Abstract
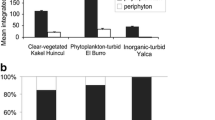
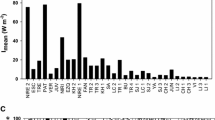
We analyzed experimentally the relative contribution of phytoplankton and periphyton in two shallow lakes from the Pampa Plain (Argentina) that represent opposite scenarios according to the alternative states hypothesis for shallow lakes: a clear lake with submerged macrophytes, and a turbid lake with high phytoplankton biomass. To study the temporal changes of both microalgal communities under such contrasting conditions, we placed enclosures in the littoral zone of each lake, including natural phytoplankton and artificial substrata, half previously colonized by periphyton until a mature stage and half clean to analyze periphyton colonization. In the clear vegetated shallow lake, periphyton chlorophyll a concentrations were 3–6 times higher than those of the phytoplankton community. In contrast, phytoplankton chlorophyll a concentrations were 76–1,325 times higher than those of periphyton in the turbid lake. Here, under light limitation conditions, the colonization of the periphyton was significantly lower than in the clear lake. Our results indicate that in turbid shallow lakes, the light limitation caused by phytoplankton determines a low periphyton biomass dominated by heterotrophic components. In clear vegetated shallow lakes, where nitrogen limitation probably occurs, periphyton may develop higher biomass, most likely due to their higher efficiency in nutrient recycling.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allende, L., G. Tell, H. Zagarese, A. Torremorell, G. Pérez, J. Bustingorry, R. Escaray & I. Izaguirre, 2009. Phytoplankton and primary production in clear-vegetated, inorganic-turbid, and algal-turbid shallow lakes from the Pampa plain (Argentina). Hydrobiologia 624: 45–60.
APHA, American Public Health Association, 2005. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewaters. Washington DC.
Axler, R. P. & J. E. Reuter, 1996. Nitrate uptake by phytoplankton and periphyton: whole-lake enrichments and mesocosm-15N experiments in an oligotrophic lake. Limnology and Oceanography 41: 659–671.
Cano, M. G., M. A. Casco, L. C. Solari, M. E. Mac Donagh, N. A. Gabellone & M. C. Claps, 2008. Implications of rapid changes in chlorophyll-a of plankton, epipelon, and epiphyton in a Pampean shallow lake: an interpretation in terms of a conceptual model. Hydrobiologia 614: 33–45.
Casco, M. A., M. E. Mac Donagh, M. G. Cano, L. C. Solari, M. C. Claps & N. A. Gabellone, 2009. Phytoplankton and epipelon responses to clear and turbid phases in a seepage lake (Buenos Aires, Argentina). International Review of Hydrobiology 94: 153–168.
Eminson, D. & B. Moss, 1980. The composition and ecology of periphyton communities in freshwaters. European Journal of Phycology 15: 429–446.
Gabellone, N. A., L. C. Solari & M. C. Claps, 2001. Planktonic and physico-chemical dynamics of a markedly fluctuating backwater pond associated with a lowland river (Salado River, Buenos Aires, Argentina). Lakes & Reservoirs: Research and Management 6: 133–142.
Goldsborough, L. G. & M. Hickman, 1991. A comparison of periphytic algal biomass and community structure on Scirpus validus and on a morphologically similar artificial substratum. Journal of Phycology 27: 196–206.
Goldsborough, L. G. & G. G. C. Robinson, 1996. Pattern in wetlands. In Stevenson, R. J., M. L. Bothwell & R. L. Lowe (eds), Algal Ecology: Freshwater Benthic Ecosystems. Academic Press, California: 77–117.
Goldsborough, L. G., R. L. McDougal & A. K. North, 2005. Periphyton in freshwaters lakes and wetlands. In Azim, M. E., M. C. J. Verdegem, A. A. Van Dam & M. C. M. Beveridge (eds). Periphyton Ecology, Exploitation and Management. CABI Publishing, Cambridge: 71–83.
Hansson, L.-A., 1988. Effects of competitive interactions on the biomass development of planktonic and periphytic algae in lakes. Limnology and Oceanography 33: 121–128.
Hansson, L.-A., 1990. Quantifying the impact of periphytic algae on nutrient availability for phytoplankton. Freshwater Biology 24: 265–273.
Hillebrand, H., C. Dürselen, D. Kirschtel, T. Zohary & U. Pollingher, 1999. Biovolume calculation for pelagic and benthic microalgae. Journal of Phycology 35: 403–424.
Izaguirre, I. & A. Vinocur, 1994a. Typology of shallow lakes of the Salado River Basin (Argentina), based on phytoplankton communities. Hydrobiologia 277: 49–62.
Izaguirre, I. & A. Vinocur, 1994b. Algal assemblages from shallow lakes of the Salado River Basin (Argentina). Hydrobiologia 289: 57–64.
Jeppesen, E., M. Søndergaard, M. Søndergaard & K. Christoffersen (eds), 1998. The Structuring Role of Submerged Macrophytes in Lakes. Springer Verlag, New York.
Libouriussen, L. & E. Jeppesen, 2003. Temporal dynamics in epipelic, pelagic and epiphytic algal production in a clear and turbid shallow lake. Freshwater Biology 48: 418–431.
Marker, A. F. H., A. Nusch, H. Rai & B. Riemann, 1980. The measurement of photosynthetic pigments in freshwater and standardization of methods: conclusions and recommendations. Archiv für Hydrobiologie Beihefte Ergebnise Limnology 14: 91–106.
Meier, P. G., D. O’Connor & D. Dilks, 1983. Artificial substrata for reducing periphytic variability on replicated samples. Developments in Hydrobiology 17: 283–286.
Pérez, G., A. Torremorell, J. Bustingorry, R. Escaray, P. Pérez, M. Diéguez & H. Zagarese, 2010. Optical characteristics of shallow lakes from the Pampa and Patagonia regions of Argentina. Limnologica 40: 1–82.
Pizarro, H., 1999. Periphyton biomass on Echinochloa polystachya (H.B.K.) Hitch. of the Lower Paraná River floodplain, Argentina. Hydrobiologia 397: 227–239.
Quirós, R. & E. Drago, 1999. The environmental state of Argentinean lakes: an overview. Lakes & Reservoirs: Research and Management 4: 55–64.
Quirós, R., A. M. Rennella, M. B. Boveri, J. J. Rosso & A. Sosnovsky, 2002. Factores que afectan la estructura y el funcionamiento de las lagunas pampeanas. Ecología Austral 12: 175–185.
Rennella, A. M. & R. Quirós, 2006. The effects of hydrology on plankton biomass in shallow lakes of the Pampa Plain. Hydrobiologia 556: 181–191.
Reynolds, C. S., 2006. Ecology of Phytoplankton. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Scheffer, M., S. H. Hosper, B. Moss & E. Jeppesen, 1993. Alternative equilibria in shallow lakes. Trends in Ecology and Evolution 8: 275–279.
Schriver, P., J. Bøgestrand, E. Jeppesen & M. Søndergaard, 1995. Impact of submerged macrophytes on fish-zooplankton-phytoplankton interactions: large-scale enclosure experiments in a shallow trophic lake. Freshwater Biology 33: 255–276.
Søndergaard, M. & B. Moss, 1998. Impact of submerged macrophytes on phytoplankton in shallow freshwaters lakes. In Jeppesen, E., M. Søndergaard, M. Søndergaard & K. Christoffersen (eds), The Structuring Role of Submerged Macrophytes in Lakes. Springer Verlag, New York: 115–132.
Stevenson, R. J., 1996. An introduction to algal ecology in freshwater benthic habitats. In Stevenson, R. J., M. L. Bothwell & R. L. Lowe (eds), Algal Ecology: Freshwater Benthic Ecosystems. Academic Press, California: 3–30.
Takamura, N., Y. Kadono, M. Nakagawa & H. O. K. Baik, 2003. Effects of aquatic macrophytes on water quality and phytoplankton communities in shallow lakes. Ecological Research 18: 381–395.
Underwood, A. J., 1997. Experiments in Ecology: Their Logical Design and Interpretation Using Analysis of Variance. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Unrein, F., 2001. Efecto de los nutrientes y el pH sobre la estructura del fitoplancton en ambientes de la llanura alluvial del Paraná Inferior. PhD Dissertation, Universidad de Buenos Aires, Buenos Aires, Argentina.
Utermöhl, M., 1958. Zur Vervollkommung der quantitativen Phytoplankton Methodik. Mitteilungen der Internationale Vereinigung für Theoretische und Angewandte Limnologie 9: 1–38.
Vadeboncoeur, Y. & A. Steinman, 2002. Periphyton function in lake ecosystems. The Scientific World Journal 2: 1449–1468.
Vadeboncoeur, Y., D. M. Lodge & S. R. Carpenter, 2001. Whole-lake fertilization effects on distribution of primary productions between benthic and pelagic habitats. Ecology 82: 1065–1077.
Van Donk, E. & W. J. van de Bund, 2002. Impact of submerged macrophytes including charophytes on phyto- and zooplankton communities: allelopathy versus other mechanisms. Aquatic Botany 72: 261–274.
Venrick, E. L., 1978. How many cells to count? In Sournia, A. (ed.), Phytoplankton Manual. UNESCO, Paris: 167–180.
Villar, C., L. de Cabo, P. Vaithiyanathan & C. Bonetto, 1998. River-floodplain interactions: nutrient concentrations in the Lower Paraná River. Archiv für Hydrobiologie 142: 433–450.
Acknowledgments
We are very grateful to the owners of the farms La Juanita and El Triunfo for allowing us the access both lakes and taking care of our experimental devices. We also thank the Laboratorio de Ecología y Fotobiología Acuática from IIB-INTECH (Chascomús) and the members of Laboratorio de Limnología (UBA) for their field assistances. We also thank Dr. Luz Allende for language revision, Dr. Rodrigo Sinistro for his assistance with the figure edition and to two anonymous reviewers and the Handling Editor for their useful comments on the manuscript. This research was supported by a grant of the University of Buenos Aires (UBACyT X838).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Guest editors: M. Meerhoff, M. Beklioglu, R. Burks, F. García-Rodríguez, N. Mazzeo & B. Moss / Structure and Function of World Shallow Lakes: Proceedings from the 6th Shallow Lakes Congress, held in Punta del Este, Uruguay, 23–28 November, 2008
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sánchez, M.L., Pizarro, H., Tell, G. et al. Relative importance of periphyton and phytoplankton in turbid and clear vegetated shallow lakes from the Pampa Plain (Argentina): a comparative experimental study. Hydrobiologia 646, 271–280 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-010-0181-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-010-0181-3