Abstract
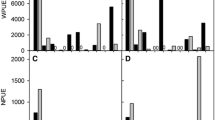
Fish play a key role in the functioning of shallow lakes. Simultaneously, fish are affected by physical in-lake factors, such as temperature and water transparency, with potential changes in their cascading effects on other communities. Here, we analysed the fish community structure and fish activity in four subtropical shallow lakes, varying in trophic state and water transparency, to assess changes promoted by temperature (i.e. summer and winter) and the light regime (i.e. day and night). We used a passive method (gillnets) during the day- and at night-time to detect changes in fish activity, but also sampled the littoral zone (during night) by point sample electrofishing to obtain a better description of the fish assemblage and habitat use. We observed different fish assemblages in the two seasons in all lakes. We captured more fish species and also obtained higher numbers (CPUE with nets) in summer. Contrary to our expectations, the visually oriented Characiformes were the most captured fish regardless of water transparency, at both day-time and night-time. We also found higher fish CPUE at night-time in all lakes. However, the differences between night and day decreased with decreasing transparency, being lower in the least clear lake, Lake Cisne. The nocturnal increase in fish CPUE (including visually oriented species) suggests that darkness serves as a good refuge for fish in shallow subtropical lakes, even at the likely cost of a lower feeding efficiency during the night. The importance of darkness seems to decrease with decreasing water transparency. We also argue that cascading effects of changes in the activity of piscivorous fish (seasonal changes in piscivores CPUE), when omni-planktivorous fish are indeed affected, may eventually reach the zooplankton, but may not be strong enough to reach the phytoplankton, regardless of water transparency.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aksnes, D. & L. Giske, 1993. A theoretical model of aquatic visual feeding. Ecological Modelling 67: 233–250.
APHA, 1985. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater. AWWA/WPCF, 16th edn. American Public Health Association, Washington, DC.
Boveri, M. B. & R. Quirós, 2007. Cascading trophic effects in pampean shallow lakes: results of a mesocosm experiment using two coexisting fish species with different feeding strategies. Hydrobiologia 584: 215–222.
Canfield, D. E. Jr., J. V. Shireman, D. E. Colle & W. T. Haller, 1984. Prediction of chlorophyll-a concentration in Florida lakes: importance of aquatic macrophytes. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 41: 497–501.
Carpenter, S. R. & K. L. Kitchell, 1993. The Trophic Cascade in Lakes. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
De Robertis, A., C. Ryer, A. Veloza & D. Brodeur, 2003. Differential effects of turbidity on prey consumption of piscivorous and planktivorous fish. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 60: 1517–1526.
García-Rodríguez, F., P. Sprechmann, D. Metzeltin, L. Scafati, D. L. Melendi, W. Volkheimer, N. Mazzeo, A. Hiller, W. von Tümpling & F. Scasso Jr., 2004. Holocene trophic state changes in relation to sea level variation in Lake Blanca, SE Uruguay. Journal of Paleolimnology 31: 99–115.
Hamley, J. M., 1975. Review of gillnet selectivity. Journal of Fisheries Research Board Canada 32: 1943–1969.
Hansson, S. & L. G. Rudstam, 1995. Gillnet catches as an estimate of fish abundance: a comparison between vertical gillnet catches and hydroacoustic abundance of Baltic Sea herring (Clupea harengus) and sprat (Sprattus sprattus). Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 52: 75–83.
Hillebrand, H. & B. Cardinale, 2004. Consumer effects decline with prey diversity. Ecology Letters 7: 192–201.
Hölker, F., 2003. The metabolic rate of roach in relation to body size and temperature. Journal of Fish Biology 62: 565–579.
Iglesias, C., G. Goyenola, N. Mazzeo, M. Meerhoff, E. Rodó & E. Jeppesen, 2007. Horizontal dynamics of zooplankton in subtropical Lake Blanca (Uruguay) hosting multiple zooplankton predators and aquatic plant refuges. Hydrobiologia 584: 179–189.
Iglesias, C., N. Mazzeo, G. Goyenola, C. Fosalba & F. Teixeira-de Mello, 2008. Field and experimental evidence of the structuring role of Jenynsia multidentata Jenyns (Cyprinodontiformes, Anablepidae) on zooplankton community structure in subtropical lakes. Freshwater Biology 53: 1797–1807.
Jacobsen, L., S. Berg, N. Jensen & C. Skov, 2004. Does roach behaviour differ between shallow lakes of different environmental state? Journal of Fish Biology 65: 135–147.
Jeppesen, E., J. P. Jensen, M. Søndergaard, T. Lauridsen, L. J. Pedersen & L. Jensen, 1997. Top-down control in freshwater lakes: the role of nutrient state, submerged macrophytes and water depth. Hydrobiologia 342(343): 151–164.
Jeppesen, E., M. Søndergaard, M. Meerhoff, T. L. Lauridsen & J. P. Jensen, 2007. Shallow lake restoration by nutrient loading reduction – some recent findings and challenges ahead. Hydrobiologia 584: 239–252.
Jeppesen, E., B. Kronvang, M. Meerhoff, M. Søndergaard, K. M. Hansen, H. E. Andersen, T. L. Lauridsen, M. Beklioglu, A. Özen & J. E. Olesen, 2009. Climate change effects on runoff, catchment phosphorus loading and lake ecological state, and potential adaptations. Journal of Environmental Quality 38: 1030–1041.
Johnsen, S., 2003. Lifting the cloak of invisibility: the effects of changing optical condition on pelagic crypsis. Integrative and Comparative Biology 43: 580–590.
Jones, J. I. & C. D. Sayer, 2003. Does the fish-invertebrate-periphyton cascade precipitate plant loss in shallow lakes? Ecology 84: 2155–2167.
Kramer, D., R. Rangeley & L. Chapman, 1997. Habitat selection: patterns of spatial distribution from behavioural decisions. In Godin, J.-G. J. (ed.), Behavioural Ecology of Teleost Fishes. Oxford University Press, Oxford: 37–80.
Lazzaro, X., 1997. Do the trophic cascade hypothesis and classical biomanipulation approaches apply to tropical lakes and reservoirs? Verhandlungen der Internationalen Vereinigung für Theoretische und Angewandte Limnologie 26: 719–730.
Lewin, W. C., N. Okun & T. Mehner, 2004. Determinants of the distribution of juvenile fish in the littoral area of a shallow lake. Freshwater Biology 49: 410–424.
Liboriussen, L., E. Jeppesen, M. E. Bramm & M. F. Lassen, 2005. Periphyton-macroinvertebrate interaction in light and fish manipulated enclosures in a clear and a turbid shallow lake. Aquatic Ecology 39: 23–39.
Linlokken, A. & T. O. Haugen, 2006. Density and temperature dependence of gill net catch per unit of effort for perch, Perca fluviatilis, and roach, Rutilus rutilus. Fisheries Management and Ecology 13: 261–269.
Meerhoff, M., J. M. Clemente, F. Teixeira-de Mello, C. Iglesias, A. R. Pedersen & E. Jeppesen, 2007a. Can warm climate-related structure of littoral predator assemblies weaken clear water state in shallow lakes? Global Change Biology 13: 1888–1897.
Meerhoff, M., C. Iglesias, F. Teixeira-de Mello, J. M. Clemente, E. Jensen, T. L. Lauridsen & E. Jeppesen, 2007b. Effects of contrasting climates and habitat complexity on community structure and predator avoidance behaviour of zooplankton in the shallow lake littoral. Freshwater Biology 52: 1009–1021.
Nagdali, S. S. & P. K. Gupta, 2002. Impact of mass mortality of a mosquito fish, Gambussia affinis, on the ecology of a freshwater eutrophic lake (Lake Naini Tal, India). Hydrobiologia 468: 45–52.
Nusch, E., 1980. Comparisons of different methods for chlorophyll and phaeopigments determination. Archiv für Hydrobiologie Ergebnisse der Limnologie 14: 14–36.
Okun, N., J. Brasil, J. L. Attayde & I. A. S. Costa, 2008. Omnivory does not prevent trophic cascades in pelagic food webs. Freshwater Biology 53: 129–138.
Olin, M., M. Kurkilahti, P. Peitola & J. Ruuhijärvi, 2004. The effects of fish accumulation on the catchability of multimesh gillnet. Fisheries Research 68: 135–147.
Pacheco, J. P., C. Iglesias, M. Meerhoff, C. Fosalba, G. Goyenola, F. Teixeira de Mello, S. García, M. Gelós & F. García-Rodríguez, 2010. Phytoplankton community structure in five subtropical shallow lakes with different trophic state (Uruguay): a morphology based approach. Hydrobiologia. doi:10.1007/s10750-010-0180-4.
Pekcan-Hekim, Z., 2007. Effects of turbidity on feeding and distribution of fish. PhD dissertation, University of Helsinki, Finland.
Pekcan-Hekim, Z. & J. Lappalainen, 2006. Effects of clay turbidity and density of pikeperch (Sander lucioperca) larvae on predation by perch (Perca fluviatilis). Naturwissenschaften 93: 356–359.
Persson, L., 1986. Temperature-induced shift in foraging ability in two fish species, Roach (Rutilus rutilus) and Perch (Perca fluviatilis): implications for coexistence between poikilotherms. Journal of Animal Ecology 55: 829–839.
Petry, A. C., A. A. Agostinho, P. A. Piana & L. C. Gomes, 2007. Effects of temperature on prey consumption, growth in mass of juvenile trahira Hoplias aff. malabaricus (Bloch, 1974). Journal of Fish Biology 70: 1855–1864.
Polis, G. A. & D. R. Strong, 1996. Food web complexity and community dynamics. American Naturalist 147: 813–846.
Portt, C. B., G. A. Coker, D. L. Ming & R.G. Randall, 2006. A review of fish sampling methods commonly used in Canadian freshwater habitats. Canadian Technical Report on Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, Ontario, Canada: 2604 pp
Prejs, A., 1984. Herbivory by temperate freshwater fishes and its consequences. Environmental Biology of Fishes 10: 281–296.
Rodríguez, M. A. & W. M. Lewis, 1997. Structure of fish assemblages along environmental gradients in floodplains lakes of the Orinocco River. Ecological Monographs 67: 109–128.
Romare, P. & L. Hansson, 2003. A behavioural cascade: top-down induced behavioural shifts in planktivorous fish and zooplankton. Limnology and Oceanography 48: 956–1964.
Scasso, F., N. Mazzeo, J. Gorga, C. Kruk, G. Lacerot, J. M. Clemente, D. Fabián & S. Bonilla, 2001. Limnological changes of a subtropical shallow hypertrophic lake during its restoration. Two years of whole-lake experiments. Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems 11: 31–44.
Schmitz, O. J., V. Krivan & O. Ovadia, 2004. Trophic cascades: the primacy of trait-mediated indirect interactions. Ecology Letters 7: 153–163.
Snickars, M., A. Sandstro & J. Mattila, 2004. Antipredator behaviour of 0+ year Perca fluviatilis: effect of vegetation density and turbidity. Journal of Fish Biology 65: 1604–1613.
Stoner, A. W., 2004. Effect of environmental variables on fish feeding ecology: implications for the performance of baited fishing gear and stock assessment. Journal of Fish Biology 65: 1445–1471.
Teixeira-de Mello, F., M. Meerhoff, Z. Pekcan-Hekim & E. Jeppesen, 2009. Substantial differences in littoral fish community structure and dynamics in subtropical and temperate shallow lakes. Freshwater Biology 54: 1202–1215.
Tejerina-Garro, F., R. Fortin & M. A. Rodriguez, 1998. Fish community structure in relation to environmental variation in floodplain lakes of the Araguaia River, Amazon Basin. Environmental Biology of Fishes 51: 399–410.
Valderrama, J., 1981. The simultaneous analysis of total Nitrogen and total Phosphorus in natural waters. Marine Chemistry 10: 109–122.
Vanni, M. J., 2002. Nutrient cycling by animals in freshwater ecosystems. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics 33: 341–370.
Acknowledgements
The landowners and managers are acknowledged for their permission to enter the lakes (MGAP, OSE, Aguas de la Costa S.A., and Rossi family). We acknowledge the financial support by the Swiss Embassy in Uruguay, to Asociación Civil I+D, and the logistic support of Daniel Panario and Gabriela Eguren from the UNCIEP Department (Faculty of Sciences). We also deeply thank Nicolás Vidal, Roberto Ballabio, Lucía Boccardi and Néstor Mazzeo for field assistance, Tinna Christensen for figure refinement, Anne Mette Poulsen for text editing, and two reviewers and Guest Editor M. Beklioglu for very constructive comments. MM and FGR are also supported by PEDECIBA and MM, FTM, CI and FGR by the SNI (Agencia Nacional de Investigación e Innovación, Uruguay).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Guest editors: M. Meerhoff, M. Beklioglu, R. Burks, F. García-Rodríguez, N. Mazzeo & B. Moss / Structure and Function of World Shallow Lakes: Proceedings from the 6th Shallow Lakes Congress, held in Punta del Este, Uruguay, 23–28 November, 2008
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gelós, M., Teixeira-de Mello, F., Goyenola, G. et al. Seasonal and diel changes in fish activity and potential cascading effects in subtropical shallow lakes with different water transparency. Hydrobiologia 646, 173–185 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-010-0170-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-010-0170-6