater streams. Limnology and Oceanography 52: 1964–1977.
Hoellein, T. J., J. L. Tank, E. J. Rosi-Marshall & S. A. Entrekin, 2009. Temporal variation in substratum-specific rates of N uptake and metabolism and their contribution at the stream-reach scale. Journal of the North American Benthological Society 28: 305–318.
Johnson, L. T., J. L. Tank & W. K. Dodds, 2009. The influence of land use on stream biofilm nutrient limitation across eight North American biomes. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 66: 1081–1094.
Kirchman, D. L., 2002. The ecology of Cytophaga-Flavobacteria in aquatic environments. FEMS Microbiology Ecology 39: 91–100.
Kominoski, J. S., T. J. Hoellein, J. J. Kelly & C. M. Pringle, 2009. Does mixing of different litter qualities alter stream microbial diversity and functioning on individual litter species? Oikos 118: 457–463.
Kominoski, J. S., T. J. Hoellein, C. J. Leroy, C. M. Pringle & C. M. Swan, 2010. Beyond species richness: expanding biodiversity-ecosystem functioning theory in detritus-based streams. River Research and Applications 26: 67–75.
Manz, W., K. Wendt-Potthoff, T. R. Neu, U. Szewzyk & J. R. Lawrence, 1999. Phylogenetic composition, spatial structure, and dynamics of lotic bacterial biofilms investigated by fluorescent in situ hybridization and confocal laser scanning microscopy. Microbial Ecology 37: 225–237.
McClain, M. E., E. W. Boyer, C. L. Dent, S. E. Gergel, N. B. Grimm, P. M. Groffman, S. C. Hart, J. W. Harvey, C. A. Johnston, E. Mayorga, W. H. McDowell & G. Pinay, 2003. Biogeochemical hot spots and hot moments at the interface of terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems. Ecosystems 6: 301–312.
Mosisch, T. D., S. E. Bunn & P. M. Davies, 2001. The relative importance of shading and nutrients on algal production in subtropical streams. Freshwater Biology 46: 1269–1278.
Murphy, J. & J. Riley, 1962. A modified single solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural waters. Analytica Chimica Acta 27: 31–36.
Muyzer, G. & K. Smalla, 1998. Application of denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (DGGE) and temperature gradient gel electrophoresis (TGGE) in microbial ecology. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek International Journal of General and Molecular Microbiology 73: 127–141.
Muyzer, G., E. C. Dewaal & A. G. Uitterlinden, 1993. Profiling of complex microbial-populations by denaturing gradient gel-electrophoresis analysis of polymerase chain reaction-amplified genes-coding for 16s ribosomal-RNA. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 59: 695–700.
Nikolcheva, L. G. & F. Bärlocher, 2005. Seasonal and substrate preferences of fungi colonizing leaves in streams: traditional versus molecular evidence. Environmental Microbiology 7: 270–280.
Nikolcheva, L. G., T. Bourque & F. Barlocher, 2005. Fungal diversity during initial stages of leaf decomposition in a stream. Mycological Research 109: 246–253.
Olapade, O. A. & L. G. Leff, 2005. Seasonal response of stream biofilm communities to dissolved organic matter and nutrient enrichments. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 71: 2278–2287.
Paul, M. J. & J. L. Meyer, 2001. Streams in the urban landscape. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics 32: 333–365.
Pinhassi, J. & T. Berman, 2003. Differential growth response of colony-forming alpha- and gamma-proteobacteria in dilution culture and nutrient addition experiments from Lake Kinneret (Israel), the eastern Mediterranean Sea, and the Gulf of Eilat. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 69: 199–211.
Pringle, C. M., 1990. Nutrient spatial heterogeneity – effects on community structure, physiognomy, and diversity of stream algae. Ecology 71: 905–920.
Rabalais, N. N., R. E. Turner & D. Scavia, 2002. Beyond science into policy: Gulf of Mexico hypoxia and the Mississippi River. Bioscience 52: 129–142.
Roberts, B. J., P. J. Mulholland & W. R. Hill, 2007. Multiple scales of temporal variability in ecosystem metabolism rates: results from 2 years of continuous monitoring in a forested headwater stream. Ecosystems 10: 588–606.
Roeselers, G., M. C. M. Van Loosdrecht & G. Muyzer, 2007. Heterotrophic pioneers facilitate phototrophic biofilm development. Microbial Ecology 54: 578–585.
Rosemond, A. D., P. J. Mulholland & J. W. Elwood, 1993. Top-down and bottom-up control of stream periphyton – effects of nutrients and herbivores. Ecology 74: 1264–1280.
Rubin, M. A. & L. G. Leff, 2007. Nutrients and other abiotic factors affecting bacterial communities in an Ohio River (USA). Microbial Ecology 54: 374–383.
Sartory, D. P. & J. U. Grobbelaar, 1984. Extraction of chlorophyll-a from fresh-water phytoplankton for spectrophotometric analysis. Hydrobiologia 114: 177–187.
Solorzano, L., 1969. Determination of ammonium in natural waters by the phenolhypochlorite method. Limnology and Oceanography 14: 799–801.
Tank, J. L. & W. K. Dodds, 2003. Nutrient limitation of epilithic and epixylic biofilms in ten North American streams. Freshwater Biology 48: 1031–1049.
Tank, J. L., M. J. Bernot & E. J. Rosi-Marshall, 2006. Nitrogen limitation and uptake. In Hauer, F. R. & G. A. Lamberti (eds), Methods in Stream Ecology, 2nd ed.: 213–238.
USEPA, 1993. Test method 300.0 for the determination of inorganic ions in water by ion chromatography. Environmental Monitoring Systems Laboratory USEPA ORD, Cincinnati, OH.
Vitousek, P. M., H. A. Mooney, J. Lubchenco & J. M. Melillo, 1997. Human domination of Earth’s ecosystems. Science 277: 494–499.
von Schiller, D., E. Martí, J. L. Riera & F. Sabater, 2007. Effects of nutrients and light on periphyton biomass and nitrogen uptake in Mediterranean streams with contrasting land uses. Freshwater Biology 52: 891–906.
Webster, J. R., P. J. Mulholland, J. L. Tank, H. M. Valett, W. K. Dodds, B. J. Peterson, W. B. Bowden, C. N. Dahm, S. Findlay, S. V. Gregory, N. B. Grimm, S. K. Hamilton, S. L. Johnson, E. Marti, W. H. McDowell, J. L. Meyer, D. D. Morrall, S. A. Thomas & W. M. Wollheim, 2003. Factors affecting ammonium uptake in streams – an inter-biome perspective. Freshwater Biology 48: 1329–1352.
White, T. J., T. Bruns, S. Lee & J. W. Taylor, 1990. Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics In Innis, M. A., D. H. Gelfand, J. J. Sninsky & T. J. White (eds), PCR Protocols: A Guide to Methods and Applications: 315–322.
Wold, A. P. & A. E. Hershey, 1999. Spatial and temporal variability of nutrient limitation in 6 North Shore tributaries to Lake Superior. Journal of the North American Benthological Society 18: 2–14.
Zar, J. H., 1999. Biostatistical Analysis, 4th ed. Prentice-Hall Inc., Upper Saddle River, NJ.
Zhao, Y., W. Li, Z. Zhou, L. Wang, Y. Pan & L. Zhao, 2005. Dynamics of microbial community structure and cellulolytic activity in agricultural soil amended with two biofertilizers. Soil Biology 41: 21–29.
Acknowledgments
We thank J. Cordova, S. Entrekin, T. Fauendorf, S. Green, K. Jankowski, J. Kominoski, B. Lima, L. Johnson, and A. Yamamuro for field and laboratory assistance. We also thank the USDA Forest Service district office in Kenton, MI, for site access, the Ottawa National Forest for logistical assistance, and the Center for Environmental Science and Technology at the University of Notre Dame for analytical assistance. This project was supported by the National Research Initiative of the USDA Cooperative State Research, Education and Extension Service (Managed Ecosystems Program grant 2003-35101-12871) to JLT, a grant from the Sigma Xi Scientific Research Society’s Grants in Aid of Research (GIAR) to TJH, and an Arthur J. Schmitt Presidential Fellowship to TJH from the Graduate School at the University of Notre Dame.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling editor: Nicholas R. Bond
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hoellein, T.J., Tank, J.L., Kelly, J.J. et al. Seasonal variation in nutrient limitation of microbial biofilms colonizing organic and inorganic substrata in streams. Hydrobiologia 649, 331–345 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-010-0276-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-010-0276-x